This disorder is often called Lou Gehrig’s disease and affects motor neurons leading to muscle weakness and paralysis
Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS)
What are the common risk factors for cardiovascular diseases? (List at least 4)
High blood pressure, high cholesterol, smoking, obesity, diabetes, poor diet, physical inactivity, and family history.
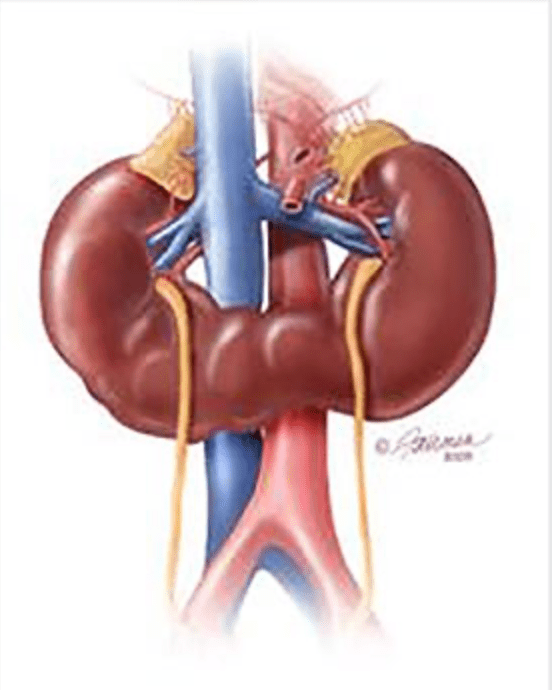
Horseshoe Kidney
What is the most common endocrine disorder?
Diabetes mellitus
This condition, often associated with liver damage from alcohol abuse or hepatitis leads to scarring of the liver with impaired function
Cirrhosis
This chronic lung disease causes inflammation and narrowing of the airways, often trigged by allergens or exercise.
Asthma
What causes Down syndrome? Be specific in the phenotype
An extra copy of chromatid 21, or trisomy 21
What is Parkinson’s Disease caused by?
This disorder results from the degeneration of dopamine producing neurons in the substantia nigra and causes tremors, rigidity, and bradykinesia
What are the symptoms of a myocardial infarction (heart attack)? (List at least 3)
Chest pain, shortness of breath, nausea, sweating, dizziness, and pain radiating to the arm, jaw, or back.
How does high blood pressure affect the kidneys?
High blood pressure damages the small blood vessels in the kidneys, reducing their ability to filter waste and excess fluids, leading to kidney scarring, decreased function, and an increased risk of chronic kidney disease (CKD) or kidney failure.
How can a tumor on a gland affect the secretion of hormones from that gland?
Hypersecretion OR Hyposecretion
This inflammatory auto immune bowel disease is often confused with ulcerative colitis and can affect any part of the digestive tract
Crohn’s Disease
This common viral infection affects the nose, throat, and lungs leading to symptoms like coughing, sneezing, and congestion
The common cold
This highly contagious viral disease eradicated in 1980 and caused severe rashes and fever. It was one of the deadliest infections in human history.
Small pox
This viral disease is transmitted by infected animals and attacks the central nervous system and is almost always fatal once symptoms appear
Rabies
How does hypertension affect the cardiovascular system and lead to cardiovascular disease?
It damages arteries, increases heart workload, and raises the risk of heart attack, stroke, and heart failure.
How do kidney stones form? What factors increase the risk of developing kidney stones (list at least 2)?
They form when minerals and salts in the urine, such as calcium and uric acid. become supersaturated and crystallize.
Risk factors: Dehydration, High sodium intake, High oxalate diet, High animal protein intake
What is the difference between type 1 and type 2 diabetes?
Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune condition where the body attacks insulin-producing pancreatic cells, leading to little or no insulin production, while Type 2 diabetes is primarily caused by insulin resistance, often linked to lifestyle factors.
What is GERD and what causes it?
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) is a chronic condition where stomach acid frequently flows back into the esophagus, causing irritation and inflammation of the esophageal lining. It occurs due to a weakened lower esophageal sphincter (LES), which fails to close properly, allowing acid to escape from the stomach.
This bacterial infection primarily affects the lungs and can cause persistent coughing, fever, and weight loss. It can be determined by a Mantoux Test or a Chest Xray
This mental health condition is often associated with extreme mood swings between manic and depressive states and is sometimes called manic depression
Bipolar disorder
What is Multiple Sclerosis caused by?
In this disorder the immune system attacks the myelin sheath of nerves leading to symptoms such as fatigue, vision problems, and difficulty walking.
A patient presents with intermittent chest pain and shortness of breath that occur during physical activity and resolve with rest. ECG and resting echocardiogram are unremarkable. What diagnostic test should be performed to evaluate exercise-induced arrhythmias?
Stress Test - evaluates heart function and detects arrhythmias by monitoring the heart's response to physical exertion.
What are the indications for a nephrectomy (removal of the kidney)? What precautions does a person living with one kidney have to take?
A nephrectomy is performed when a kidney is severely damaged or poses a health risk, such as in kidney cancer, severe trauma, chronic infection (pyelonephritis), hydronephrosis, or non-functioning kidneys due to congenital defects or disease. After nephrectomy, a person with one kidney should take the following precautions: staying hydrated, maintaining a balanced diet low in sodium and protein, avoiding nephrotoxic medications (like NSAIDs), and limiting high-impact activities to prevent kidney injury.
A patient presents with unintentional weight loss, heat intolerance, excessive sweating, palpitations, tremors, and increased appetite. On physical examination, the patient has a visibly enlarged thyroid gland (goiter). Lab results show low TSH and elevated T3/T4 levels. What is the most likely diagnosis? MUST explain symptoms.
Hyperthyroidism.
weight loss, heat intolerance, excessive sweating, palpitations, tremors, and increased appetite ---> High Thyroid Hormone, which increases metabolic rate
low TSH and elevated T3/T4 levels ---> Enough circulating T3/T4 indicates low TSH secretion from pituitary.
The presences of stones in this pear shaped organ can lead to severe abdominal pain, nausea, and may need surgical removal
Gallstones
This genetic disorder causes thick, sticky mucus build up in the lungs leading to frequent lung infections and difficulty breathing
This common joint disorder leads to the breakdown of cartilage and leads to pain and stiffness.
Osteoarthritis
- Tau protein build up and tangles
- Neurofilament Light Chain
A patient presents to the hospital with shortness of breath, fatigue, and bilateral leg swelling. Physical examination reveals pulmonary crackles and pitting edema. What is the most likely diagnosis? Explain what the disease is, and your diagnosis must explain each symptom.
The most likely diagnosis is Congestive Heart Failure (CHF). Shortness of breath results from fluid buildup in the lungs due to left heart dysfunction, while fatigue occurs due to poor tissue perfusion. Bilateral leg swelling, pitting edema, and jugular venous distension indicate systemic venous congestion from right heart failure. Pulmonary crackles suggest fluid accumulation in the alveoli due to increased left atrial pressure.
n chronic kidney disease (CKD), progressive loss of kidney function leads to fluid retention, electrolyte imbalances, toxin accumulation, hypertension, anemia, and bone disease, increasing the risk of cardiovascular complications. How does chronic kidney disease affect cardiovascular health?
Hypertension develops from fluid retention and activation of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS), leading to increased cardiac workload. Left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH) occurs due to chronic hypertension and volume overload. lectrolyte imbalances, such as hyperkalemia and calcium-phosphate abnormalities, contribute to arrhythmias and vascular calcification. Anemia from reduced erythropoietin production leads to increased cardiac strain.
What is diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA), and why is it dangerous?
Without insulin, cells cannot use glucose for energy, so the body breaks down fat for fuel, producing ketones, which accumulate and cause acidosis.
it can lead to severe dehydration, electrolyte imbalances (especially potassium shifts), altered mental status, and coma.
What is Celiac Disease
This autoimmune disorder is triggered by gluten consumption and leads to damage of the small intestine’s villi, causing malabsorption and gastrointestinal distress
What problem with pulmonary edema cause?
It makes it difficult for oxygen to reach the bloodstream
This genetic disorder was recently cured by CRISPR gene editing and affects erythrocytes.
Sickle cell disease