What is a pronoun? Who is 1st, 2nd, and 3rd?
Takes place of a noun; refers to me/myself/I, you/yourself, and everyone else (him, her, they)
What is the simple subject?
Can be an "understood you," Must be a noun, pronoun; The "who" or "what" of the verb
Ex. The dog likes to bark loudly/My friend Alex
What must each clause have?
What do we capitalize in a sentence?
Proper nouns, the word 'I,' the first word of each sentence, the first word of a quotation
Where does the subject go on the diagram?
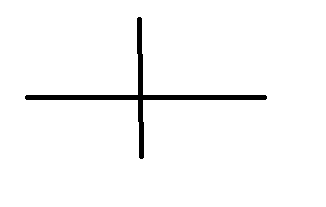 The left side of the T shape
The left side of the T shape
What is an adverb?
Modifies an adjective (really cute), verbs (run quickly), and other adverbs (very easily).
Not and never are ALWAYS adverbs
What is a predicate?
Transitive verb, intransitive verb, and all linking verbs.
Ex. We love English
S Predicate
What is an independent clause?
The main clause, must be included in every sentence, does not start with a relative pronoun (that, which, who, whom, whose), subordinating conjunction (after, since, before, while), or a noun clause identifier (that, who, what, when, where, why).
When do we underline/italicize?
Underlining and italicizing mean the same thing. We underline titles of long things: newspapers, movies, novels, plays, etc.
Where does the verb and direct object go?
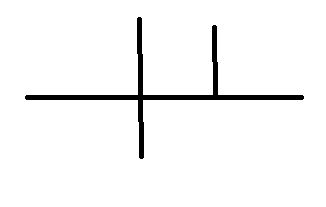 the right and far right side of the T shape
the right and far right side of the T shape
What is the difference between a helping verb and a linking verb?
Linking verb = links two words together (ex: is, be, am, are, was, etc).
Helping verb = helps an action verb or linking verb.; can be the same as a linking verb but depends on how many verbs are in the sentence (i.e, if the sentence has four verbs, the first three are helping).
What is a direct object?
A noun or pronoun that is NEVER in a prepositional phrase, follows an action verb.
To find it, say: "subject, verb, what" AKA "I like English, I like what? I like English"
What is a dependent clause? What are the subcategories of a dependent clause?
The subordinate clause, starts with a relative pronoun, subordinating conjunction, or a noun clause identifier.
Adv dep cl, adj dep cl, n dep cl
When do we use quotation marks?
Titles of shorts things: short stories, poems, songs, articles, episodes of TV shows, etc
What shape marks a prepositional phrase AND where does the prep go?
Tenses often refer to action verbs (av) or adverbs (adv). Name the tenses and provide an example word in its different variations.
Past (jumped), present (jump), future (will jump)
What is an appositive/appositive phrase?
A noun or pronoun that follows and renames another noun or pronoun.
Ex. We will read the book To Kill a Mockingbird
What are the different purposes of a sentence?
Declarative (dec) = makes a statement and ends in a period .
Interrogative (int) = asks a questions and ends in a question mark ?
Imperative (imp) = gives a command and ends in a period .
Exclamatory (exc) = expresses strong feelings and ends in an exclamation point !
We moved to Alachua, FL last year.
We are traveling to Madrid, Spain over the summer.
How do we include an appositive?
In parenthesis 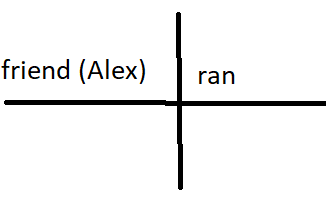
What is a preposition AND what is the difference between the category FANBOYS and its umbrella term?
Preposition shows the relationship between a noun or a pronoun OR a pronoun and some other word in the sentence. EX: Sally went across the field. Prepositional phrase = across the field
Conjunctions join phrases or clauses; FANBOYS are present in Coordinating Conjunctions (CC) and is an acronym for the words: for, and, nor, but, or, yet, so
What is a predicate nominative?
A noun or a pronoun which follows a linking verb and renames the subject.
To locate the pn, say "subject, linking verb, what or who? EX: He is a nice guy. He is what? guy
What are the different sentence types which we have identified thus far?
Simple sentence (ss) = one independent clause
Compound sentence (cd)= two or more independent clauses
Complex sentence (cx) = one independent clause + one or more dependent clause
Compound - complex sentence (cd-cx) = two or more independent clauses + one or more dependent clause
What are the rules for a comma with a nda?
Comes before or after the noun of direct address.
Tom, would you hand me the phone? OR Please don't sit there, Sue.
Where do we put an interjection or an nda?
Outside of the clause, separate from the rest of the diagram