What are the five steps of design thinking? How are they divided into two major phases? What are these two major phases?
Empathize, Define, Ideate, Prototype, Test
Finding the right problem: empathize, define
Finding the right solution: ideate, prototype, test
What is the difference between latent needs and blatant needs?
Blatant needs = problems that users are aware of and can articulate.
Latent needs = problems that users are unaware of, and can only be identified through observation of behavior
Name at least 3 rules of brainstorming
Defer judgement.
Go for quantity, not quality.
Encourage wild ideas. Build on other's ideas.
Be visual.
How/why does risk change when bringing a new product to market?
as you move from a design, to engineering, to tooling, to manufacturing, to distribution, to sales, your risk increases because it becomes increasingly expensive to make changes to the product.
What are the 3 key areas a new product must fulfill to create a successful innovation?
The "sweet spot" of innovation is at the intersection of feasibility, viability, and desirability.
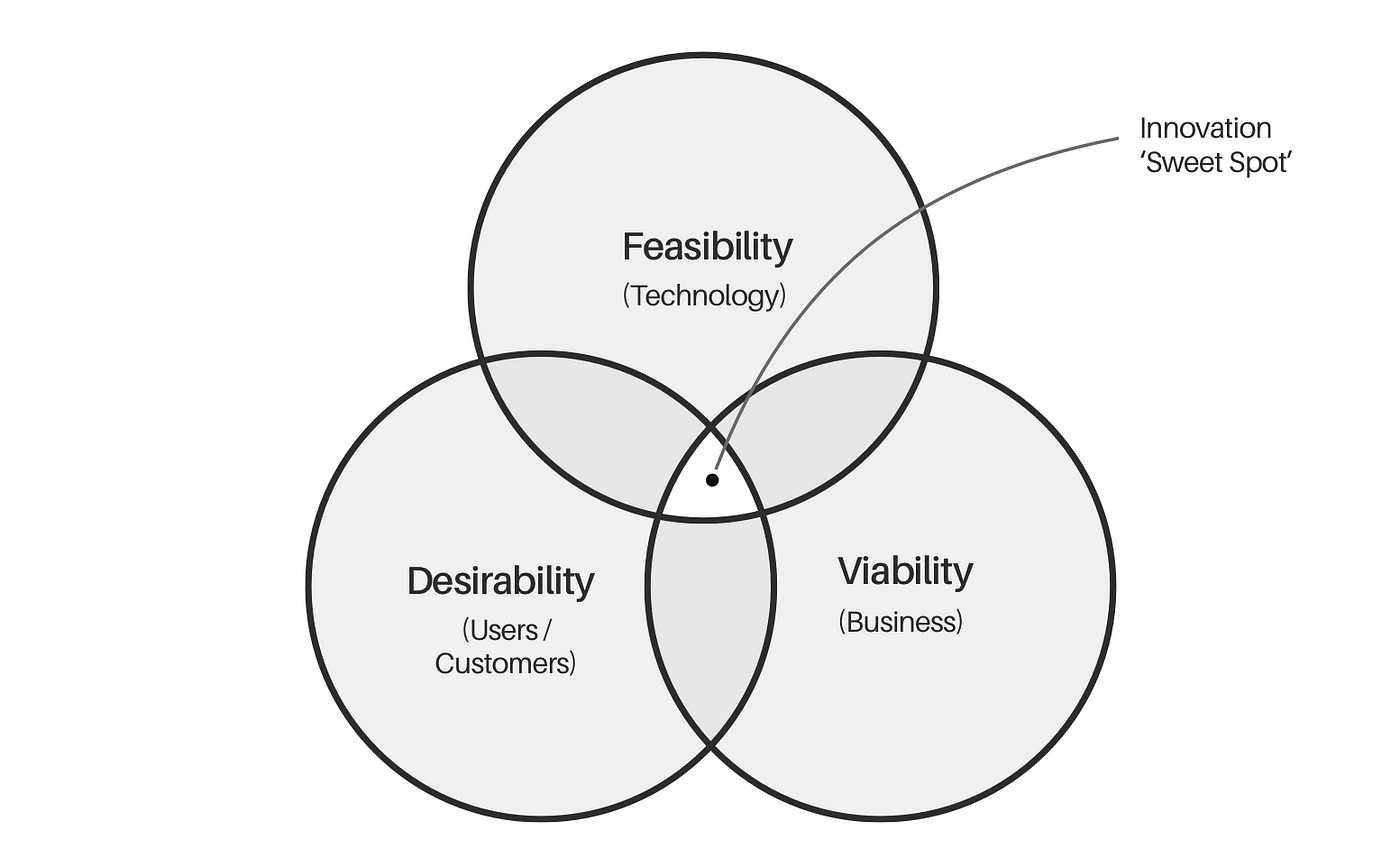
What is a "visionary" design approach, and how is it different from user-centered design?
The visionary thinks they know what is best (and is probably wrong), but a user-centered approach considers the voice of the customer to drive design decisions.
What are the 3 primary sources used in discovery research?
1. The company and/or client
2. The world (greater societal trends & contexts)
3. People with lived experiences (the users)
What is the purpose of prototyping?
Prototypes are for learning something about your product. If you don't learn anything, it was kind of a waste of time.
Why should a business bother spending money to support need-finding & conceptualization?
The cost of need-finding & conceptualization is much, much, much cheaper than the cost of making, distributing, & selling a product that nobody wants.
What is the "fuzzy front end" of innovation?
The fuzzy front end of innovation is the starting point where opportunities are identified and concepts are developed prior to entering the formal product development process. It is messy, non-linear, and requirements are often changing.
What is the benefit of describing user personas?
1. defines a representative user
2. grounded in details to paint a picture
3. can make it simpler to describe user needs & pain points
Name 3 examples of ethnographic user research.
Ethnographic user research: journal study, fly-on-wall observation, guided tour, activity shadow, in-depth interview
Not technically ethnographic research: focus groups, buddy groups, experiential research, retail audit
Definitely not ethnographic research: phone survey, web survey, mall intercepts
What is the process for arriving at 3 holistic concepts? How do you turn these holistic concepts into a final single concept?
Use "functional decomposition" to break down the product in terms of features, then brainstorm & converge on top 3 implementations for each feature. The three holistic concepts are just testing vehicles to explore your top implementations. After user testing, you combine the best features to form the final single concept.
What is the difference between verification testing, validation testing, and product design specifications? When do they happen?
Verification - am I building the product right?
Validation - am I building the right product?
These are tested using product design specifications. They should be used throughout the conceptual design process, and must be officially tested before moving on to the engineering phase of product development.
In the design process, Why should a company use multi-disciplinary teams rather than individuals working in silos?
Problems rarely lie within the boundaries of individual functional areas, but rather sprawl messily across the functions. You need people who can navigate across these areas.
How does divergent and convergent thinking fit into the design thinking process? Why are these separate activities?
Empathize - diverge
Define - converge
ideate prototype - diverge
prototype test - converge
If you do both at the same time, you will strongly limit the ideas that will come from the design process. It also helps collaboration and decision making.
Name the 3 fundamental tools for convergence during the "define" stage.
clustering
mind mapping (concept mapping, cognitive mapping)
experience mapping (customer journey, interaction, subway, swimlane)
What is the difference between:
1. a low-fidelity prototype (mock-up)
2. a form study model
3. a proof-of-principle/concept model
4. user experience model
5. visual model
6. alpha prototype
1. a low-fidelity prototype (mock-up) -just the idea, as simple as possible for quick feedback
2. a form study model - just the shape
3. a proof-of-principle/concept model - show something is feasible
4. user experience model - functions needed for hands on testing
5. visual model - only looks, no function
6. alpha prototype - fully working, close to final production
Explain how decisions are made in product design
Pugh matrix is a tool.
Justify with evidence.
Stage gates for decision makers
Don't overthink things, because it is an iterative process.
How does FMEA work?
Failure modes and effects analysis
Score failure modes by severity, probability of occurring, and likelihood of escaping detection, to calculate the risk priority number.
You presented your final design concept to the CEO of your company. Why should they trust your idea?
Need to show evidence to make compelling arguments, based on user research & testing.
You must convince them 1. you have identified the right design problem and 2. you have identified the right solution.
How can you systematically define your problem statement?
1. Converge on user research to identify pain points.
2. Write several problem statements.
3. Evaluate problem statements (good ones are human-centered, avoids proposing a solution, and leaves room for creative freedom)
4. Sort & prioritize problem statements by impact & feasibility
5. (optional) present problem statement as a "theory of change"
Name 3 reasons why you should avoid focus groups during concept preference testing
unnatural environment
can't simulate use of product
psychosocial effects (group think, polarization, social facilitation, social desirability bias)
What is an MVP and why should I make one?
MVP = minimum viable product.
Test customer's interest in the market without fully developing all product features. Test your business assumptions and confirm that customers will pay for certain features before fully developing them.
How can you tell if a product is well designed?
Story of development
Data to show efficacy
iterative user testing
feasible, viable, desirable