Match Code: OAE screen, complete eval, limited eval.
a. 3 to 6 Hz tested
b. pass or refer
c. 12 frequencies obtained
What are the three factors for declaring a response present?
A. Limited
B. Screen
C. Compete
Verify noise floor is below 10 dB, Amplitude emission is greater then -10 dB and SNR is greater then 6 dB
What are the four types of waves that can be recorded during an EEG? What frequencies are they at?
Alpha: 8k-13k
Delta: 500-4k
Theta: 4k-8k
Beta: 13k-30k
What is the difference in sleep for sedation and general anethesia?
What is the goal time for each child who doesn't pass their newborn hearing screening?
sedation is a lighter sleep.
1 month retest, 3 month diagnosis, 6 month early intervention
Which of the following are ways to enhance WI?
a. an ECochG
b. increase stimulus rate
c. decrease intensity level
d. compare rarefraction and condensation waves
What is the "WNL" range for latency-intensity functions?
A&D
20 to 63 microseconds
What are the labels for an ABR? MLR? LLR? And MMN?
What does N400 test? P600?
ABR- roman numerals I-VII
MLR- Na, Pa, Nb, Pb
LLR- P1, N1, P2, N2
MMN- N400, P600
n400- semantics
p600- syntax
What are factors of an OAE interpretation? What are non-factors?
Factors: subject state, frequency being tested, physiological noise, probe fit, averaging time, biological noise
Non-Factors: body position and temperature, state of arousal, time of day, attention to stimulus
What are three clincial uses for a child and OAE? And three uses for an Adult and OAE?
Child- ototoxic monitoring, newborn hearing screening, pediatric evaluation, pseudohypacusis
Adult- malingering, cochlear vs retro pathology, tinnitus, ototoxicity, noise exposure screen tool
True or False; Adults use 10 dB steps while infants sue 5 dB steps while finding threshold.
true.
false; adults are 5. kiddos are 10.
Which of the following are indicators of a retrocochlear pathology?
a. ILD is greater then 0.3 between ears
b. W5 latency is > 6.5 ms @ 80 dB
c. WI-WIII > 2.3 ms
d. WI-W5 > 4.4 ms
With a conductive hearing loss the _____________ will be prolonged but the ___________ will be WNL.
All of the above.
Absolute latency, Interpeak latencies.
Which test has a large stimulus artifact?
Which stimulus is the best for an ASSR?
Which test uses single pulse trains for stimuli? Test uses the speech sound "da"? Deviant stimuli?
eABR largest artifact.
ASSR- Mixed Modulation
Single Pulse Trains- eABR; "da" is cABR; deviant is MMN.
Match: TEOAE, DPOAE
a. tone intensity at 80-83 dB
b. Freq. range 500-20k
c. Intensity at 65/55 dB
d. Freq. range 500-5k
e. "present" criterion SNR above 6 dB
What type of pathology would cause a "refer" but OHC function is WNL?
TEOAE: A, D, E
DPOAE: B, C, E
Conductive hearing loss
True or False; Correct if False:
1. When using a contralateral recording technique, W1 will generally increase in size which facilitates identifying W1.
2. Latency is the most robust charcateristic of an ABR.
3. In general, the later the potential the smaller in amplitude the response will be.
1. false. with contralateral w1 will be absent.
2. true
3. false; its greater in amplitude.
What is best location for the bone oscillator for an ABR?
a. frontal bone
b. upper mastoid
c. parietal bone
d. lower mastoid
B. upper mastoid
What are the normative values for each absolute lantency? Interpeak latency? and interaural latency difference?
WI: 1.6 WIII: 3.8 WV: 5.6
WI-III: 2.0 WIII-WV: 1.8 WI-WV: 4.0
ILD < or equal to .20 ms
Which two characteristics are preserved in a cABR?What are clinical uses for a cABR?
What are three things that can affect an MLR response?
Time and Periodicity.
Diagnosing language delays and/or APD
CNS dysfunction. Age, Drugs
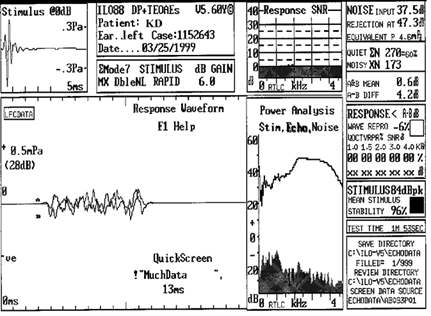
What type of OAE is this? Does this PT have normal OHC fucntion? Why or Why not?
TEOAE. No, test results indicate not WNL.
Response doesnt meet any of the criteria.
Match Wave to Generator: I-VII
a. MGB
b. cochlear nucleus
c. Distal CNVIII
d. Lateral Lemniscus
e. Proximal CNVIII
f. Superior Olivary Complex
G: Inferior Colliculus
a. 7
b. 3
c. 1
d. 5
e. 2
f. 4
g. 6
When testing a newborn, if the air conduction thresholds are WNL do we need to test bone? If theyre not within normal what do we test bone to determine?
If AC WNL, no need to test BC.
If AC isnt WNL, use BC to determine type and degree of hearing loss.
As frequency decreases, latency will __________.
As intensity increases, latency will _________.
As intensity increases, amplitude will _________.
Increases.
Decreases.
Decreases.
Match: 40 hz, ASSR, eABR, cABR, MLR, LLR, MMN
a. picks out peak and trough of wave 5; creates score 0-30
b. look at latency from 70-300 msec
c. look at latency from 100-300 msec
d. find 3 to 4 peaks every 25 msec
e. phase coherence and F test determines presence
f. peak pick wave 5; will be earlier and larger in amplitude then ABR
g. look at waves; latency from 10 to 70 msec
a. cABR
b. LLR
c. MMN
d. 40 hz
e. MLR
f. eABR
g. ASSR
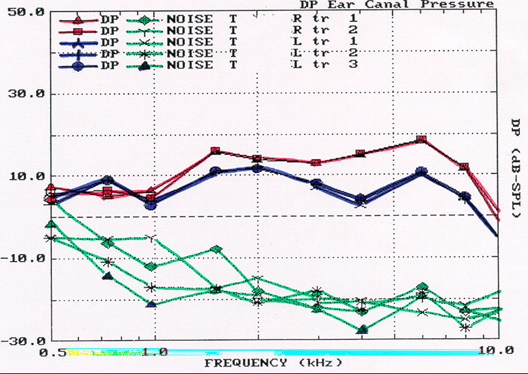
What type of OAE is this? What are the results? How do you know?
DPOAE. TEST is Pass/Present.
All criteria are met.
Match generators: 40 hz, 80 hz, LLR, MMN, cABR/eABR
a. CNVIII thru the MGB
b. brainstem and cortex
c. brainstem
d. cortex and frontal lobe
e. thalamus, primary and secondary auditory cortex
a. ABR
b. 40 HZ
c. 80 HZ
d. MMN
e. LLR
What are the 5 things to review when determing if a resposne is present or not?
Is it replicable?
is the correlation coefficient greater then .70?
is the noise below 0.05?
does the waveform follow physiological principles?
is w5 within latency norms?
With a neurodiagnostic ABR, the impedance of each electrode should be no more than _________ kohms and have no more than __________ kohms between each electrode.
How do these values differ for infants?
5 and 2 kohms.
Kiddos are 3 for each and 1 in between.
Match Filters: MMN, MLR, LLR, ASSR, 40 hz, eABR, cABR
a. 10-300
b. 100-2000
c. 1 to 30
d. 30-3000
e. 30-100
f. 10-100
g. 10 or 30 to 100
a. MLR
b. cABR
c. MMN
d. eABR
e. LLR
f. 40 Hz
g. ASSR