The most common type of eczema seen in infants.
What is atopic dermatitis?
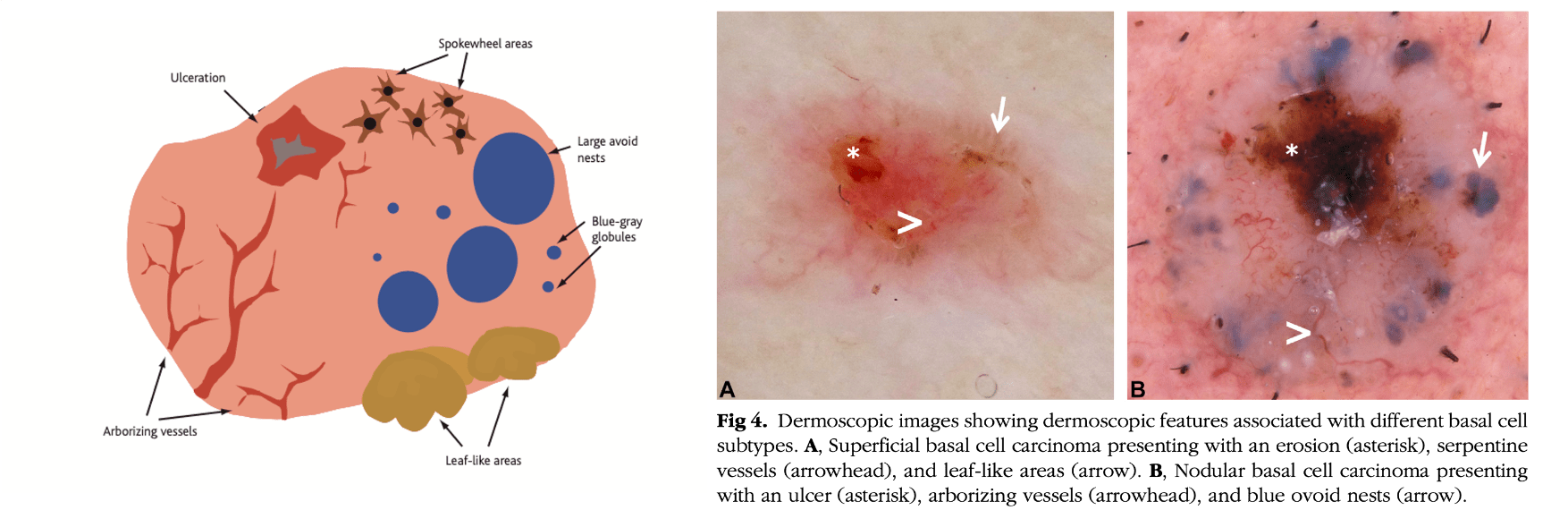
This dermoscopic feature, commonly seen in basal cell carcinoma, appears as branching red lines on a pink or pearly background.
What is arborizing blood vessels?
This systemic disease is considered the most common association with this painful dermatologic condition.
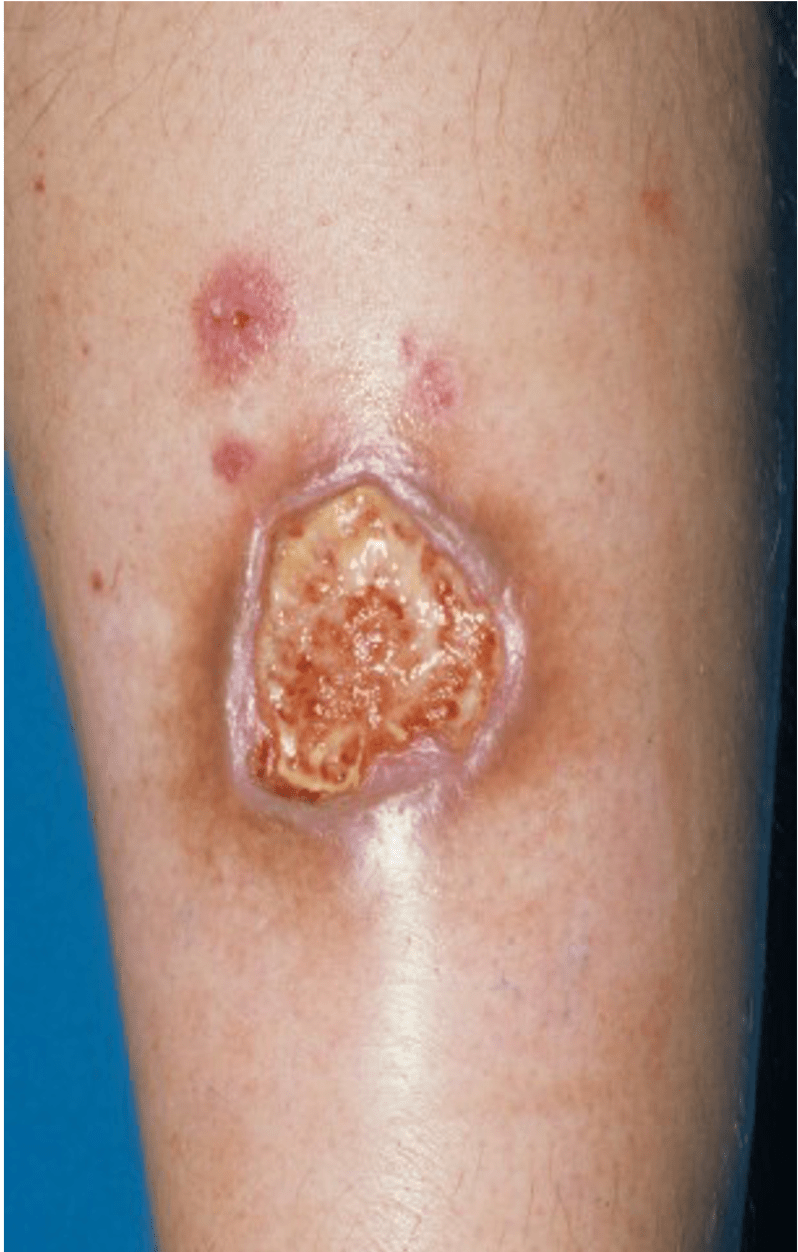
What is inflammatory bowel disease?
Pyoderma gangrenosum - idiopathic (30-50%), or associated with systemic diseases (50-70%):
1. IBD (30%) – UC or CD
2. Arthritis (20%) – seronegative arthritis, IBD spondylitis, RA
3. Hematologic disease (15-25%) – AML/CML, MDS, hairy cell leukemia, IgA monogammopathy
4. Autoinflammatory syndromes - PAPA, PASH, PAPASH, and in a small proportion of SAPHO
PG variants & systemic associations
Classic/Ulcerative (w/ IBD, RA, IgA-MG), atypical/Bullous (w/ hema ca), pustular (w/ IBD), pyoderma/pyostomatitis vegetans (w/ IBD)
The sensory innervation to the face, motor innervation to the muscles of mastication, parasympathetic innervation to the parotid, and parasympathetic and sympathetic innervation of the lacrimal glands are supplied by this cranial nerve.
What is Trigmenial nerve?
This topical antibiotic is commonly used to treat mild to moderate acne.
What is topical clindamycin?
Posterior fossa malformation, hemangioma, arterial anomalies, cardiac anomalies, eye abnormalities and sternal clefting can be seen in this syndrome.
What is PHACES syndrome?
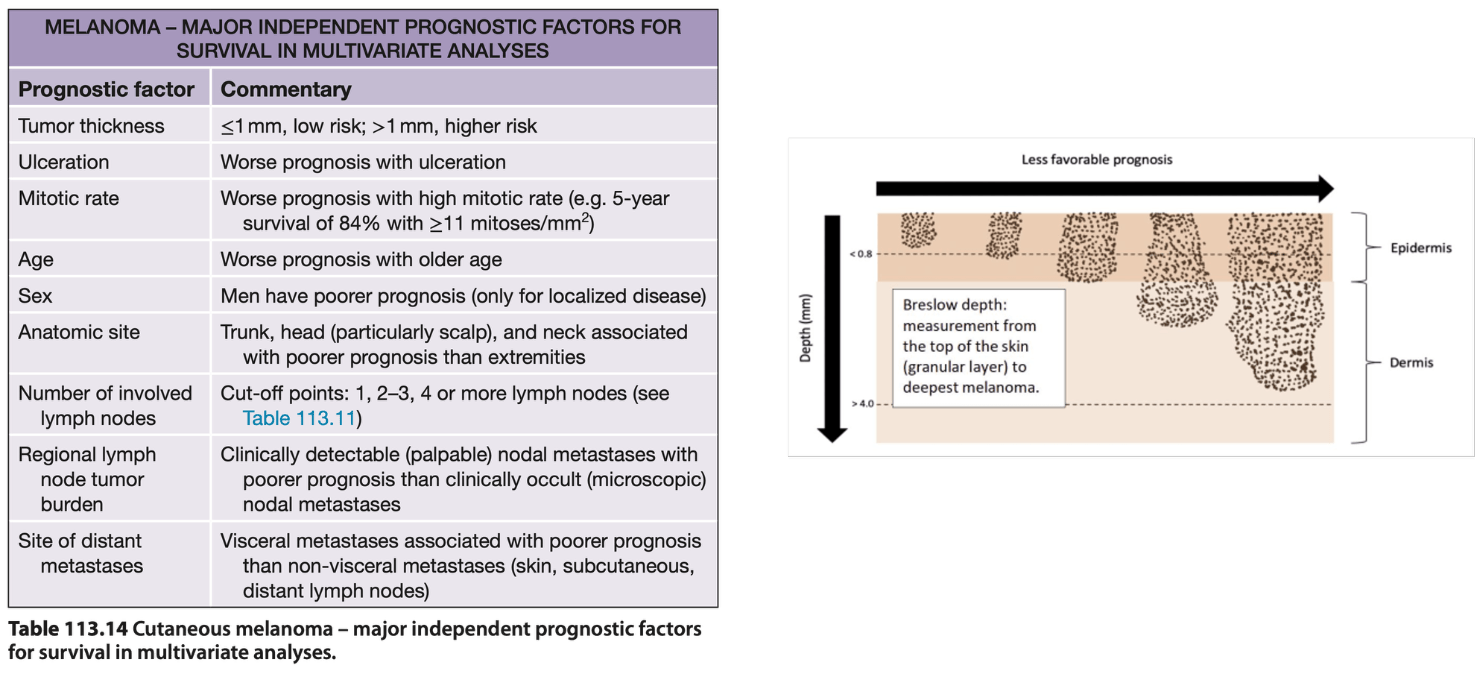
This histopathologic feature is considered the single most important prognostic factor influencing survival and staging in localized stage I and II cutaneous melanoma.
What is Breslow thickness?
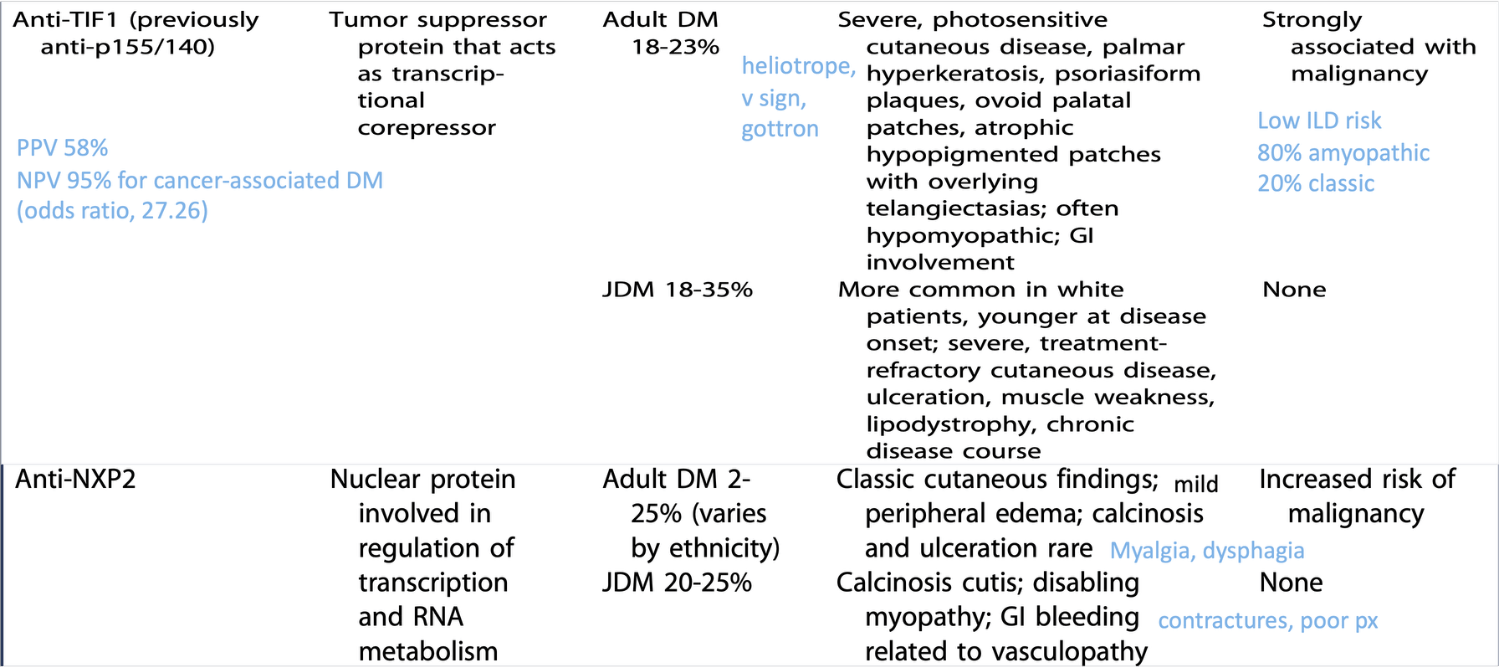
In adult patients with dermatomyositis, the presence of this myositis‑specific autoantibody is strongly associated with an underlying malignancy.
What is anti-TIF1?
Cancer-associated DM – Anti-TIF1 + AntiNXP2
Light waves traveling in phase, time and space. This is a required property that differentiates laser from other forms of light.
What is coherence?
This oral JAK inhibitor works primarily on JAK1 and JAK2 and is FDA approved for the treatment of alopecia areata since 2018.
What is Baricitinib?
These firm white or yellow papules and pustules are typically seen on an infant’s cheeks and nose and are due to maternal hormones.
What is neonatal acne?
This virus is necessary for the development of Kaposi sarcoma and is commonly found in patients with HIV.
What is HHV-8?

Other HHV-8 associated disorders? primary effusion lymphoma, multicentric Castleman disease
Most sensitive and specific marker for KS? IHC detection of latency-associated nuclear antigen (LANA-1) of HHV-8 helps to differentiate from important HE ddx such as KHE, spindle cell hemangioma, mod differentiated angiosarcoma (all negative HHV-8)
When detected in blood of HIV-positive men - HHV-8 strongly predicts their subsequent development of KS
This medication is FDA-approved for both moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis and Crohn’s disease.
What is Rinvoq/Upadacatinib?
Rinvoq (upadacatinib) – JAK1 inhibitor
•FDA for mod-sev Crohn’s > 12 years (starting dose is 45 mg)
•FDA for mod-dev AD > 12 years (approval of two dose strengths 15 and 30 mg)
•Other Rinvoq FDA approvals – axial spondylarthritis, ankylosing spondylitis, ulcerative colitis, psoriatic arthritis, rheumatoid arthritis
*What other JAK inhibitors are approved in AD (PO/T)?
*MoA mnemonic: Upa (up=JAK1), Abro (A=JAK1), Bari (Bi=JAK1/2), Ruxo (Repeat=JAK1/2), Tofa (Tri=JAK1/2/3)
A skin graft that includes both the epidermis and part of the dermis.
What is split-thickness skin graft?
An immunosuppressive agent that has a risk of myelosuppression and requires screening of TPMT level before using.
What is Azathioprine?
A blistering disorder in neonates caused by mutations in keratin 5 and 14.
What is Epidermolysis Bullosa Simplex?
This rare autosomal dominant condition is characterized by multiple lesions (see photo) involving sun exposed sites that rapidly grow and then spontaneously regress, often leaving scars. It usually presents in early adulthood (3rd decade).
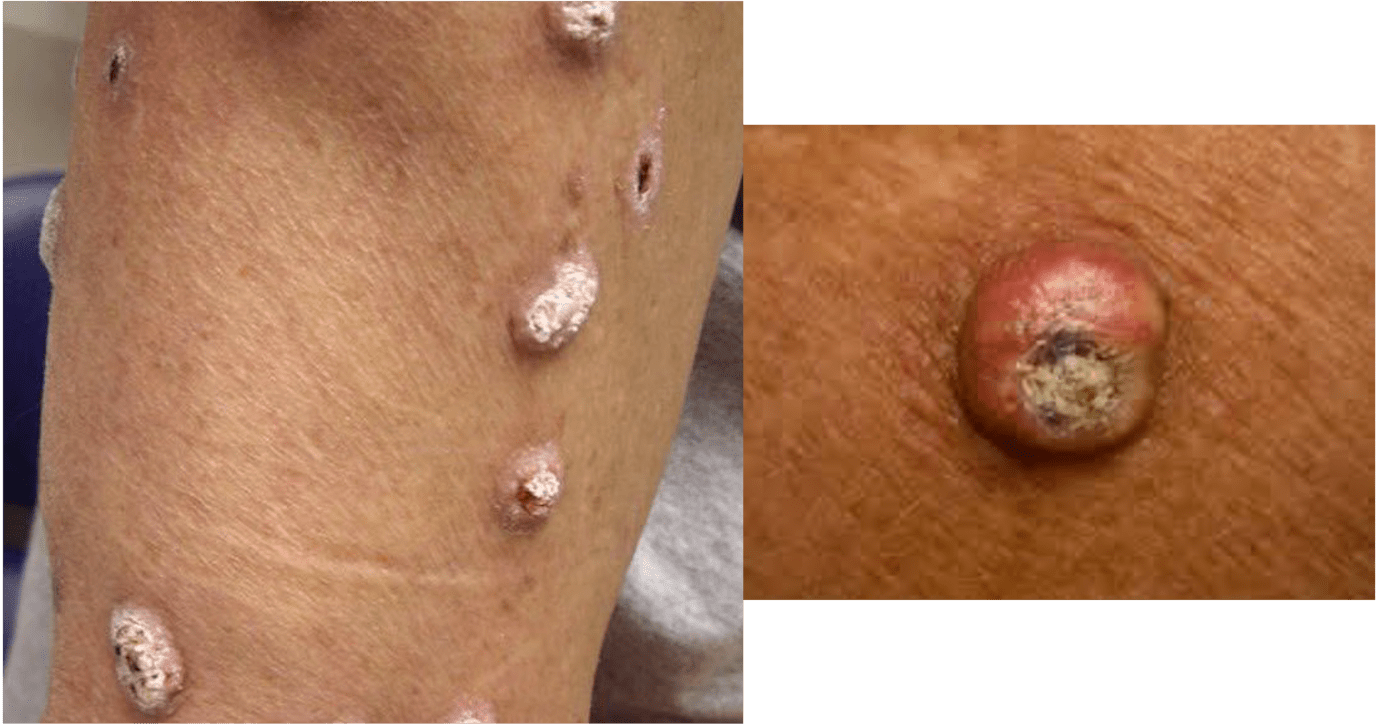
What is Ferguson-Smith syndrome?
Ferguson-Smith: AD inheritance (mx in TGFBR); rapid onset of multiple KAs; onset third decade, sun-exposed areas, and resolves spontaneously
Grzybowski: sporadic; 1000s of milia-like KAs in later adulthood; can involve airway; a/w scarring, ectropion, and mask-like facies. Mnemonic: “Old (later onset) Grizzlies Growl (airway affected)”
Other associations: Muir-Torre syndrome (classic KAs, or KAs w/ sebaceous differentiation)
This IgG autoantibody directed against BMZ is associated with an increased relative risk for malignancy in patients presenting with this ocular finding in association with other mucosal erosions and scarring.
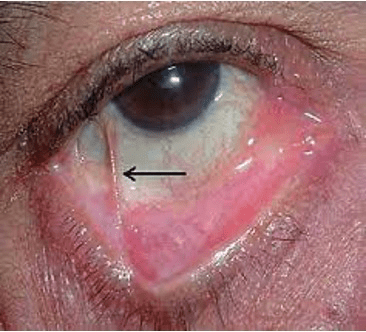
What is anti-Laminin 332/Laminin 5/Epiligrin?

A term for skin necrosis resulting from intravascular injection of fillers.
What is vascular occlusion?
This patient population is particularly at higher risk of developing an adverse cutaneous drug reaction from Hydroxychloroquine.
What is Dermatomyositis?
This rare genodermatosis presents with photosensitivity, poikiloderma and increased risks of cutaneous malignancies in children.
What is Rothmud-Thomson Syndrome?
Approved by the FDA in 2018 for adult patients with relapsed or refractory MF or SS after at least one prior systemic therapy, this CCR4-directed monoclonal antibody was evaluated against vorinostat in a pivotal trial.
What is Mogamulizumab?
Mogamulizumab targets the CC chemokine receptor 4 (CCR4), which is consistently expressed on malignant T cells in MF/SS, resulting in their destruction via antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity.
- MAVORIC trial - ORR 28% (skin 42%, blood 68%, LN 17%)
- Mogamulizumab associated rash “MAR” - indistinguishable from disease progression, skin biopsy needed to differentiate
This human monoclonal antibody targeting type I interferon receptor subunit 1 has been FDA-approved since 2021 for the treatment of moderate to severe SLE in adults. It has also emerged as a promising option for refractory CLE with demonstrated efficacy in CLE among SLE patients in two randomized clinical trials.
What is Anifrolumab/Saphnelo?
FDA approved biologics in SLE
1.Anifrolumab (Saphnelo)
• Target: Type I interferon receptor subunit 1 (IFNAR1)
• Approval: 2021 for SLE (w/out severe active lupus nephritis or neuropsychiatric SLE)
• Also being studied for: Cutaneous lupus and lupus nephritis (ongoing phase 3 trials)
2.Belimumab (Benlysta)
• Target: B-lymphocyte stimulator (BLyS / BAFF)
•Approval: 2011 for adults with SLE, 2020 expanded for lupus nephritis
This local anesthetic agent can induce methemoglobinemia by oxidizing iron in red blood cells from ferrous to ferric, impairing hemoglobin transport of oxygen.
What is Prilocaine?
This 1st generation antihistamine (H1-receptor antagonist) is preferred to treat cold urticaria and is FDA approved for anorexia nervosa because of its ability to increase appetite and weight gain.
What is Cyproheptadine?