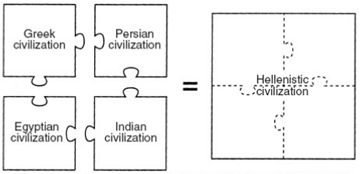
What caused the historical development depicted in this illustration?
1. Fall of the Roman Empire
2. The collapse of Greek civilization
3. Spread of Buddhism
4. The expansion of Alexander the Great’s empire
4. The expansion of Alexander the Great’s empire
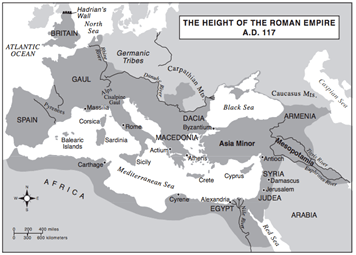
Which statement is best supported by the information on this map?
(1) The Roman Empire extended over three continents.
(2) Rivers kept invaders out of the Roman Empire.
(3) Alexandria served as the eastern capital of the Roman Empire.
(4) Carthage was eventually destroyed by the Romans.
(1) The Roman Empire extended over three continents.
What factors led to the fall of Rome?
Name two Economic factors that led to Rome's downfall.
Which geographic factors contributed to the formation of independent city-states in ancient Greece?
(1) tropical rainforests
(2) fertile farmland
(3) navigable rivers
(4) mountainous topography
(4) mountainous topography
(3) navigable rivers

Many world historians would argue that the aqueducts shown in the photograph above exemplify Rome’s attempt to
1. Develop monumental architecture as a unifying force
2.Utilize slave labor in their armies
3.Connect their world to the Far East and the Han dynasty
4.Build massive structures to create religious unity within a multicultural empire
1. Develop monumental architecture as a unifying force
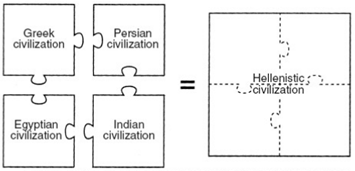
Which claim is supported by the illustration above?
1. Persian and Greek civilization were isolated from one another
2. Alexander the Great’s empire led to cultural diffusion between the civilizations he conquered
3. Armed conflict between Indian and Egyptian civilizations led to the creation of Hellenistic civilization
4. Greek, Persian, Egyptian, and Indian civilizations used Hellenistic irrigation to grow crops
2. Alexander the Great’s empire led to cultural diffusion between the civilizations he conquered
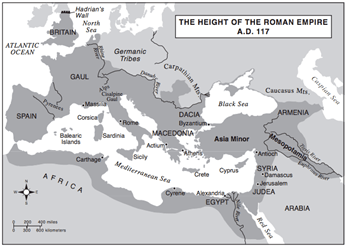
Based on the information provided by this map, which body of water was most likely the center of Roman trade?
(1) Red Sea
(2) Black Sea
(3) Atlantic Ocean
(4) Mediterranean Sea
(4) Mediterranean Sea
What factors led to the fall of Rome?
Name two Social factors that led to Rome's downfall.
Which of the following describes an impact of Alexander’s conquests?
The spread of Greek culture such as language and philosophy
An empire lasting until the early 7th century, creating a Pax Alexandria in which trade flourished
The creation of the largest land empire in history
The beginning of communications between Greece and the Qin Dynasty
The spread of Greek culture such as language and philosophy
Purposes and Kinds of Roman Roads
Why did the Romans build roads? The Romans considered a well-organized and efficient transportation system a basic element of proper administration; i.e. an indispensable element in creating and maintaining the Roman state. The earliest highways or main roads were constructed for the use of the military, and their economic benefit for civilians was a later byproduct and not the main reason for their creation.
What is the point of view of the author of this excerpt?
(1) Roman roads were built primarily to keep order in the empire.
(2) The Roman economy would not have prospered if it were not for the roads in the empire.
(3) Neglect of the Roman road system led to the collapse of the empire.
(4) The Romans were the best road builders during the Classical period.
(1) Roman roads were built primarily to keep order in the empire.
What was one of the most important contributions of the Greek city-state of Athens?
(1) development of direct democracy
(2) diffusion of a monotheistic belief system
(3) promotion of the equality of all humans
(4) creation of a writing system using hieroglyphics
(1) development of direct democracy
How did the geography of the Italian peninsula influence the development of the Roman Empire?
(1) The unnavigable rivers in the northern part of the peninsula protected the Romans from their neighbors.
(2) The harsh climate prevented agricultural production on the Italian peninsula.
(3) The lengthy, rugged seacoast encouraged frequent invasions of the Italian peninsula.
(4) The location of the peninsula contributed to Roman control of the Mediterranean region.
(4) The location of the peninsula contributed to Roman control of the Mediterranean region.
What factors led to the fall of Rome?
Name two Geographic factors that led to Rome's downfall.
Which of the following led to the fall of Alexander’s empire?
Repeated attacks from northern invaders
Widespread economic failure
Massive outbreaks in disease
Lack of a clear line of succession
Lack of a clear line of succession
•Roman women could own property. •Roman women could make wills leaving their property to whomever they chose.
A valid conclusion drawn from these facts is that Roman women
(1) had the right to vote
(2) enjoyed some legal rights
(3) were equal to men
(4) could hold political offices
(2) enjoyed some legal rights
Which term is most closely associated with Hellenism under Alexander the Great?
(1) cultural diffusion
(2) pacifism
(3) theocracy
(4) natural rights
(1) cultural diffusion
At the height of its power, which ancient civilization controlled the entire coastal region surrounding the Mediterranean Sea?
(1) Phoenician
(2) Qing
(3) Roman
(4) Carthaginian
Roman
What factors led to the fall of Rome?
Name two military factors that led to Rome's downfall.
Why was slavery so much more prominent in Greco-Roman civilization than in India or China?
1. Slavery became entrenched throughout the Greco-Roman economies.
2. Romans regarded slaves as “barbarians”.
3. Chinese slavery became a major source of labor for agriculture
d. Indian slavery became the sole source of manufacturing
1. Slavery became entrenched throughout the Greco-Roman economies.
China under the Han dynasty and the Roman Empire were similar in that both grew wealthy because they (1) developed extensive trade networks
(2) created classless societies
(3) encouraged democratic ideals
(4) established free-market economies
(1) developed extensive trade networks
The city-state of Sparta was characterized by
democratic institutions
an emphasis on temple worship
an emphasis on warfare
an emphasis on warfare
Purposes and Kinds of Roman Roads
Why did the Romans build roads? The Romans considered a well-organized and efficient transportation system a basic element of proper administration; i.e. an indispensable element in creating and maintaining the Roman state. The earliest highways or main roads were constructed for the use of the military, and their economic benefit for civilians was a later byproduct and not the main reason for their creation. The military nature of the roads continued to be essential as Romans expanded into territory outside Italy. In the province of Arabia Petraea (which included what is now Jordan), the movement of troops and ease of communication for the army and Roman administration were the primary reasons for construction of the Via Nova, one of the many viae militares or military roads built in conquered provinces. However, smaller, shorter, and less well-constructed local roads (actus) or tracks (callis) also increased in territory after it was brought under Roman control. Nevertheless, the main public highways (viae publicae) normally began as military roads and only gradually evolved into civilian conduits [passageways].
Western Europe
Sub-Saharan Africa
Mongolia
South Asia
Western Europe
The fall of Rome was
a rapid, cataclysmic event.
due entirely to military failures.
not a singular event, but a long process of change.
the end of Roman civiliation.
not a singular event, but a long process of change.
Which of the following can be concluded based on the images above?
In both regions, women had same level of freedom
Women enjoyed more freedom in Sparta than in Athens
Women enjoyed more freedom in Athens than in Sparta
In both regions, women had equal rights to men
Women enjoyed more freedom in Sparta than in Athens
15.Where was this document written?
Ancient Greece
Ancient Rome
Ancient Egypt
Gupta Empire
16. What was the purpose of these “Tables?”
To have laws binding both plebeians and patricians
To punish lower classes and slaves
To show favoritism to the patricians
To remove freedom from the people
Ancient Rome
To have laws binding both plebeians and patricians