The phase when DNA is replicated in a eukaryote .
What is S?
This enzyme splits the original DNA strand in two, starting the process of Replication.
What is Helicase?
This is the end result of replication.
What is two identical strands?
On this strand, DNA polymerase works in a single continuous process.
What is the leading strand?
Identify C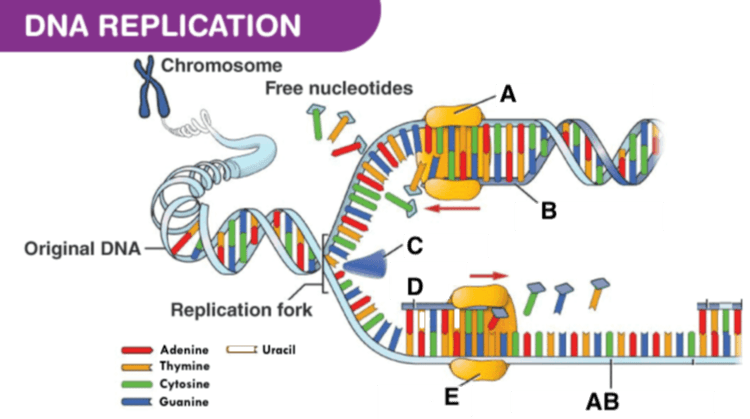
what is Helicase?
DNA polymerase needs a _______ to be able to add nucleotides complementary to template strand.
What is a RNA primer?
This enzyme adds complementary base pairs to both strands.
What is DNA Polymerase?
DNA is always replicated (built) in this direction. (looking at the new strand)
What is 5' to 3'?
This strand is worked in the opposite direction of the Helicase.
What is the Lagging strand?
Identify A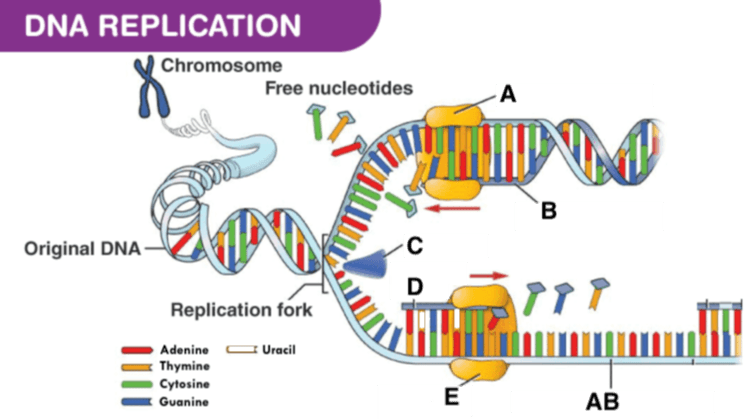
What is DNA polymerase?
The number of origin points in a prokaryote
What is one?
This is the name for the area opened by Helicase.
What is a replication fork?
After replication of DNA each identical chromosome is made up of a template strand and a newly constructed strand.
What is semi-conservative replication?
The lagging strand is made up of this type of segment.
What are Okazaki fragments?
Identify E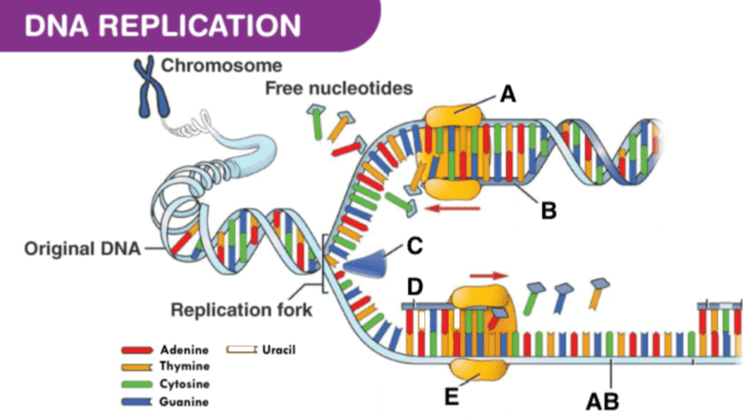
What is DNA primase?
The structure of a eukaryotic chromosome.
What is a linear strand?
This enzyme removes the Primer set by Primase.
What is RNAase?
This is the last thing that occurs before the end of replication.
What is Ligase filling in the gaps left by DNA Polymerase?
The strand that works towards the replication fork.
What is leading strand?
Identify D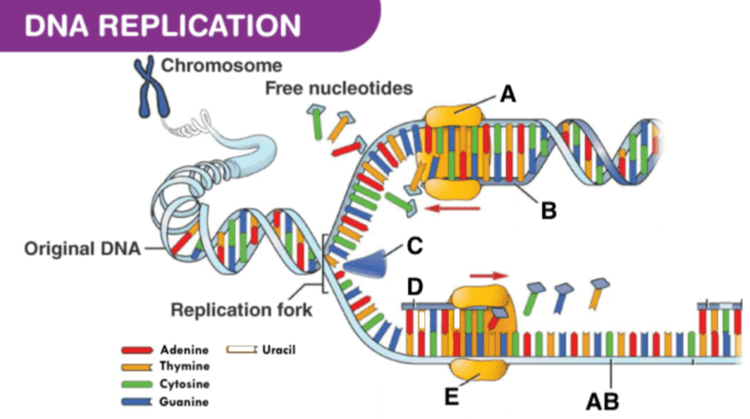
What is the lagging strand?
The template strand of DNA is “read” in this direction in prokaryotes.
What is the 3’—>5’ direction?
This enzyme is responsible for joining together the Okazaki fragments on the lagging strand.
What is DNA Ligase?
This many replication forks can exist on the same strand of DNA at once.
What is more than one?
The lagging strand creates Okazaki fragments for this reason.
What is DNA polymerase traveling away from the Helicase?
Identify AB
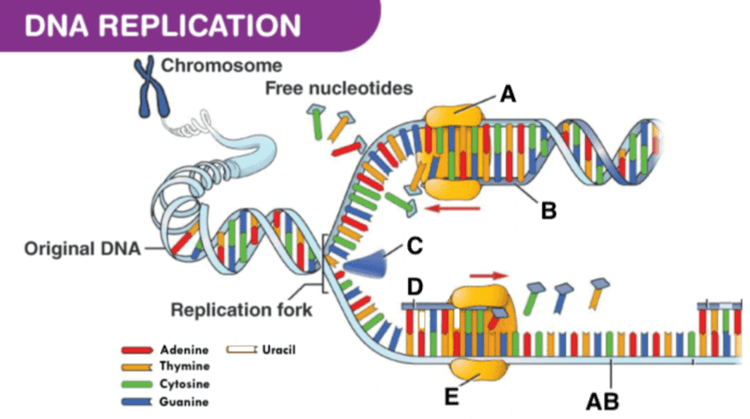
What is the template DNA strand?