Constriction of the airways and difficulty or discomfort in breathing
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)
Name the Oxygen delivery devices that you may see in the Progressive Care setting.
Nasal Cannula
Venti Mask
NRB
High flow
CPap/BiPap
What is the most common diagnostic used for issues/concerns surrounding the lungs
Chest X-Ray (CXR)
Name this item.

Nebulizer
PH= 7.55
pCO2= 27
HCO3= 23
Respiratory Alkalosis w/ no compensation
Acute infection of the lung parenchyma, including alveolar spaces and interstitial tissue
Pneumonia
Name a common medication used to help open the airways.
Bronchodilators
What information does an Arterial Blood Gas (ABG) give?
PH, PaCO2, HCO3, PaO2, SaO2
BONUS: Lactate
What is this device and what is it used for?
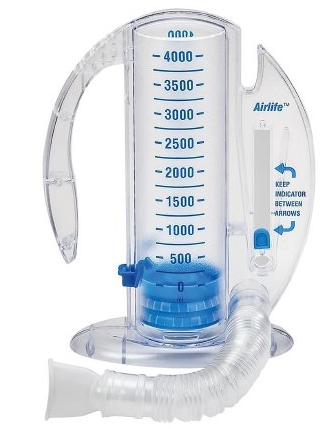
BONUS: Should the patient inhale or exhale in the device?
Incentive Spirometer
It measures the volume of your breath. It can help the lungs heal after surgery or in cases of lung disease and conditions that fill the lungs with fluid.
INHALE- spirometer works when you inhale because of the resistance it places on your breath. Exhaling into the spirometer will not help your lungs.
PH= 7.24
pCO2= 32
HCO3= 13
Metabolic Acidosis w/ no compensation
Uncontrolled airway inflammation/narrowing
Asthma (w/ ARF)
Interventions that can be done to help improve secretion removal
–Hydration
–Early mobility
–Coughing
–Humidified aerosolization
Test done to identify severity of pulmonary impairment...

Pulmonary Function Test (PFT)
What are these used for?
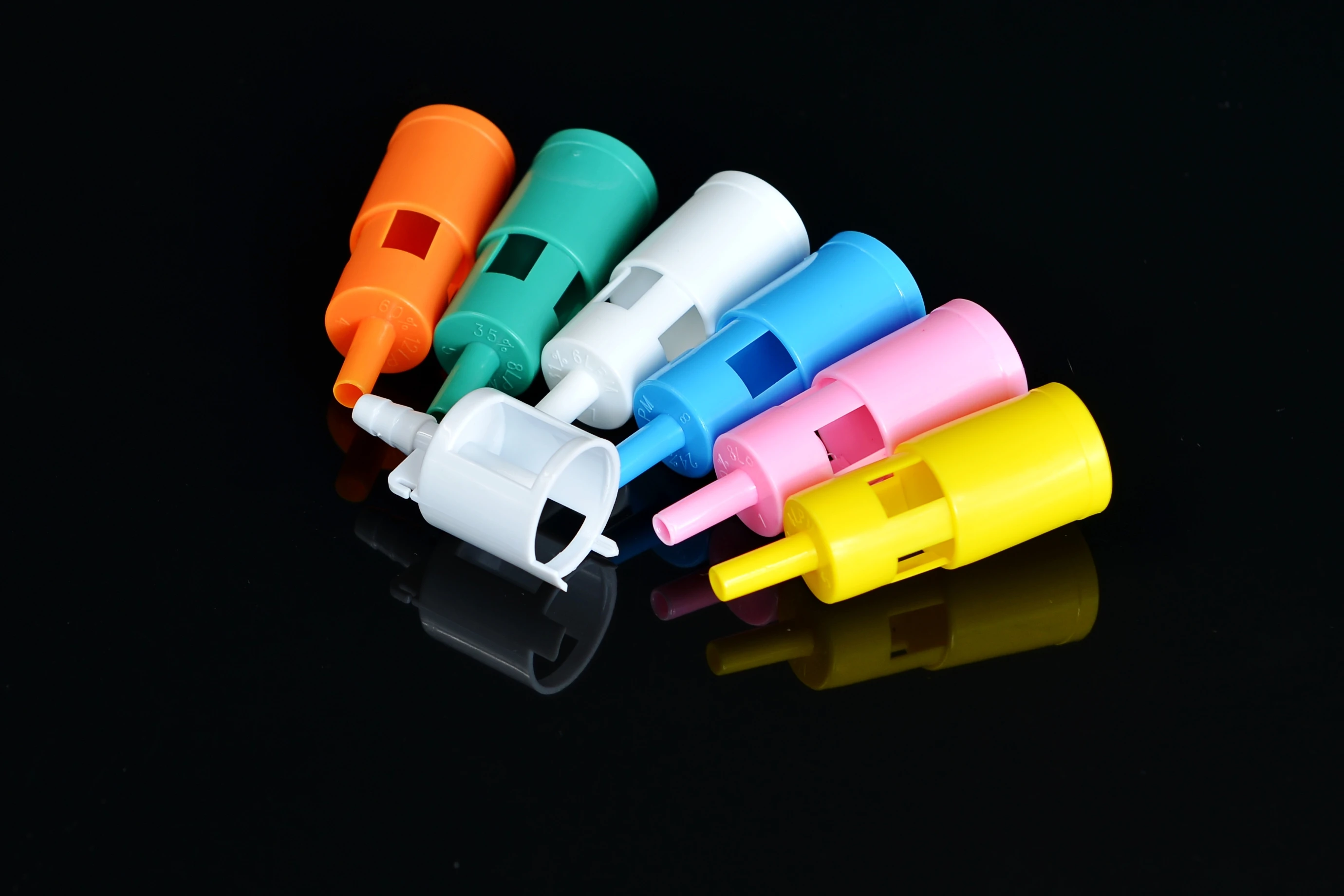

Different FiO2 for Venti Masks
PH= 7.7.30
pCO2= 50
HCO3= 24
Respiratory Acidosis w/ no compensation
Non-cardiac pulmonary edema caused by ↑ alveolar capillary permeability
Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS)
Along with management of secretions, what other method of treatment would we expect with a patient with Pneumonia?
Antibiotic Therapy
What testing method, besidees a CXR and ABGs, would you expect to see ordered when ruling out a PE?
CT Chest w/ PE Protocol
How many liters of O2 is required fro each oxygen device?
NC
Venti
NRB
NC- up to 6L
Venti- up to 15L (depending on the desired FiO2/valve being used)
NRB12-15L (crank it all the way up)
High flow (flowmeeter goes up to 75L.. titrated by RT)
CPap/BiPap- patient dependant
PH= 7.62
pCO2= 44
HCO3= 45
Metabolic Alkalosis w/ no compensation
Obstruction of blood flow to one or more arteries of the lung by a thrombus lodged in a pulmonary vessel.
Pulmonary Embolism
Name 2 different treatments for Pulmonary Embolism after an official diagnosis has been made.
Thrombolytics (Heparin)
Surgery (Thrombectomy)
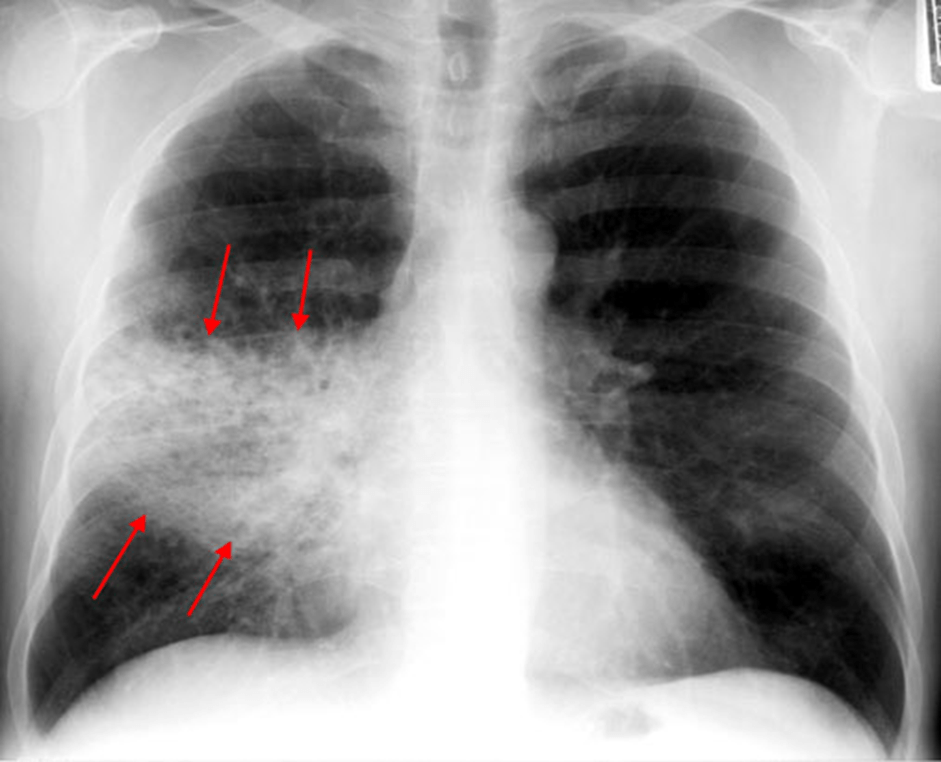
Pneumonia
Name this item?

Oropharyngeal Airway
PH= 7.45
pCO2= 47
HCO3= 29
Metabolic Alkalosis w/ FULL compensation
•Over 130 lung conditions
•Characterized by fibrosis +/or inflammation
•Lung tissue (interstitium) damage leads to inflammation
•Fibrosis and scarring
Interstitial Lung Disease (ILD)
Progressive Care is able to take patients up to what FiO2% on High Flow?
60% (increases above 60% for ambulation, turns, ect. is okay)
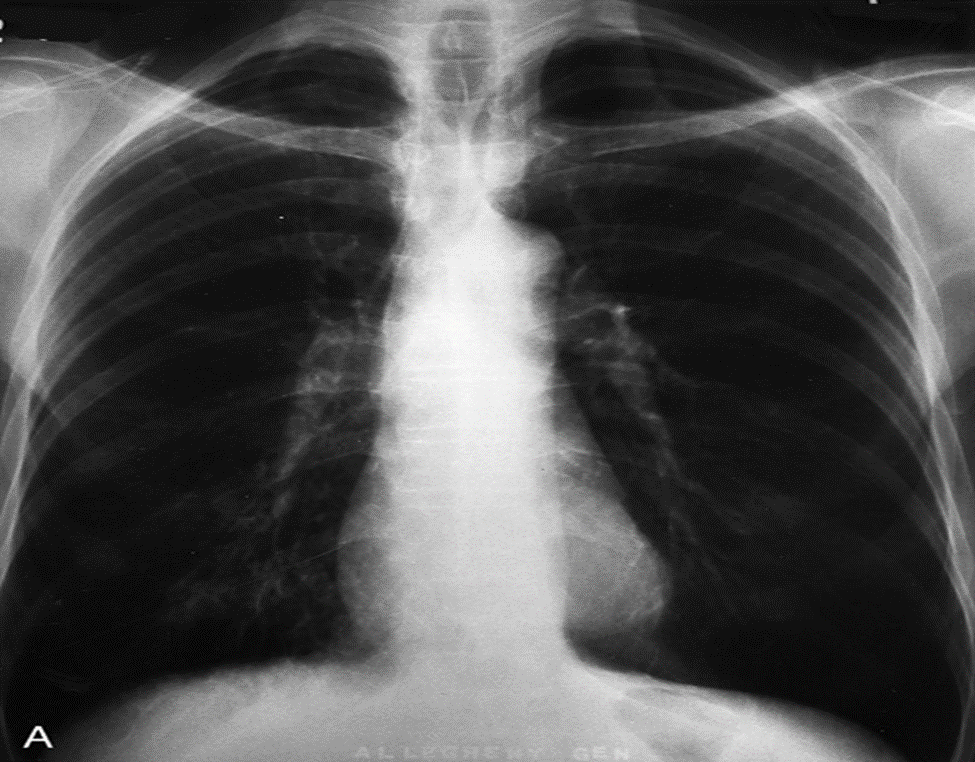
COPD
Demonstrate the proper way to put together a Venti Mask.
PH= 7.20
pCO2= 68
HCO3= 36
Respiratory Acidosis w/ PARTIAL compensation
–PaO2 less than 60 mm Hg
AND
–PaCO2 greater than 50 mm Hg
WITH
–pH less than or equal to 7.30
Pulmonary system is no longer able to meet metabolic demands
Acute Respiratory Failure (ARF)
Your patient's respirations are dropping and they are becoming less responsive. What action should you take?
Call 5-5555 and ask for an Adult STAT Airway
BMV or NRB (COVID times)
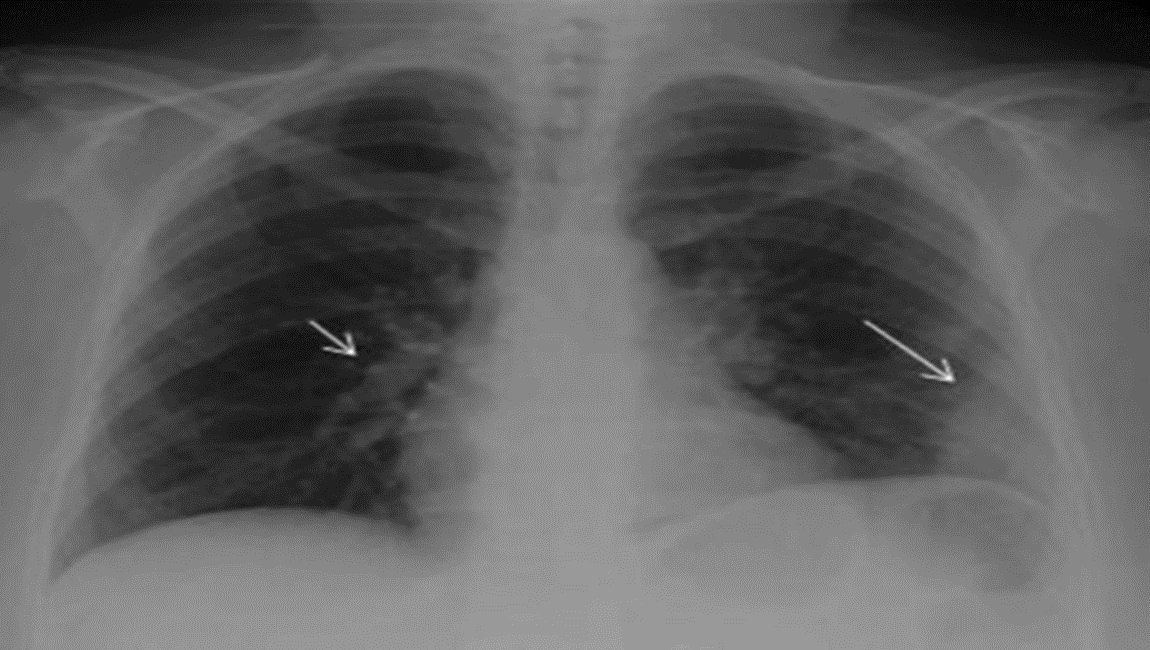
Pulmonary Embolism
Name this item...
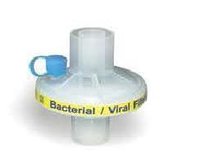
Hepa Filter
PH= 7.52
pCO2= 30
HCO3= 32
Mixed Alkalosis w/ no compensation