This is the most common site of diverticula, which is involved in 90% of patients with diverticulosis
Sigmoid colon
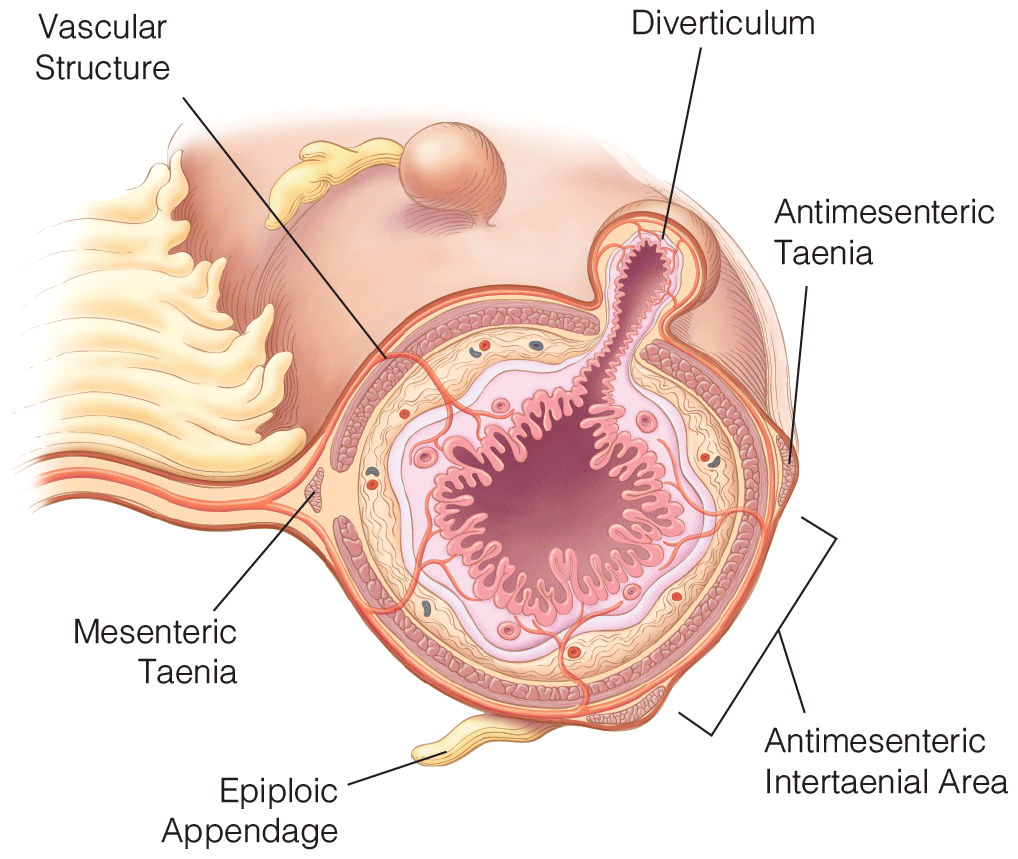
Diverticula are actually pseudodiverticula because they involve herniation of only the mucosa and submucosa through the muscularis at particular sites between the mesenteric taenia and one of the antimesenteric taenia. Name the structure(s) that occur at these sites of colonic wall weakening
Blood vessels
Name one of the classic symptoms of uncomplicated acute diverticulitis
LLQ abdominal pain, low-grade fever, irregular bowel habits, possible urinary symptoms if affected colon ajacent to bladder
This is the best diagnostic test for suspected diverticulitis
CT with PO AND PR contrast
According to the article, the high rate of early operation for diverticulitis in young patients (<40) is likely due to it being misdiagnosed as this disease
Acute appendicitis
Contrary to popular belief, consumption of three specific foods do NOT increase the incidence of diverticulitis or diverticular bleeding. Name one of the three
Nuts, corn, or popcorn
If microperforation of a thin-walled diverticulum occurs causing localized inflammation, this layer of the bowel wall remains relatively normal
Mucosa
Name three conditions that define complicated diverticulitis (article lists 5)
Obstruction, abscess formation, fistula formation, free perforation, significant bleeding
This is the time period after acute diverticulitis has subsided that colonoscopy should be performed
6-8 weeks
Describe the mechanism that leads to the development of giant diverticula
"Ball-valve" mechanism where intermittent occlusion of neck of diverticulum by fecal material traps air in the diverticulum
This is the prevalence of diverticula (NOT diverticulitis) in elderly patients over 85
80%
The Western diet is associated with development of diverticulosis because it is high in something and low in something else. Name these two.
High in refined carbs, low in fiber
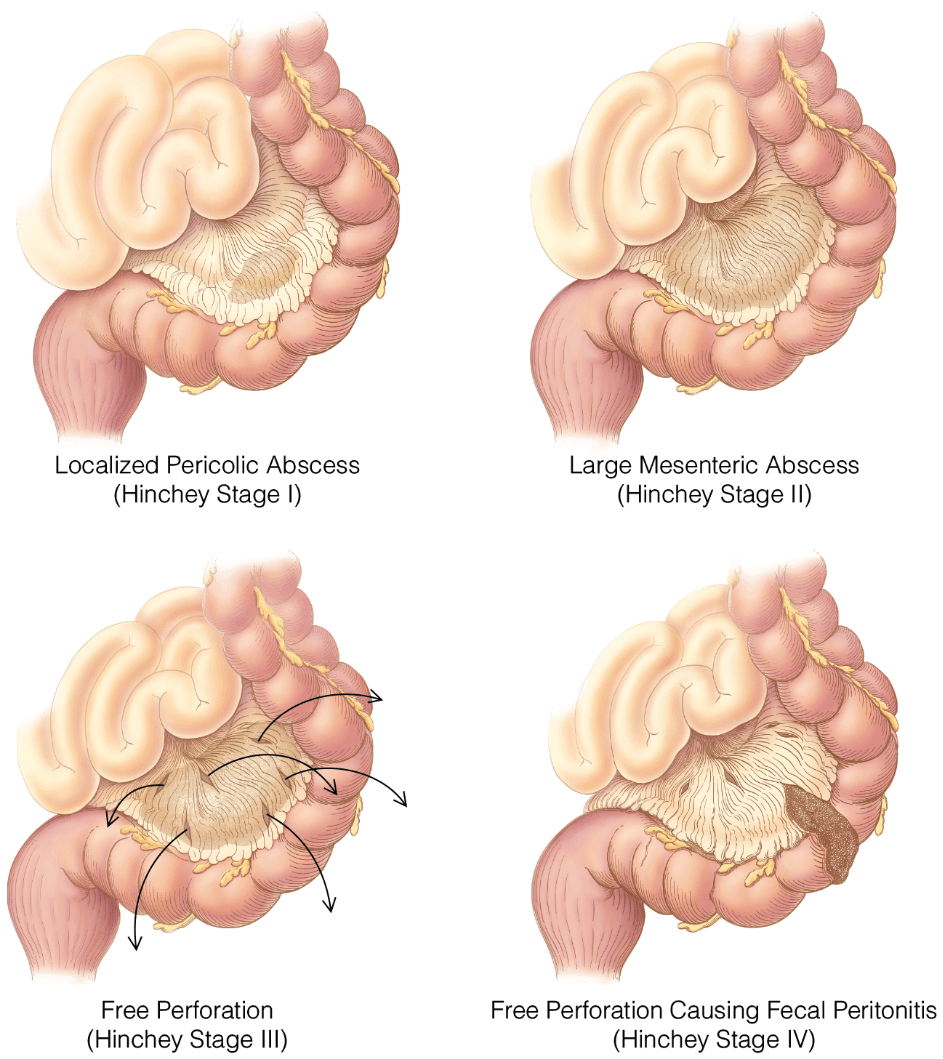
Name the Hinchey stage(s) associated with free perforations in diverticulitis, and name the disease that can cause free perforations is it important to distinguish perforated diverticulitis from
Hinchey stages III (purulent peritonitis) and IV (fecal peritonitis), distinguish from perforated colon CA
Name the type imaging study (be specific) and describe how it can contrast (hint hint) diverticula from malignancies
Double contrast barium enema, malignancy suggested by an abrupt transition to an abnormal mucosa over a relatively short segment; diverticulitis is usually characterized by a gradual transition into diseased colon over a longer segment,
This subgroup of immunocompromised patients should NOT undergo prophylactic colectomy for asymptomatic diverticulosis (be specific)
Renal transplant
Name the components of the Saint triad (3 conditions that frequently co-occur)
Diverticulosis, cholelithiasis, and hiatal hernia


In the US, this percentage of lower GI bleeding is caused by diverticulosis
33%
Name 4 of the 5 classic findings of colovesical fistula seen on CT (images here don't necessarily have all 6)
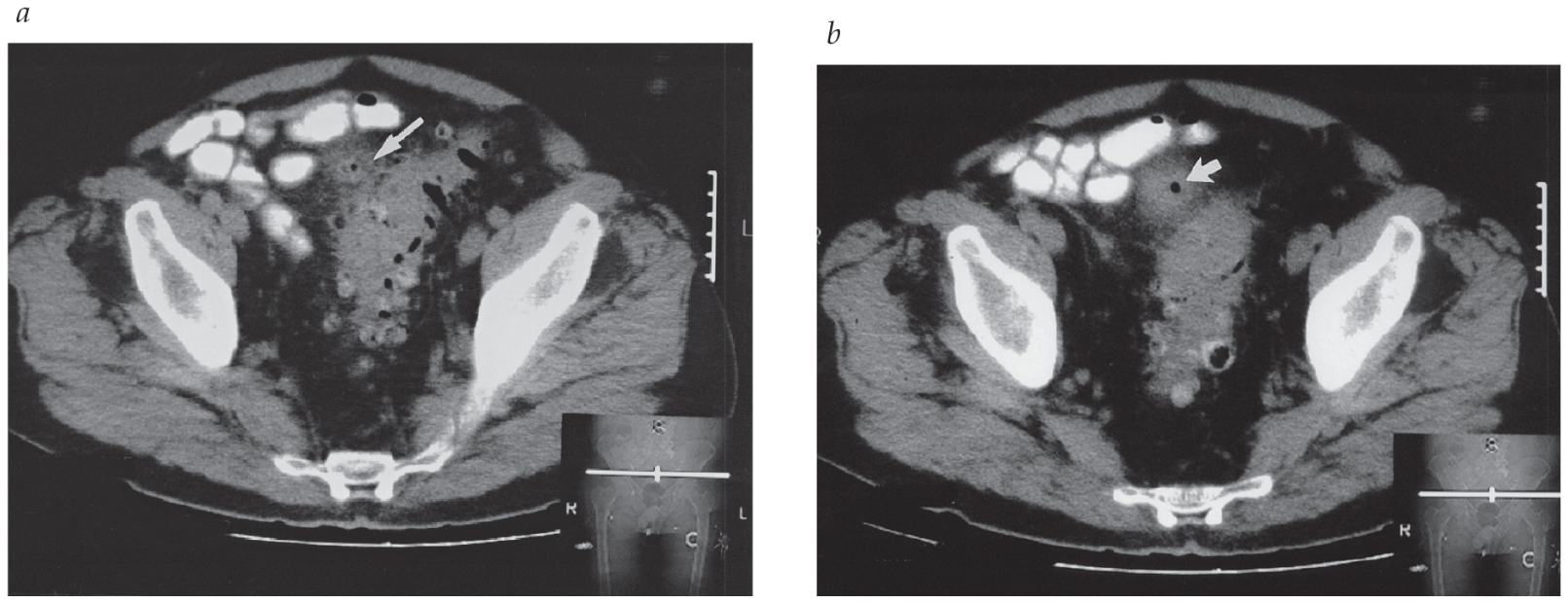
Sigmoid diverticula
Thickening of bladder and colon
Opacification of fistula tract
Air in bladder
Abscess
This type of atypical diverticulitis is shown in the imaging
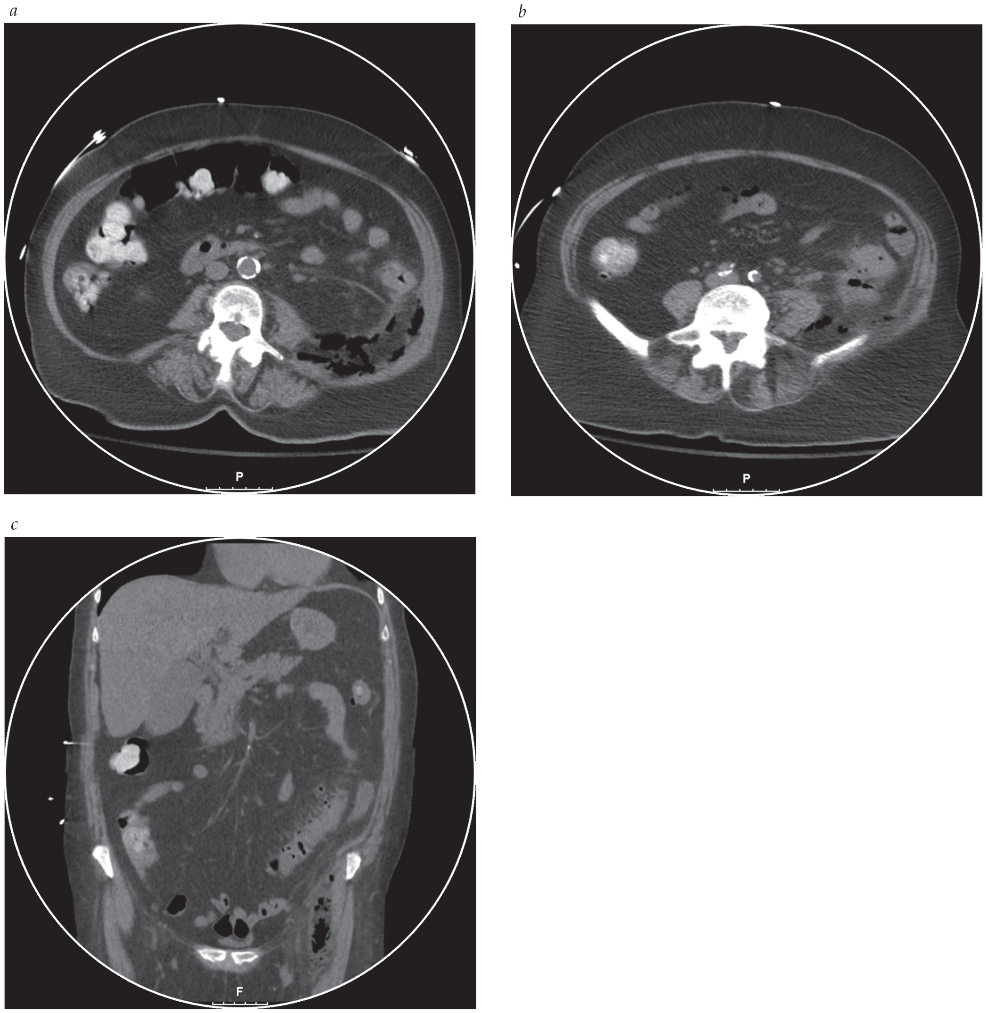
Diverticulitis with retroperitoneal abscess
Describe all 4 stages of the Hinchey classification of diverticulitis
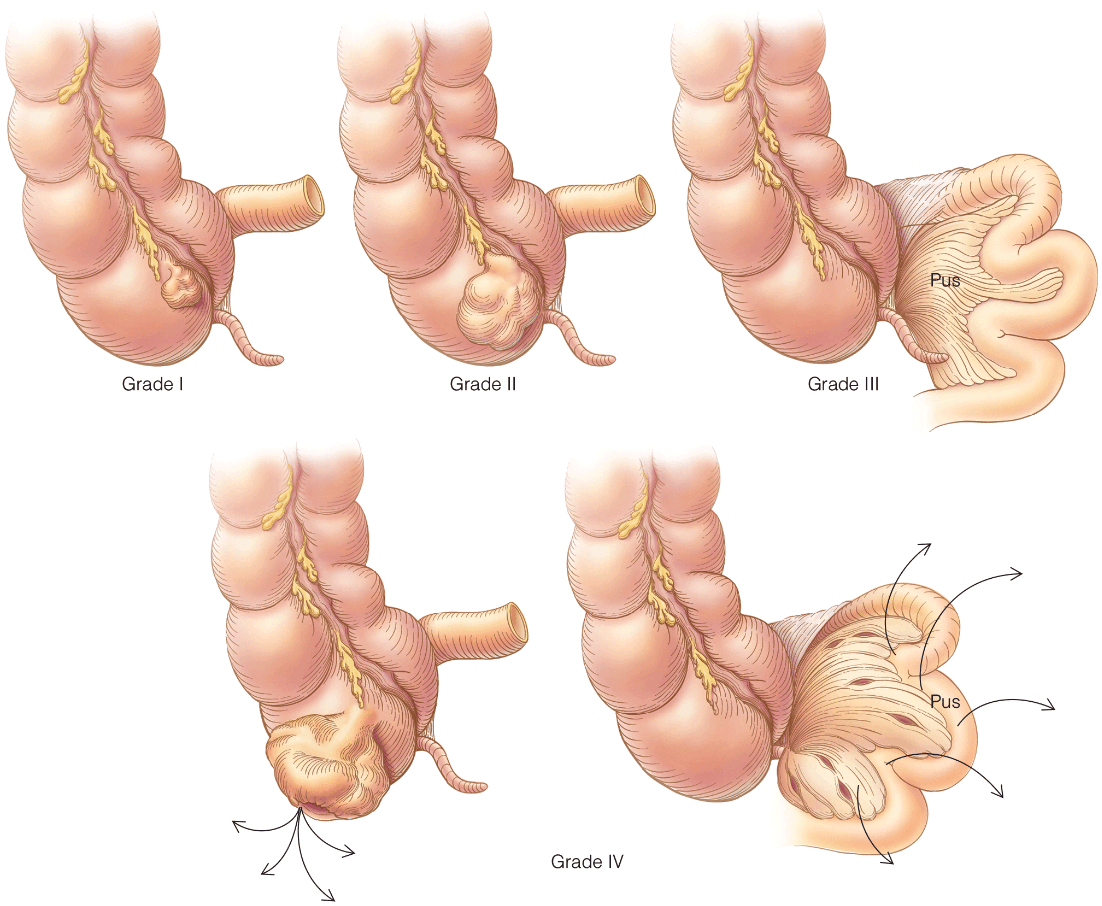
Describe the 4 grades of cecal diverticulitis
Grade 1 refers to inflamed diverticulitis, Grade 2 to inflamed cecal mass, Grade 3 to localized abscess and fistula, Grade 4 to diffuse peritonitis or free perforation
Name 5 of the 6 differential diagnoses of uncomplicated diverticulitis mentioned in the article
Gynecologic/urinary disorders
Perforated colon CA
Crohn disease
Ischemic Colitis
Epiploic appendagitis
Appendicitis
Name A - D in this angiogram (C is an anatomic location in the bowel) 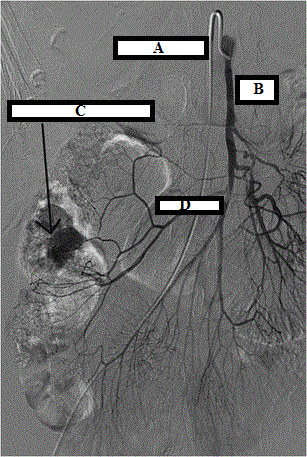
A: angio catheter selecting SMA
B: SMA
C: right/ascending colon (with contrast extravasation from diverticular bleed)
D: Right colic artery
Name the 4 necessary conditions described in the article for diverticulectomy in patients with cecal diverticulitis
1. Carcinoma can be ruled out
2. Resection margins free from inflammation
3. Ileocecal valve and blood supply of bowel not compromised
4. Perforation, gangrene, and abscess are present