What is the hardest mineral known to man so far?
What is Diamond.
What is the subatomic particle that has no charges but does have mass?
What is: a neutron
A streak test used to identify minerals requires —
F studying crystals with a magnifying glass
G scratching the mineral with an iron nail
H identifying the color of the powdered mineral
J observing how it reflects light from its surface
What is:
H identifying the color of the powdered mineral
The appearance of the surface of a mineral when it reflects light is known as -
What is Luster
A student investigates how liquids of different densities interact by pouring kerosene, grape juice, and corn syrup into a graduated cylinder. The liquids separate into layers with kerosene on top, grape juice in the middle, and corn syrup on the bottom.
What statement BEST describes the corn syrup?
A.) Corn syrup is less dense than grape juice but more dense than kerosene.
B.)Corn syrup has a density between kerosene and grape juice.
C.)Corn syrup is the most dense of the three liquids.
D.)Corn syrup is the least dense of the three liquids.
What is :
C.)Corn syrup is the most dense of the three liquids.
Will Talc scratch Quartz?
Explain why or why not.
What is the subatomic particle that is not in the nucleus, but does have a small mass?
What is: an electron
A student used a battery, wires, and a bulb to test if each of the samples will complete the circuit causing the bulb to light. Next, the student shined a bright light on each of the samples. Which physical properties is the student investigating?
A.)Streak and hardness
B .) Luster and conductivity
C.)Streak and conductivity
D .) Hardness and luster
What is:
B.) Luster and Conductivity
The capability of a substance to be molded and shaped, or hammered into sheets without breaking is known as-
What is :
Malleability
A student pours rubbing alcohol, water, and syrup into a graduated cylinder. The liquids separate into layers with rubbing alcohol on top, water in the middle, and syrup on the bottom.
What statement BEST describes the rubbing alcohol?
A.)Rubbing alcohol has the same density as water.
B.)Rubbing alcohol is the most dense of the three liquids.
C.)Rubbing alcohol is more dense than water but less dense than syrup.
D.)Rubbing alcohol is less dense than water and syrup.
D.)Rubbing alcohol is less dense than water and syrup.
Which two physical properties of minerals can be observed by scratching the mineral against other substances?
A) Color and streak
B.) Luster and streak
C.) Streak and hardness
D.) Hardness and luster
What is: Streak and Hardness
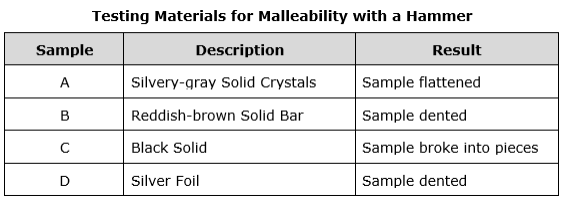
Which sample is most likely a nonmetal?
A.) Sample A
B.) Sample B
C.) Sample C
D.) Sample D
What is:
C.) Sample C
Which of the following lists of properties best describes nonmetals?
F.) Brittle, shiny, conductor
G.) Malleable, shiny, conductor
H.) Brittle, dull, insulator
J.) Malleable, dull, insulator
What is:
H.) Brittle, dull, insulator
The capability of a substance to be stretched into thin wires without breaking is known as
What is: Ductility
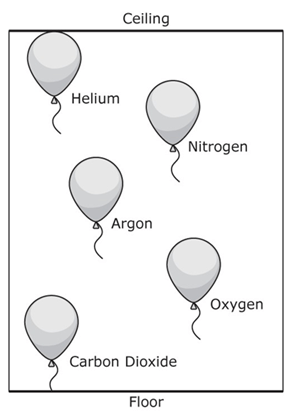
What conclusions can the student make about the potions of the balloons and their density?
The density of nitrogen is _____ and then helium. Carbon dioxide is ______ the dense of all the gases.
Less, Greater, Least, Most
What is :
Greater, Most
A student is testing several minerals in science class. First, the student scratched the minerals across a tile and then scratched the minerals with a copper penny and a steel tool. What physical properties is the student testing?
A.) Color and state
B.) Streak and hardness
C.) Luster and conductivity
D.) pH and fracture
What is :
B.) Streak and hardness

Based on the physical properties observed, the student should classify this sample as a a/an —
A compound
B nonmetal
C metal
D metalloid
What is:
D: Metalloid
Refer to the below Mohs Hardness Scale table. Which of the following is a correct statement about a mineral with a hardness rating of 7?
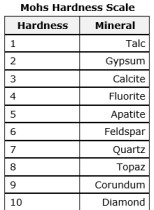
A The mineral can scratch Apatite and every mineral with a hardness scale number lower than 7.
B The mineral cannot be scratched by Apatite, but can be scratched by Feldspar.
C The mineral can scratch Calcite, but cannot scratch Apatite.
D The mineral can scratch Apatite and every mineral with a hardness scale number higher than 7.
What is :
A The mineral can scratch Apatite and every mineral with a hardness scale number lower than 7
The ability of one mineral to scratch another mineral is determined by the mineral’s...
What is Hardness
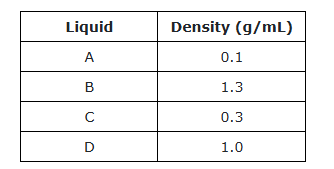
A new liquid with a density of 0.8 g/mL will .....?
A.) Float above liquid A
B.)Settle between Liquid C and D
C.) stay suspended just beneath liquid C and above liquid B
D.) Rest between Liquid A and C
What is :
B.) Settle between Liquid C and D
A student found a pretty rock while hiking with her family. She discovered that the rock will scratch glass, but not her steel knife. According to the Mohs Hardness Scale shown Below, what does the student know about the rock?
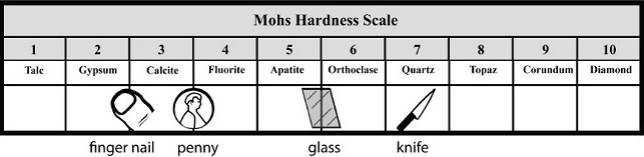 F.) It is harder than quartz, but softer than topaz.
F.) It is harder than quartz, but softer than topaz.
G.) It is harder than corundum, but softer than gypsum.
H.) It is harder than calcite, but softer than fluorite.
J.) It is harder than fluorite, but softer than quartz.
What is :
J.) It is harder than fluorite, but softer than quartz.
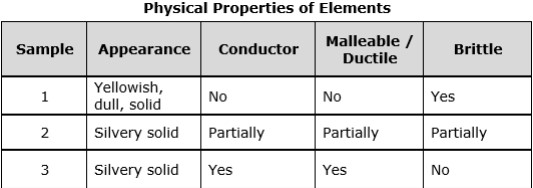
How would you classify sample 3 on the table above?
F Metal
G Nonmetal
H Metalloid
J Compound
What is :
F.) Metal
Hematite is a mineral that comes in a variety of colors including black, grey, silver, brown and red. A streak test is used to help determine the identity of hematite. Why would a streak test be conducted on hematite to determine its identity?
A The streak changes depending on the color of hematite.
B The streak is the same color no matter the color of the hematite.
C The streak determines the hardness of the hematite.
D The streak changes depending on the luster of the hematite.
What is:
B The streak is the same color no matter the color of the hematite.
The ability of an element to allow energy (heat or electrical) to flow through it is called?
What is Conductivity
When the liquids are placed in a column, liquid D will 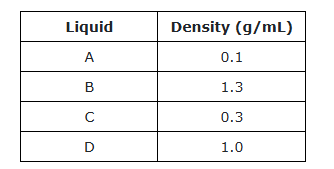
A.) float below liquid C and directly above liquid A
B.) sink below liquids A and C but above liquid B
C.)stay suspended just beneath liquid C and above liquid B
D.) Float on top of liquid A
What is
B.) sink below liquids A and C but above liquid B