Symptoms and Related Disorders
Name 2 disorders where psychoses is prevalent.
Unipolar Depression
Bipolar Disorder
Delusional Disorder
Schizophrenia
Name 3 red flags from the Suicide Risk Assesment.
- Indirect statements and verbal signs - Direct verbal warnings - Having a plan - Past attempts - Hopelessness - Clinical syndromes / personality disorders - Age and gender - Serious physical illness / pian - Religion - Rigid thinking - Impulsivity - Stressful events - Deliberate Self harm - Release from hospitalisation - Therapist / clinician inattention
Name a reason why some one would want to hurt themselves, proposed by the DSM 5.
1. To obtain relief from a negative feeling or cognitive state.
2. To resolve an inter-personal difficulty.
3. To induce a positive feeling state.
Lack of conscious access to memory, typically of a stressful experience. The fugue subtype involves loss of memory for one’s entire past or identity.
 What is Dissociative Amnesia?
What is Dissociative Amnesia?
Complex Attention
§ Sustained Attention
• The ability to focus on one specific task for a continuous period of time without being
distracted
§ Divided Attention
• The ability to process 2 or more responses or react
to 2 or more different demands simultaneously -
Multitasking
§ Selective Attention
• The ability to select from many factors or stimuli
and to focus on only one while filtering the rest
§ Processing Speed
o Executive Functioning
§ Planning
§ Decision Making
§ Feedback / error utilization
§ Overriding habits
§ Cognitive Flexibility
o Learning and Memory
§ Immediate memory
§ Recent Memory
§ Long-term memory
o Language
§ Expressive Language
§ Receptive Language
o Perceptual-motor
§ Visual perception
§ Visio-constructional
• copying a drawing and assembling blocks
§ Perceptual-motor
• Integrate perception with movement
§ Praxis
• gestures
§ Gnosis
• ability to recognize faces
o Social Cognition
§ Recognition of Emotions
• Ability to recognize emotions on a face
§ Theory of mind
• Understand point of view / mental state of the
other person
What are Neurocognitive Domains?
Name a Positive, negative and disorganized symptom of schizophrenia
Bonus 50: name a movement symptom as well
Bonus 100: name all Positive, negative and disorganized symptoms of schizophrenia
Positive symptoms: Delusions, hallucinations
Negative Symptoms: Avolition, alogia, anhedonia, blunted affect, asociality
Disorganized Symptoms: Disorganized behaviour, disorganized speech.
Movement symptoms: Catatonia, Catatonic immobility
Which of the following is not a risk factor for suicide?
Depression
Hopelessness
Anxiety
Aggressive / impulsiveness
Hospitalisation for depression
Psychotic Symptoms
Being widowed
Sociodemographic risk factors
Environmental risk factors
Being widowed
A treatment for Deliberate Self Harm (DSH)
What is [insert answer]?
Possible answers:
CBT (C'mon dawg it's always CBT, therapy's love child)
DBT (Dialectical Behaviour Therapy)
Psychodynamic treatments
Drug therapy (In some cases)
How many symptoms are needed for Conversion Disorder (Functional Neurological Symptom Disorder)?
One or more symptoms of altered voluntary motor or sensory function.
Specify symptom type:
With weakness or paralysis
With abnormal movement (e.g., tremor, dystonic movement, myoclonus, gait disorder)
With swallowing symptoms
With speech symptom (e.g., dysphonia, slurred speech)
With attacks or seizures
With anesthesia or sensory loss
With special sensory symptom (e.g., visual, olfactory, or hearing disturbance)
With mixed symptoms
A disturbance in attention i.e. reduced ability to direct, focus, sustain, and
shift attention and awareness i.e. reduced orientation to the environment
Comes about due to poising of medication, surgery, alcohol/ drug,
malnutrition, head surgery
Is reversable quickly
Can have hallucinations and delusions
a disturbance in attention i.e. reduced ability to direct, focus, sustain, and
shift attention and awareness i.e. reduced orientation to the environment
What is Delirium?
How many of these criteria do you need to get diagnosed with schizophrenia and for how long?
Delusions
Hallucinations
Disorganized speech
Disorganized or catatonic motor behavior
Negative Symptoms
Bonus 50: What is the exeption?
2 or more lasting for at a month
Bonus: Only one symptom is necessary if delusions are bizarre or if the auditory hallucinations are first or third person
There are objective and subjective indicators for suicide.
What is Beck’s Suicide Intent Scale?
Objective Indicators:
Isolation during attempt
Likelihood of intervention
Precautions taken against discovery
Actions taken to get help
Preparations for death
Preparations for attempt
Suicide note
Subjective Indicators:
Purpose of attempt
Expectations of death
Perception of method’s lethality
View of attempt’s seriousness
Desire to live or Die
Perceptions of Rescueability
Premeditation
Acting out was the substitute for remembering traumatic childhood experiences and was unconsciously aimed at reversing that early trauma
If these early memories and feelings cannot be symbolised or represented in the mind, they remain unconscious and unprocessed and will continue to be expressed in action.
What is Self-harm as a way to communicate by Freud?
If you say "What is Freud?", fine but you get half points
Self-harm may be a communication of difficulties faced at points of transition in life and the challenges these pose (Freud)
Dissociative Identity Disorder (DID) has 2 major theories.Name them both
1. Posttraumatic model – development of other selves is for protection of the truama on the self
2. Sociocognitive model. – the result of learning to enact social roles
Part of the brain affected by Alzheimer's Disease.
What is Prefrontal Cortex?
This phase marks the onset of deterioration and usually appears during the late teen and mid 20s. As the individual is still quite young, parents tend to notice that something is not quite right. Symptoms are predominantly negative and milder They include:
1. Withdrawn and uninterested in others
2. Express beliefs that are unusual but not delusional
3. Strong perceptual experience w/o full blown hallucinations
4. Speak in a somewhat disorganized way but still coherent
Bonus 50: name the other phases as well
What is Prodromal Phase?
Bonus: Active phase and Residual phase
Hint: Dromos means road, so you are on the road to becoming a 21st century schizoid man
Egoistic suicide
Altruistic suicide
Anomic suicide
Fatalistic suicide
Bonus 50: Name the 2 key variables from this theory
What is Durkheim and sociological theory?
Bonus: Social integration and Social Regulations.
Self-injury can be understood as a morbid form of self-help, temporarily alleviating distressing symptoms, and attempting to heal, to attain some measure of spirituality and to establish a sense of personal order.
What is Self-harm as a sign of Hope?
Trivia: There is a specific region in the brain activates by hopefull thoughts: The anterior cingulate cortex.
It involves thinking about the self, reflecting on the past, and anticipating the future, particularly with an emotional lens (Hope).
Name 3 types of Amnesia, except Dissociative, HA HA.
Bonus 50: Name another one
Bonus 50: the memory loss is more extensive. THE PERSON FORGETS WHO HE IS AND ESCAPES FROM HIS LIFE
Localized amnesia - a failure to recall events during a circumscribed period of time, is the most common form of dissociative amnesia. Localized amnesia may be broader than am- nesia for a single traumatic event.
Selective amnesia - the individual can recall some, but not all, of the events during a circumscribed period of time. Thus, the individual may remember part of a trau- matic event but not other parts.
Generalized amnesia - a complete loss of memory for one’s life history, is rare. Individuals with generalized amnesia may forget personal identity.
Systematized amnesia - the individual loses memory for a specific category of information.
Dissociative Amnesia - are frequently unaware (or only partially aware) of their memory problems.
Bonus: What is Dissociative fugue?
The biggest difference between Major Neurocognitive Disorder and Mild Neurocognitive Disorder
What is the instrumental capabilities of daily life?
Major Neurocognitive Disorder: deficits in cognitive ability that are acquired (as opposed to developmental), typically represent decline, and may have an underlying brain pathology.
Mild Neurocognitive Disorder: neurological disorders involving cognitive impairments beyond those expected based on an individual’s age and education, but which are not significant enough to interfere with instrumental activities of daily living
3 of these
1. Stupor (i.e., no psychomotor activity; not actively relating to environment)
2. Catalepsy (i.e., passive induction of a posture held against gravity)
3. Waxy flexibility (i.e., slight, even resistance to positioning by examiner).
4. Mutism (i.e., no, or very little, verbal response [exclude if known aphasia]).
5. Negativism (i.e., opposition or no response to instructions or external stimuli).
6. Posturing (i.e., spontaneous and active maintenance of a posture against gravity).
7. Mannerism (i.e., odd, circumstantial caricature of normal actions).
8. Stereotypy (i.e., repetitive, abnormally frequent, non-goaldirected movements).
9. Agitation, not influenced by external stimuli.
10. Grimacing.
11. Echolalia (i.e., mimicking another’s speech).
12. Echopraxia (i.e., mimicking another’s movements).
Bonus 50: Umbrella term for these symptoms
What is Catatonia?
Bonus: What are psychomotor features?
Beck has created a theory that uses 3 types of measurements to assess suicidality
Bonus 50: Name the theory as well
Hint: One of them was in a previous question. Or not if you picked this one first, sucks to suck
The Beck Depression Inventory (BDI)
The Suicide Intent Scale (SIS)
The Beck Hopelessness Scale (BHS)
Bonus: Beck and Hopelessness Theory
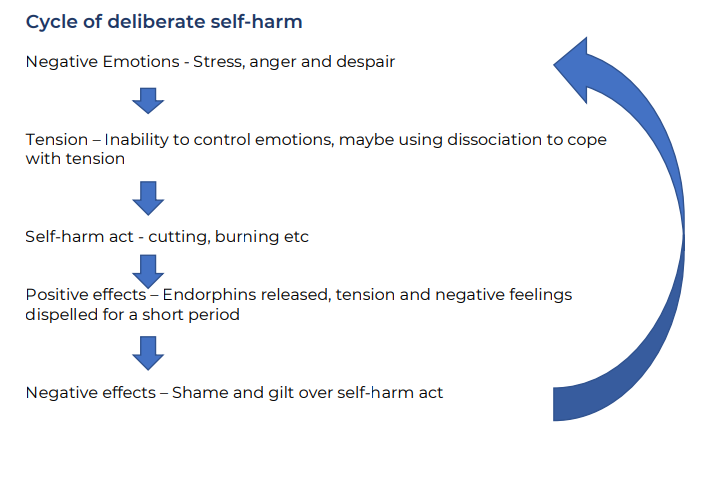
Name ALL the steps of the Cycle of deliberate self-harm
What is the essential feature of Depersonalization / Derealization Disorder?
The essential features of depersonalization/derealization disorder are persistent or recurrent episodes of depersonalization, derealization, or both. Episodes of depersonalization are characterized by a feeling of unreality or detachment from, or unfamiliarity with, one’s whole self or from aspects of the self.
Name the funniest risk factor for Alzheimer's
Being single... DANG
