DNA Basics
PCR
VNTRs/STRs
Analyzing Fingerprints
100
What does DNA stand for?
Deoxyribonucleic Acid
100
What does the polymerase chain reaction do?
It makes copies of an original DNA template.
100
What is a VNTR?
VNTR stands for variable number tandem repeat. It is a segment of DNA where a sequence between 9-100 bases long repeats a variable number of times between people.
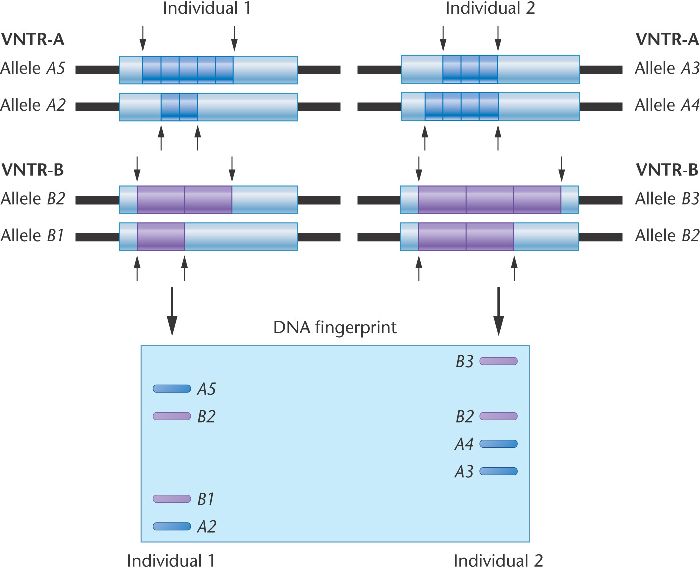

100
 DNA evidence is collected from the scene of a burglary. Which of the three suspects most likely committed the crime?
DNA evidence is collected from the scene of a burglary. Which of the three suspects most likely committed the crime?
Suspect 2 most likely did it because this suspect's DNA matches the crime scene DNA.
200
What is the shape or structure of DNA?
Double helix (or spiral staircase, twisted ladder)


200
How does PCR help forensic scientists collecting DNA from a crime scene?
PCR can make copies of the DNA found in a crime scene sample, even if it contains very small amounts of DNA.
200
What is an STR?
VNTR stands for short tandem repeat. It is a segment of DNA where a sequence between 2-5 bases long repeats a variable number of times between people.
200
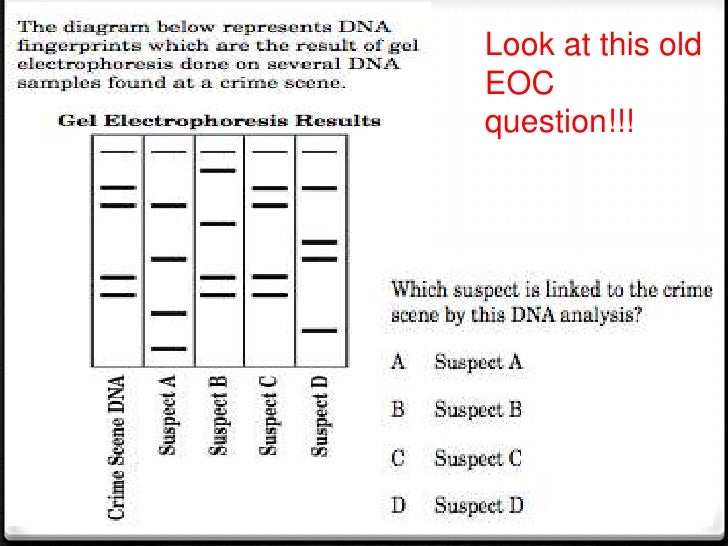
Suspect C probably committed the crime because this suspect's DNA matches the crime scene.


300
What are the four chemical letters of DNA?
Adenine (A), Thymine (T), Cytosine (C), and Guanine (G)
A, T, C, G
300
What happens during the denaturation step of PCR?
The sample is heated to 95° C, causing the two strands of DNA to separate into single strands.

300
What is a restriction enzyme?
A restriction enzyme is an enzyme that cuts DNA at a specific 6-8 nucleotide sequence.


300
 A murder victim was found and was in an apparent struggle with the murderer. A bit of skin was found underneath the victim's fingernails and sent out for DNA fingerprinting. Which of the suspects most likely committed the crime?
A murder victim was found and was in an apparent struggle with the murderer. A bit of skin was found underneath the victim's fingernails and sent out for DNA fingerprinting. Which of the suspects most likely committed the crime? Suspect 1 is a match for the specimen found under the victim's fingernails so most likely committed the murder.
Suspect 1 is a match for the specimen found under the victim's fingernails so most likely committed the murder.400
How do the nucleotides, or chemical letters, of DNA, pair up with each other?
A pairs with T
C pairs with G


400
What happens during the annealing step of PCR?
The sample is cooled to around 50-60° C, allowing short DNA primers to bind to certain sequences of the DNA template.


400
How are VNTRs and STRs used to identify or distinguish people through their DNA?
The number of times that the repeated sequence repeats changes from person to person. This represents part of the less than 1% of DNA sequence that differs between people.
400
500
What is at least one of the three major problems with using DNA evidence?
1. Any person's DNA code is very long (~3 billion letters long) and too large to analyze completely.
2. Any two people's DNA sequence are over 99% the same (we have to find the differences to identify someone).
3. DNA at a crime scene is often collected in very small amounts.
500
What happens during the extension step of PCR?
The sample is heated to 72° C, allowing DNA polymerase to copy the DNA around the primers.

500
How can restriction enzymes be used to distinguish two people's DNA?
Restriction enzymes will cut two different people's DNA in different places, causing a different band pattern when the samples are run on a gel.
500
 Which of these sets of twins are identical?
Which of these sets of twins are identical? The B and C sets of twins are identical. The A and D sets of twins are fraternal.
The B and C sets of twins are identical. The A and D sets of twins are fraternal.