A patient with pneumonia has a respiratory rate of 28 breaths/min and an spO2 of 88% RA. What is your priority?
Administer oxygen
Name this rhythm:
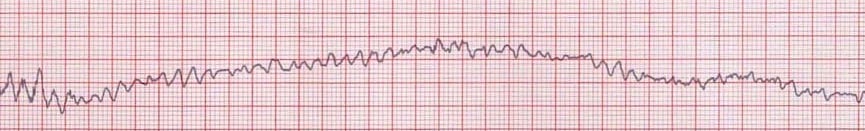
What is ventricular fibrillation?
Image from: https://litfl.com/ventricular-fibrillation-vf-ecg-library/
What is considered a normal ICP?
5-15mmHg
What must the nurse ensure is completed prior to instilling anything into a patient’s newly placed NG or OG tube?
Xray to confirm correct placement
These are the necessary changes for a renal diet.
What is restricted protein, low potassium and low sodium?
Where is the Cricothyrotomy Kit kept?
A patient in the ICU develops ventricular tachycardia (VT) with a pulse and blood pressure of 100/60 mmHg. What is the next best step?
Administer IV amiodarone
What is the earliest indicator of a potential rise in ICP?
Change in LOC
This is the next step a RN will do when a patient vomits coffee-ground material.
What is collect a sample for a hem-occult?
What is the best method to monitor fluid balance in a critically ill patient with AKI?
Daily weight
Which finding is most indicative of impending respiratory failure?
Tripoding - Use of accessory muscles and paradoxical chest wall movement
Whats the "Gold Standard" Treatment for a myocardial infarction?
TNK can be initiated within this time frame from "last known normal"?
What is 0-4.5 hours?
What diagnosis might the nurse expect in patient with firm/distended abdomen and a sustained intrabdominal pressure >20mmHg?
Abdominal compartment syndrome
Which action is most important for the nurse to monitor after administering desmopressin?
Monitor Serum sodium levels for hyponatremia
A 45-year-old patient is admitted to the ICU following a traumatic chest injury. The patient suddenly develops severe dyspnea, hypotension, distended neck veins, and absent breath sounds on the right side. What is the next immediate action?
Perform an emergency needle decompression in the second intercostal space, midclavicular line
This is the maximum length of a NORMAL QRS complex?
What is 0.12 seconds?
What does this acronym mean: B.E. F.A.S.T.?
Balance, eyes, face, arm, speech/slur, time.
This suction setting is always used on GI bleeds.
Low continuous suction
You would suspect this if your patient with Acute Renal Failure presents with a sudden onset of shortness of breath.
What is fluid overload?
Your postop patient suddenly develops wheezing, rales, expiratory grunting, cyanosis, mottling, and jugular venous distention (JVD). These are all potential symptoms of this syndrome.
What is ARDS?
These 3 classic signs/symptoms can be seen in a patient with cardiac tamponade.
What is JVD, pulses paradoxus, and decreased SBP?
Name three interventions if you suspect a patient is having an acute stroke.
Stay with patient
Call a BAT
Check blood glucose
Obtain 12-lead EKG
What symptoms may be present in a patient with hepatic failure--Name 4?
Jaundice, ascites, hepatic encephalopathy, coagulation abnormalities, dark urine, pruritis, nausea/vomiting, fatigue
Name three symptoms of Diabetes insipidus.
Polydipsia, Polyuria, Hypernatremia, High serum osmolarity, nocturia, fatigue, dehydration