This enzyme begins chemical digestion of proteins
Pepsin
Name any 1 of 3 enzymes that complete carbohydrate digestion
Maltase, Sucrase, Lactase
These are used for the physical break down of food in the mouth
Teeth
This organ releases bicarbonate ions into the small intestine to neutralize acids from the stomach
Pancreas
This is partially digested food that enters the small intestine. (has the consistency of puree soup)
Chyme
Type of bonds WITHIN a water molecule
Covalent
This enzyme digests polysaccharides into disaccharides and is located in the mouth.
Salivary amylase
This enzyme breaks lipids into fatty acids and glycerol in the small intestine
Lipase
The organ where digestion finishes and absorption of nutrients takes place.
small intestine
These are finger like tubes found on the walls of the intestine to increase surface area and absorb nutrients
Villi
When lipids are digested, they break down into what?
1 glycerol and 3 fatty acids
What makes water SO amazing!
it's polarity due to hydrogen bonding. 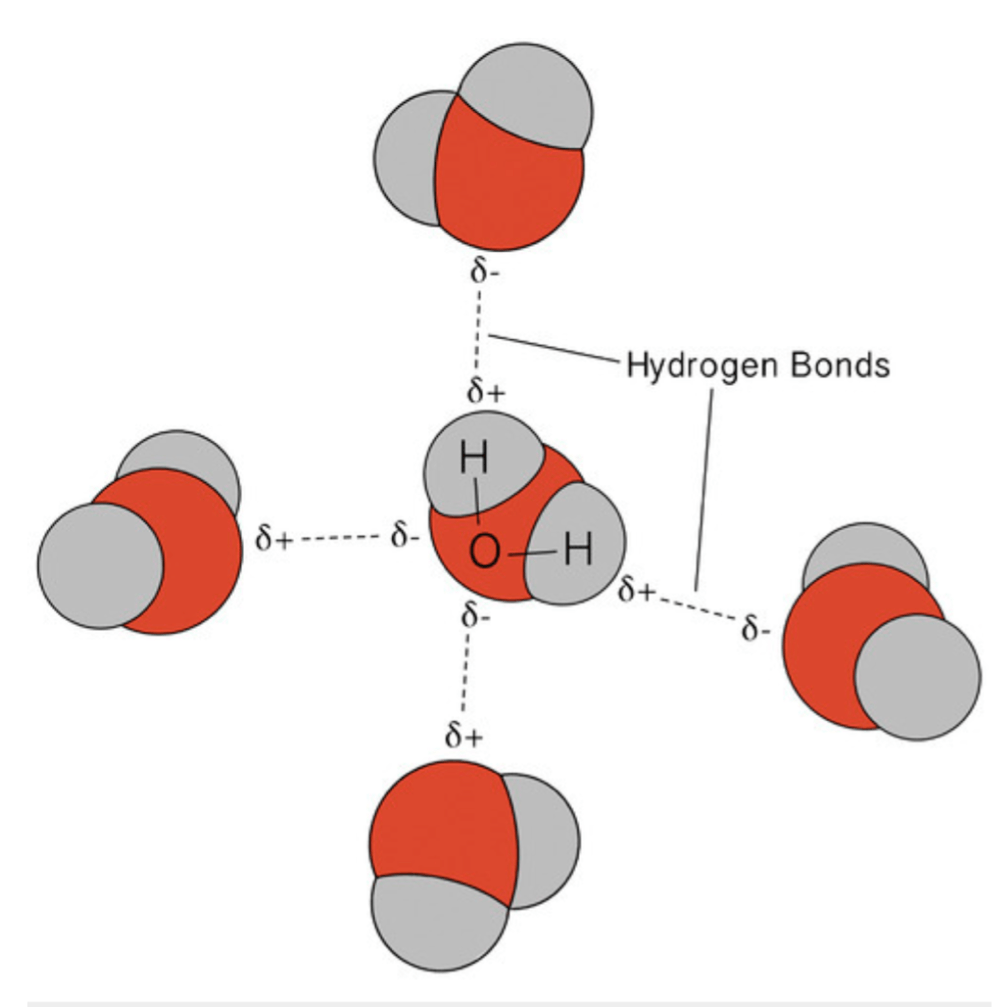
This enzyme completes protein digestion, breaking dipeptides down into individual amino acids and is released from the small intestine
Peptidase
This acid is found in the stomach and creates a very acidic environment
HCl (Hydrochloric acid)
This is an open area at the back of the mouth where the nose and mouth come together
Pharynx
3 functions of this organ are to synthesize vitamins B and K, the elimination of waste, and to absorb water.
Large intestine
What monomers are carried to the cells by the bloodstream from the small intestine?
Amino acids and glucose (monosaccharides)
As a result of hydrogen bonding, water's tendency to stick to itself.
cohesion
These enzymes break down proteins into shorter peptides in the small intestine and are released from pancreas.
Trypsin and chympotrypsin
This substance keeps the food lubricated and keeps the walls of the stomach from being digested by its own secretions
Mucus
This tube carries food from the pharynx to the stomach
Esophagus
Name the wave of muscular contractions that push food along the digestive tract
Peristalsis
This is a small pouch located at the junction of the small and large intestine. It can become infected and require surgery.
Appendix
As a result of hydrogen bonding, water's tendency to stick to OTHER things.
Adhesion
This enzyme breaks starch (polysaccharide) into disaccharides in the small intestine.
Pancreatic Amylase
This emulsifies fats into smaller fat globules in the small intestine
Bile
What is the name of the first part of the small intestine
Duodenum
What are the 4 accessory organs?
Salivary glands, pancreas, liver, gall bladder
How are fats absorbed and carried to the cells?
Absorbed by the LYMPH in the villi and carried to the subclavian vein and then dumped into the blood stream.
1. Universal solvent
2. Cohesion
3. Adhesion
4. Surface tension
5. Capillary Action