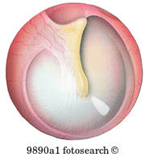
 Label landmarks of Tymapnic Membrane.
Label landmarks of Tymapnic Membrane.
Should have: pars flaccida, pars tensa, umbo, cone of light, superior malleolar fold, annular ligament
What are the three "canals" of the cochlea?
What are the three inner ear fluids? What are their sodium and potassium levels (low/high)?
Scala Vestibuli, Scala Media, Scala Tympani.
Perilymph; high sodium, low potassium.
Endolymph; low Na, high K
Cortilymph; high Na
Match the anatomy to their resonant peaks:
Pinna, Concha, Meatus
a. 2500 hz
b. 6000 hz
c. 5000 hz
a. meatus
b. pinna
c. concha
What are the two theories of cochlear movement?
which is also known as the cochlear amplifier?
Passive and Active.
Active is the amplifier.
Name all 12 Cranial Nerves. Give their function: sensory, motor or mixed.
Olfactory; Sensory. Optic; Sensory. Oculomotor; motor. Trochlear; Motor. Trigeminal; Mixed. Abducens; Motor. Facial; Mixed. Vestibulocochelar; sensory. Glossopharyngeal; mixed. Vagus; mixed. Accessory; motor. Hypoglossal; motor.
Label parts of pinna.
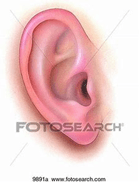
Should have: helix, antihelix, lobula, tragus, antitragus, crura, concha bowl, intertragic notch
Label Organ of Corti.
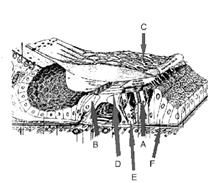
A. OHC
B. IHC
C. tectorial membrane
D. reticular lamina
E. deiter cells
F. basilar membrane
Define/Describe the headshadow effect.
The interaural time and intensity difference of a stimulus.
Match: Cochlear Microphonic, Summating Potential, Action Potential
a. extracellular fluid around hair cells changes
b. neural firing, generated by nerve
c. generated by OHC's
BQ: Where does endocochlear potential come from?
a. summating
b. AP
c. CM
BQ. Stria Vascularis
Which of the following are types of cell communication?
a. paracrine
b. autocrine
c. endocrine
d. direct contact
e. all of the above
E. all of the above.
Ear Canal:
Which portion of the canal is ossesous?
Glands are located in the ______ portion. What are the two types of glands?
To straighten out a childs canal you pull ____ & ____.
Medial 2/3rds.
Lateral; Apocrine and Sebaceous.
Back and Down.
Match: Apex, Base, OHC, IHC
a. amplifyies sound on the way to IHC
b. narrow, higher hz, stiff
c. sends signal to brain
d. wide, less stiff, lower hz
a. OHC
b. base
c. IHC
d. apex
Match: Area Ratio Transformation, Ossicular Chain Lever Action and Catenary Lever Action
a. rotation of malleus and stapes creates a fulcrum
b. increases sound pressure level by 6 dB
c. increases sound pressure level by 2 dB
d. TM is 17.2x larger than oval window
e. increase SPL by 25 dB
f. The buckling of the TM
Area Ratio: D and E
Ossicular Lever: A and C
Catenary: F and B
Match Vestibular Anatomy: linear acceleration, angular
a. utricle
b. semicircular canals
c. saccule
a. linear
b. angular
c. linear
What are the three main players in neural communication?
Sodium, Potassium and Calcium
Tympanic Cavity:
The roof is called the __________.
The head of the malleus and bulk of incus occupy the _________ ________. The floor fo the cavity is made up of _______ bone (of the skull).
Tegmen tympani.
Epitympanic Recess.
Tympanic plate of the Temporal
a. medial geniculate body
b. cochlea
c. auditory cortex
d. cochlear nucleus
e. inferior colliculus
f. superior olivary complex
g. lateral lemniscus
BQ: Where is the first place we get ipsilateral and contralateral information? Which structure is aka "the highway"?
B-D-F-G-E-A-C
Superior Olivary Complex.
Lateral Lemniscus.
ME mass is an obstacle to _____ frequencies while stiffness is an obstacle to ______ frequencies.
If ME increases in ______, there's an increase in low frequency off the TM.
High. Low.
Stiffness.
Which vestibular anatomical structures cotain otoconia? What is the "big kahuna" balance sensory organ called?
Utricle and Saccule; Macculae.
What are the THREE outputs of the vestibluar system? Describe them.
Vestibulo-Ocular: stabilizes vision during head movement.
Vestibulo-Colic: Stabilizes the head.
VestibuloSpinal Reflex: Stabilizes the whole body
What are the 8 ligaments and muscles of the midde ear?
What lives on the medial wall of the tympanic cavity?What about the anterior wall?
Superior, Lateral and Anterior Malleolar. Posterior and Superior Incus ligaments. Annular ligament. Stapedius and Tensor Tympani.
Medial: Oval window, Round window, Promontory and the Prominence of the CNVIII canal. Anterior: Tendon of tensor tympani and the eustachian tube.
Name the three pairs of semicircular canals.
What are they filled with (liquid wise)?
Which two vestibular organs are 90 degrees offset from each other?
Left Anterior Right Posterior, Rigth Anterior Left Posterior, Horizontal Lateral; full of endolymph.
Utricle and Saccule
Acoustic Reflex:
What muscle does it tighten?
It is a (unilateral/bilateral) reaction.
It's purpose is to _________.
An ART helps distinguish which two types of hearing loss?
Stapedius.
Bilateral.
Purpose is to serve as volume control, protect us from our own voice and a NIHL. Preserves speech intelligibility and betters SNR.
ART distinguishes Cochlear vs Retrocochlear HL.
Explain the traveling wave theory.
Footplate of the stapes pushes fluids, fluids travels the length of the cochlea, cuasing the basilar membrane to displace. a particular frequency grows in amplitude and then dies out.
List 5 characteristics about Inner and Outer Hair Cells.
Inner: one row, 3500 cells, vase shaped, 70 stereocilia, 95% afferent, supported by phalangeal cells, medial portion of tunnel, type 1 nerves
Outer: 3 to 5 rows, 12000 to 13500 cells, phallax shaped, 150 stereocilia, 5% afferent, lateral tunnel, have actin, supported by deiter cells, type 2 nerves, "w" shape