Paralleling
Define the difference between Primary and Secondary, Scatter Radiation
Primary Radiation: penetrable/useful beam that is used to penetrate receptor
Secondary Radiation: created when the primary beam is interacted with matter
Scatter radiation is also an example of secondary radiation, x-ray is beam that is deflected from the path of matter
When the x-ray machine is operating at 70 kV how much total filtration is required
2.5mm
What are the two types of digital sensors
CCD (charged coupled device) and CMOS (complementary metal oxide semiconductor)
Which landmarks can be found between 8 and 9 and are they radiolucency or radiopaque
incisive foreman- radiolucency
medial palatal suture- radiolucency
What is the order of taking x-rays during a FMX
maxillary right canine- mandibular right canine; maxillary right premolar PA- mandibular right molar PA
premolar right BW- molar left BW
When taking bitewings what is the vertical and horizontal angulation
vertical angulation: +10 degrees
horizontal angulation: central x-ray beam thru the contact points
What are the two planes you have to line up when you are taken a panoramic
What part of the x-ray tube makes up the electron cloud
Filament circuit
What are shielding recommendations are used to protect the operator
stand behind a protective barrier
stand at least 6 feet away from the x-ray tubehead
operator perpendicular or 90-135 degree angle to the beam
What are the two different intensifying screens and what is the light they emit?
Calcium tungsten screens emits blue light
Rare earth screens emits green light
What is the small projection that is found posterior to the maxillary tuberosity
Hamulus
to avoid overlapping the center of the x-ray beam should be directed thru the proximal contacts of the teeth
When taking PA of the posterior and anterior how is the receptor placed for each PA
Anterior PA: vertical
Posterior PA: Horizontal
When taking a extraoral x-ray if the image comes out with an exaggerated smile what is the error and how would you fix it
Chin is tipped down, the Frankfort plane is angled down; bring chin up and have the Frankfort plane parallel with the floor
What is the purpose of the anode
convert electrons into x-ray photon, which is used for the primary beam
Define the ALARA concept
as low as reasonably achievable, all radiation exposure must be kept to a minimum
Which side of the package should be towards and away from the tubehead
towards tubehead: raised indicator dot, solid white
Away tubehead: flap side and lead foiled backing
what landmark can be found between the premolars on the mandible
mental foreman
Foreshortening: teeth will feel short and blunt, excessive vertical angulation; reduce vertical angulation
elongation: teeth will feel long and distorted, flat vertical angulation; increase vertical angulation
When using a size one sensor how many x-rays are taken of the anterior teeth
7
What are two of the common uses for a CBCT
implant placement
extraction/ exposure of impacted teeth
endodontic assessment
evaluation of TMJ
orthodontic evaluation
evaluation of lesion and abnormalities
trauma evaluation
define how wavelengths and frequency effects the x-rays?
short wavelengths= high frequency
long wavelengths= low frequency
useful beam is comprised of short wavelengths and high frequency
What is the maximum permissible dose for a person who works with radiation
50 mSv/year (0.05 Sv/year)
Define Direct imaging and Indirect imaging. Give one example of each
Direct imaging- x-radiation directly to the computer with image software. CCD or CMOS
Indirect imaging- after sensor is exposed to x-radiation it uses a scanner to convert image. PSP plates
What is this landmark
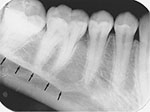
mylohyoid ridge
When taking a pediatric occlusal image what size of sensor would you use
Size 2
What is the difference between the paralleling and bisecting technique
paralleling technique: paralleling to the long axis of the tooth
bisecting technique: receptor is directly against the tooth, the central ray is 90 degrees to the imaginary bisector
What is the error and the correction

patient teeth are position too far back on the bite-block; patient should have teeth position in the bite-block grove, teeth should appear edge to edge
Define these parts of the the x-ray tubehead:
Lead Collimator, Aluminum disk, and focal spot
Lead Collimator: used to restrict the x-ray beam
Aluminum disk: used to filter out the unused/ longer wavelengths
Focal Spot: part of the anode that converts the electrons into x-ray photons
Which type of PID would be most effective in reducing patient exposure?
16 inch rectangular collimator
What are the parts of the film packet and what are each part used for?
x-ray film: has an indication dot that helps establish film orientation, holds the image
paper film wrapper: shields the film from light
lead foil sheet: position behind the film to shield the film from backscatter
outer package wrapping: protect film from exposure to light and oral fluid
What is this landmark
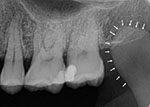
coronoid process
Define the buccal object rule
to be able to find if the image is located on the buccal or lingual of the tooth by moving the Horizonal angulation
Same, Lingual, Opposite, Buccal
When taking an image of tooth # 24 and 25 using the bisecting technique what is the vertical angulation
-15 to -25
What is the #5 landmark

hyoid bone