Example of a loop diuretic
What is furosemide (Lasix)
It's normal for this reason
What is isotonic?
This "pillar" is also a mild diuretic and anti-hypertensive. It is contraindicated with oral potassium supplement.
What is Spironolactone or Aldactone?
This is the most serious toxic effect of acute acetaminophen overdose.
What is hepatotoxicity?
Don't administer a diuretic in the hospital without this helpful plastic tool.
What is a urinal?
Chlorothiazide (Diuril), hydrochlorothiazide (Hydrodiuril)
What is thiazide diuretic.
This hormone can have a profound effect on your potassium levels.
What is insulin?
This "pillar" helps with cardiac remodeling. Keeping our heart in a lean football shape instead of a big old basketball.
What is ACE/ARB/ARNI, Lisinopril, Losartan or Entresto.
A 5 year old patient has the flu with a fever. This NSAID is not indicated for children.
What is low dose aspirin?
This is what you check prior to administration of an diuretic.
What is serum electrolytes (potassium!).
An agent acting on distal tubule? Potassium-sparing diuretics
What is spironolactone (Aldactone)
3.5-5.0 is considered normal
What is serum potassium levels?
This "pillar" is the heart "vacation" medication. It lowers both heart rate and blood pressure.
What is a beta blocker? Metoprolol or Carvedilol?
When studying pharmacology, it is important to be familiar with your reversal agents. This reversal agent is for opioids.
What is naloxone (Narcan)?
What is blood pressure?
Administration of this supplement is contraindicated for patients taking spironolactone (Aldactone).
What is potassium supplement?
This "pillar" also treats type 2 diabetes. It would be contraindicated in someone with chronic urinary tract infections.
What is SGLT2i, Jardiance or Farxiga?
When monitoring a patient with an opioid epidural (morphine) the nurse will be assessing and re-assessing this.
What is vital signs, must include respiratory rate, level of consciousness and Sp02.
This clinical manifestation can indicate excessive potassium loss.
What is low blood pressure and cardiac arrhythmias?
This diuretic is the most potassium wasting.
What is loop diuretic furosemide (Lasix)?
Just like sugar & sodium preserve foods we eat (Jam & Pickles) they also preserve us when we can't eat and drink.
What is IV Fluids?
Isotonic: NS
Hypotonic 1/2 NS
Hypertonic Dextrose 5% & NS
Together these four pillars are the guideline directed medical therapy for heart failure with reduced ejection fraction.
What is BB, ACE/ARB/ARNI, SGLT2i & MRA. Or metoprolol, Lisinopril, Jardiance & Spironolactone?
As discussed in class last week 80% of people taking IV opioids have this itchy side effect.
What is prutitis?
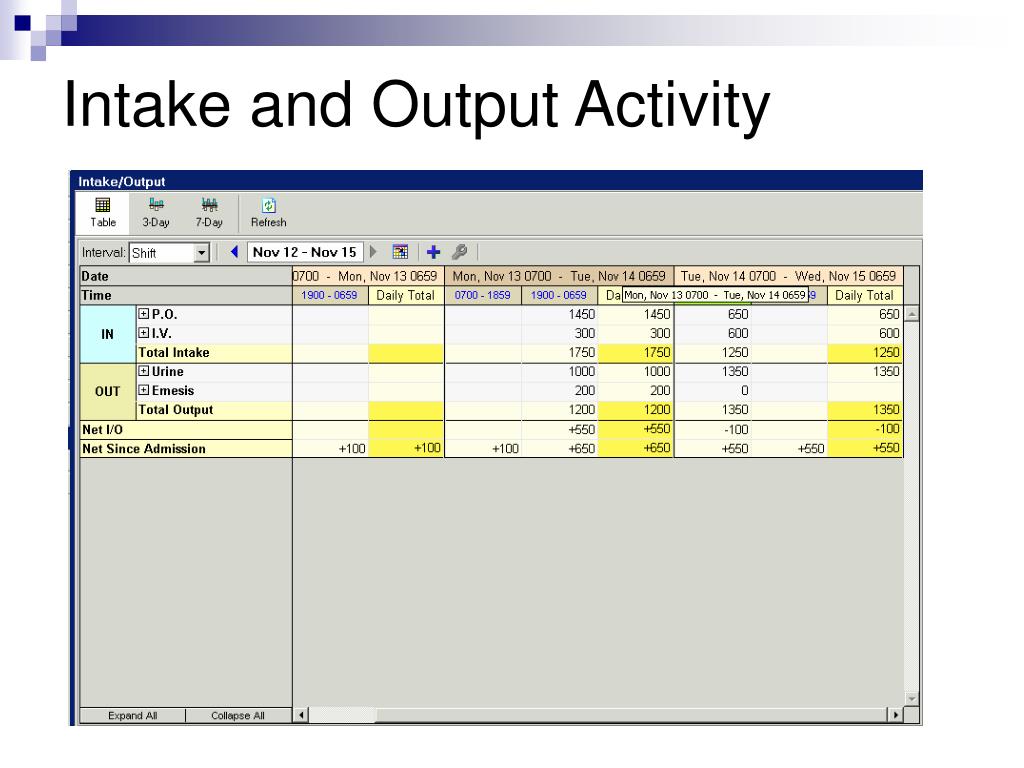
Strict monitoring of this is often ordered with any patient receiving a diuretic.
What is intake and output?