these are two extremely common histological findings seen in Alzheimer's diseae
What are Amyloid-B plaques and tau tangles?
this is the main pharmacologic therapy for mild-severe AD
What are AChE inhibitors?
Lecanemab, an anti-Aβ antibody, can remove Aβ plaques from the brain, however, it is contraindicated in many patients due to this specific AE
ARIA => amyloid related imaging abnormalities (edema , hemorrhage) 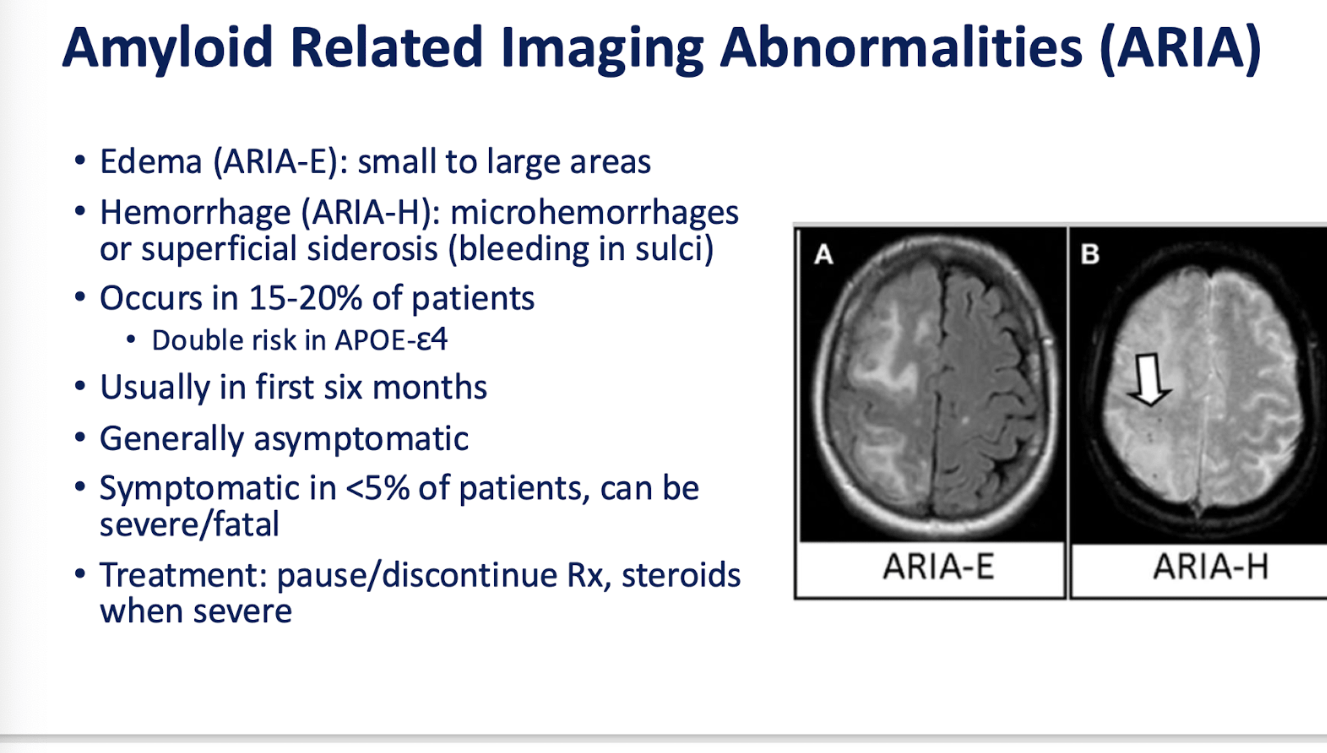
name that disease!

What is MSA?
name that pathology: "wet, wobbly, wacky"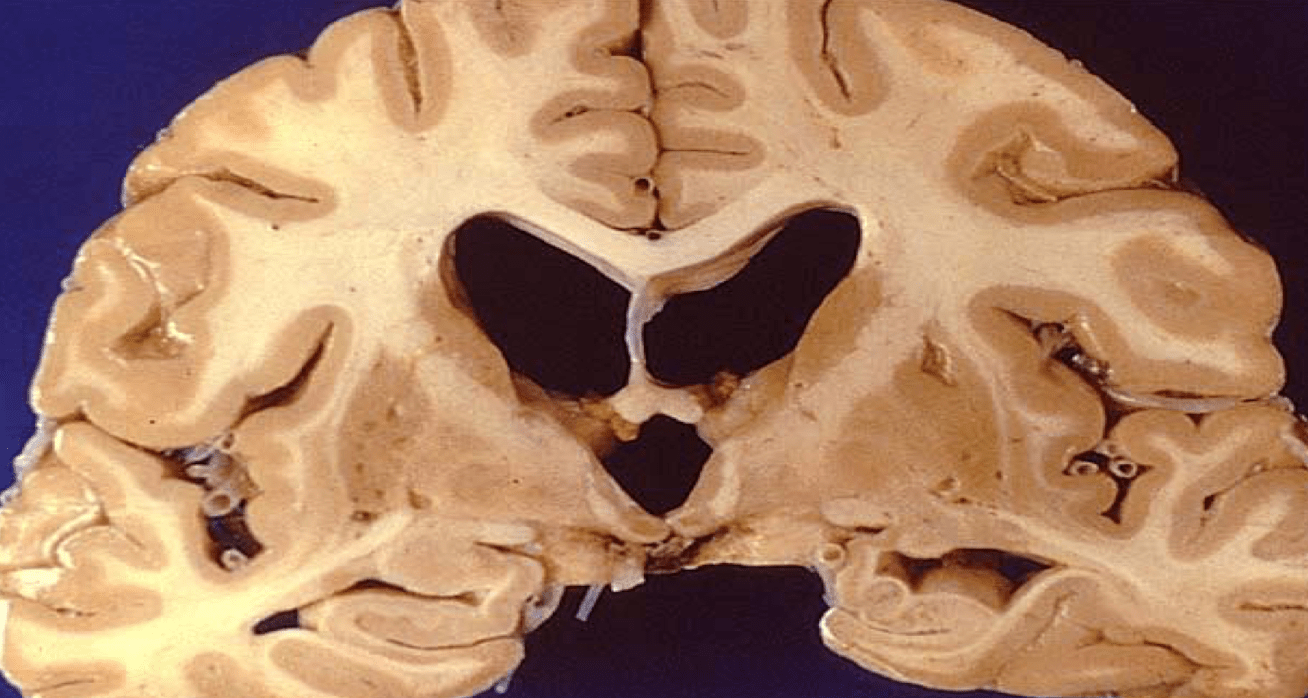
normal pressure hydrocephalus
these enzymes cleave amyloid precursor protein to produce amyloid beta
What are B-secretases?
AB42 (toxic amyloid in AD) levels decrease is CSF and plasma in patients with AD, what is the hypothesized reason for this
There is more AB42 in the brain, but it's all getting deposited in plaques, so there is less in CSF and plasma
this is the MAIN difference between MCI and dementia
dementia = functional impairment!
this enlargement of both the lateral and third ventricle suggests what pathology
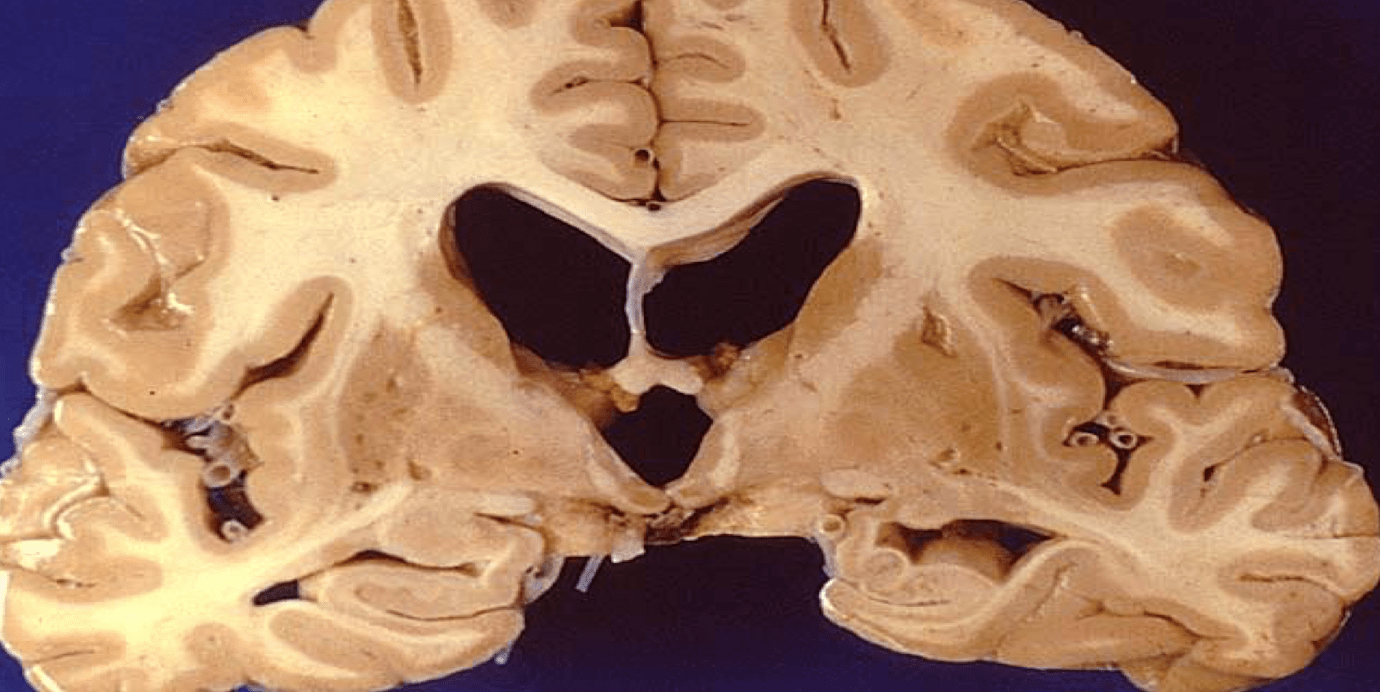
hydrocephalus of some sort
**in this case specifically normal pressure hydrocephalus
This gross brain specimen would be indicative of what kind of dementia?
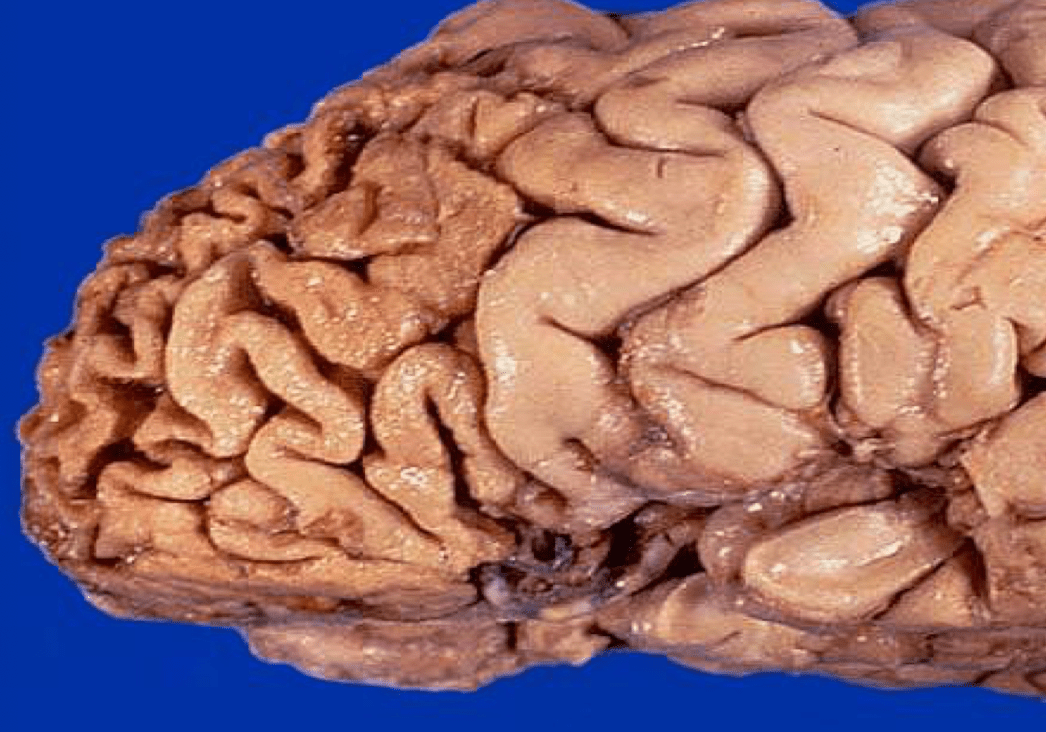
What is FTD?
tau has this molecular modification in AD
What is hyperphosphorylation?
What is ApoE4?
Current AD diagnosis is base on positive core 1 biomarkers. What are those biomarkers (hint: there are 3)?
amyloid PET
or
CSF Aβ42/Aβ40
or
plasma pTau217
name 3 common secondary causes of dementia
1. B12 deficiency
2. Wernicke encephalopathy
3. Wilson's disease
4. tertiary syphilis
5. HIV associated cognitive disorder
Three of the following symptoms must be present for an individual to be diagnosed with this dementia variant

What is Behavior variant of FTD?
**"The midlife crisis"
What is this chart telling us?
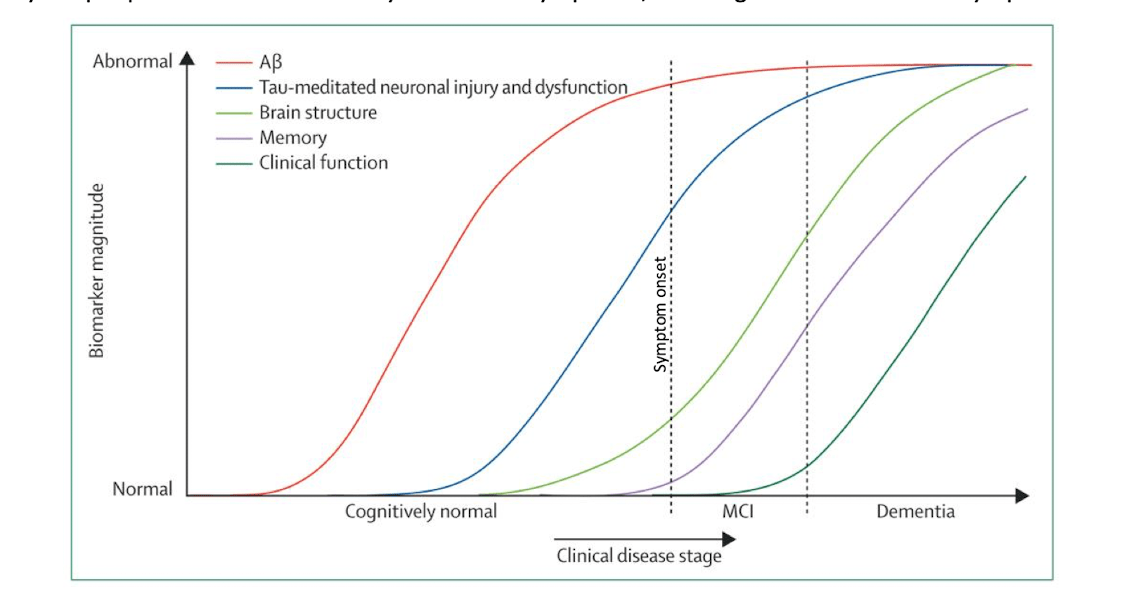
amyloid plaque formation starts 15 yrs before symptom onset and tau tangles begin to accumulate closer to onset
this is the typical amyloid level in a patient with symptomatic AD
What is >50?
also known as multi-infarct dementia, this dementia results in slow processing speed, executive function impairment, lack of insight, and mood changes
What is vascular dementia?
BONUS: Where in the brain does this happen>
this is a rapidly progressive dementia syndrome with myoclonus
What is CJD?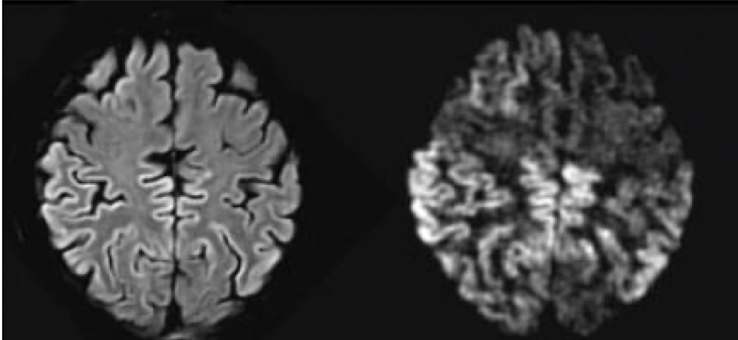
these pyramidal-shaped neurons consist of ....
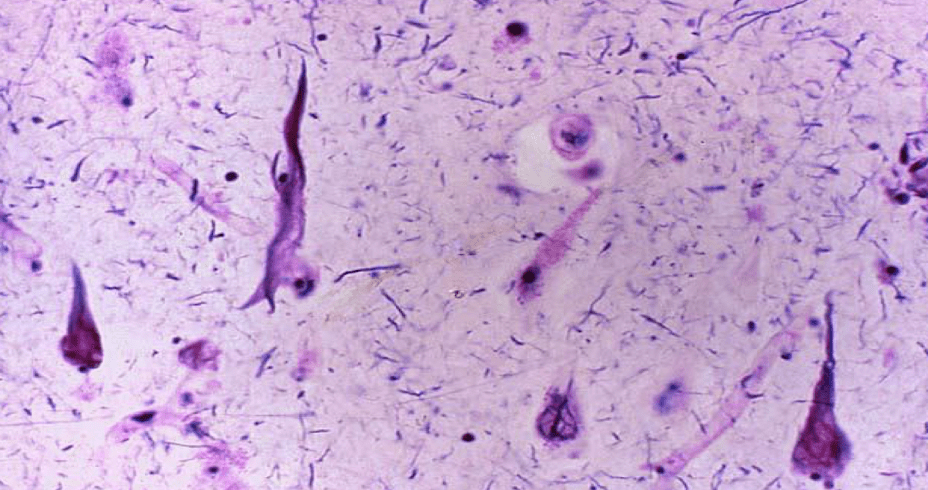
abnormally hyperphosphorylated tau protein
Why are pTau181 and pTau217 levels better reflective of amyloid, not tau pathology?
amyloid deposition stimulates tau phosphorylation before the tay is forming tangles
this drug is a NMDA receptor antagonist that can be used in moderate to severe AD to try and temporarily slow the decline of pts
What is memantine?
The following symptoms are supportive features of what type of dementia?

What is DLB?
these are the general findings seen with frontotemporal dementia
*younger onset: 50s-60s
*there is a behavioral variant (R frontal)
*primary progressive aphasias (L frontal or L temporal)
*other tauopathies may be present (PSP, CBD)
this pathology shows numerous small white matter infarcts that are present in what kind of dementia?
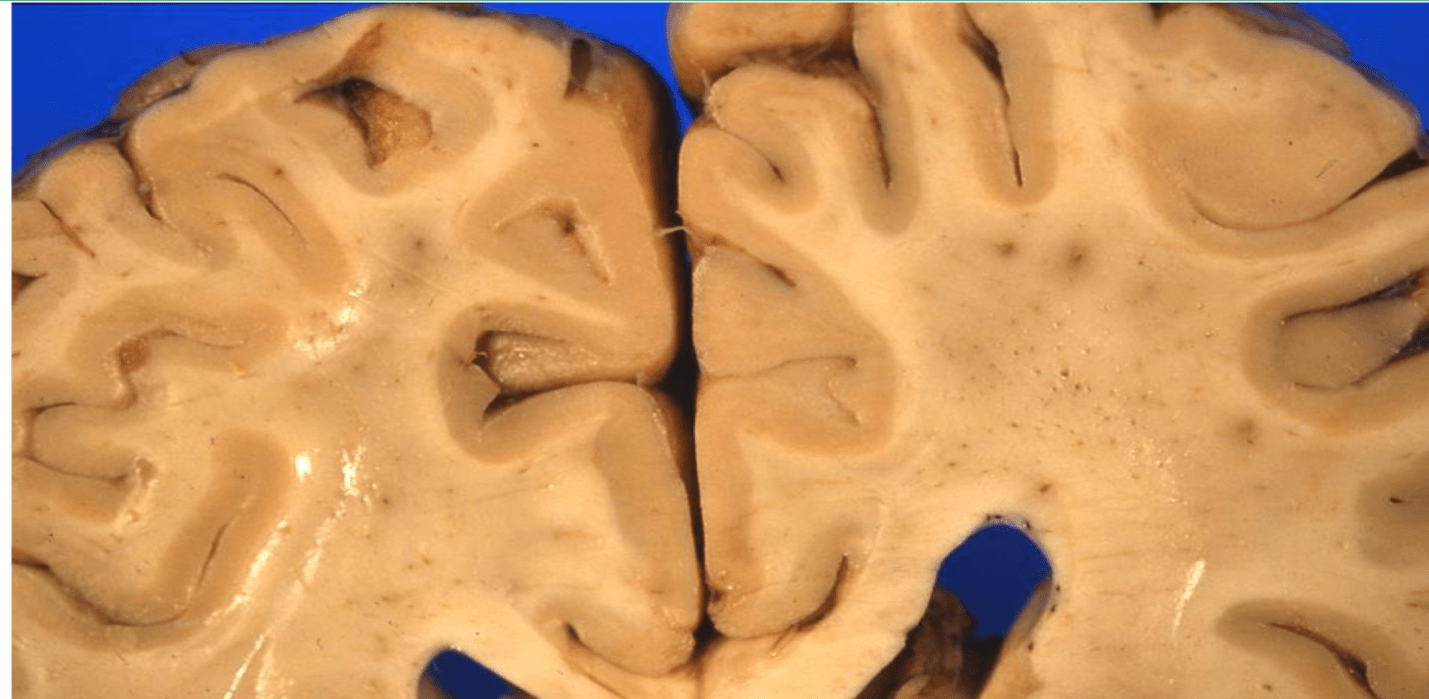
What is vascular dementia?