The double-stranded structure of DNA.
What is a double-helix?
Enzyme that does the unwinding and separating of DNA.
What is helicase?
Product of transcription.
What is mRNA?
Product of translation.
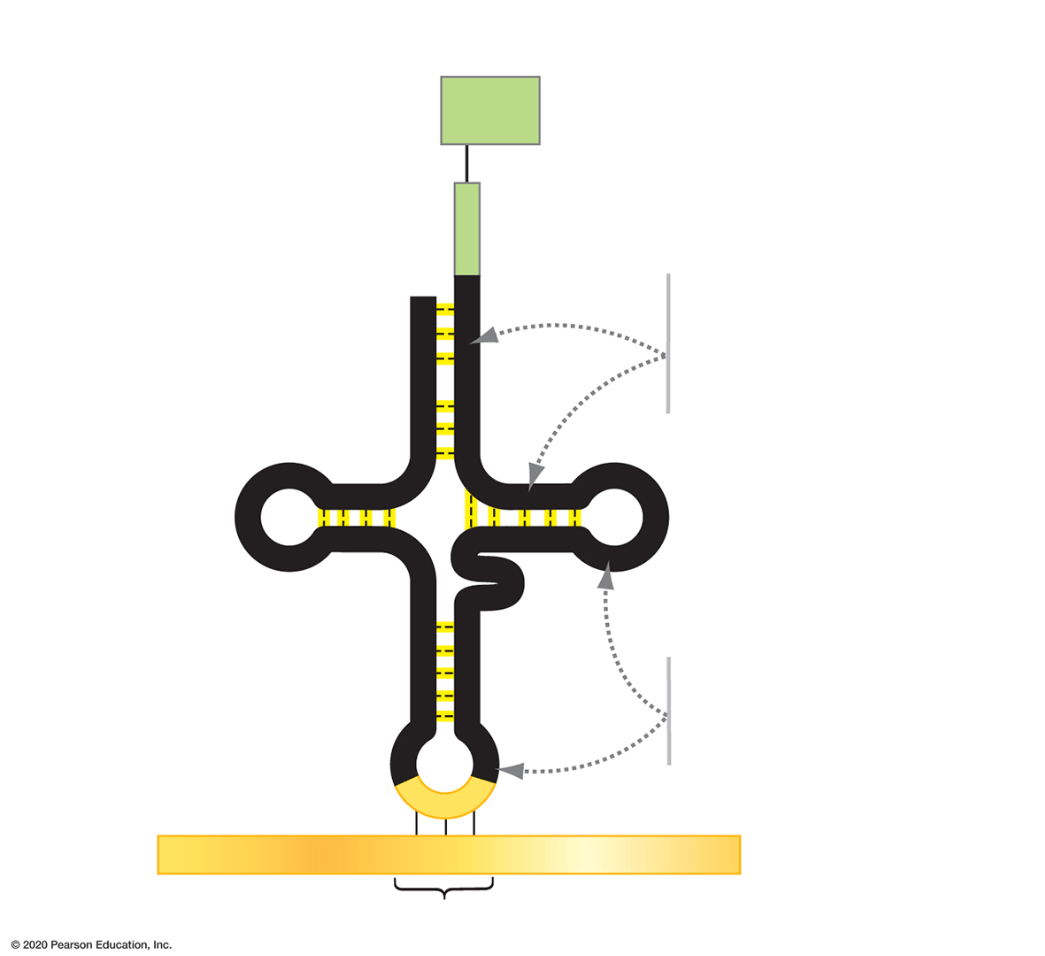
This structure is called ____.
What is a tRNA?
That adenine always binds to thymine and guanine always binds to cytosine is called this.
What is complementary base pairing?
Enzyme that polymerizes daughter strand using DNA template.
Enzyme involved in synthesizing mRNA.
What is RNA polymerase?
Complementary sequence on the ribosome that binds to mRNA.
What is the ribosomal binding site?
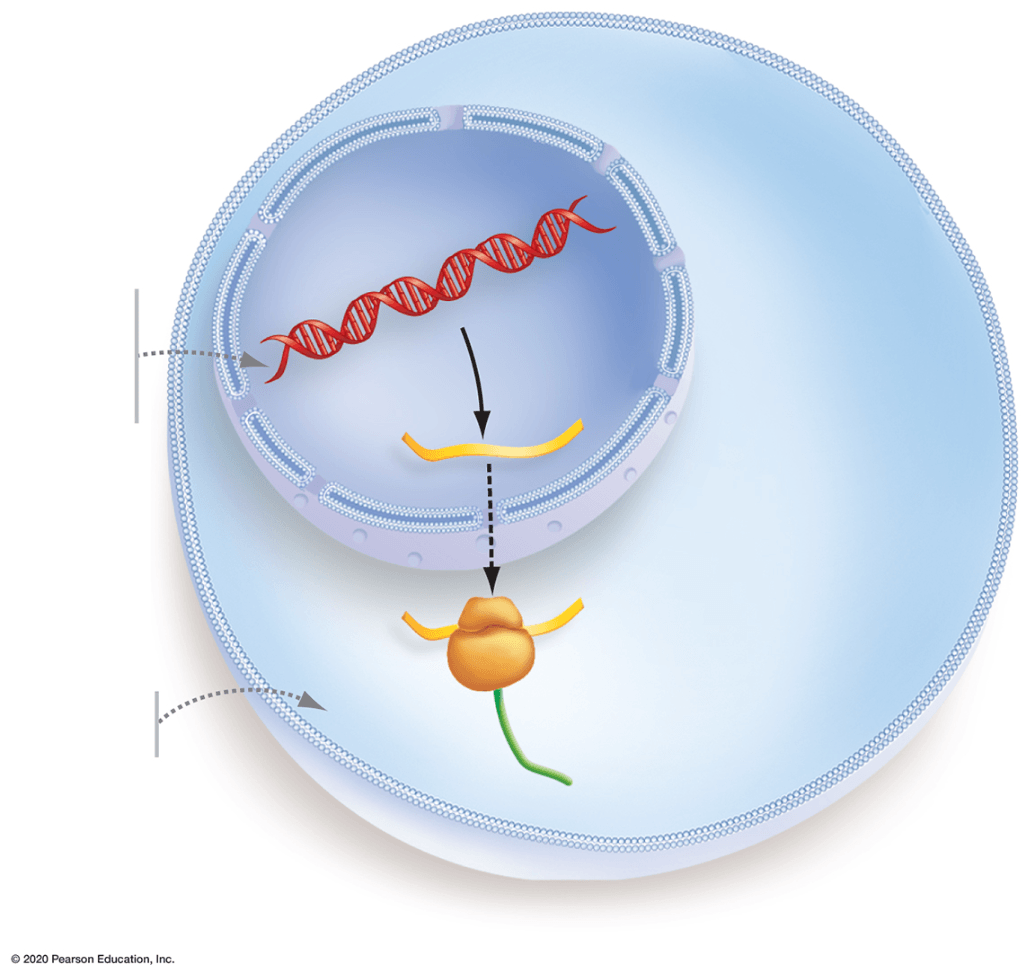
This process is called _____.
What is protein synthesis?
The two DNA strands run in opposite direction.
What is antiparallel?
Short, complementary RNA sequences that have to bind first before replication begins to know where replication begins.
What are primers?
Helper proteins that bind to the promoter region.
What are transcription factors?
Triplets of nucleotides.
What is a codon?

This is called _____.
What is the Genetic Code?
What are hydrogen bonds?
Enzyme that cuts DNA to relieve strain caused by unwinding and pastes DNA back together after strain caused by twisting is relieved.
What is a topoisomerase?
Molecule that binds to RNA polymerase to help it bind to DNA.
What is a sigma factor?
AUG tells the cell where to begin constructing the protein.
What is a start codon?
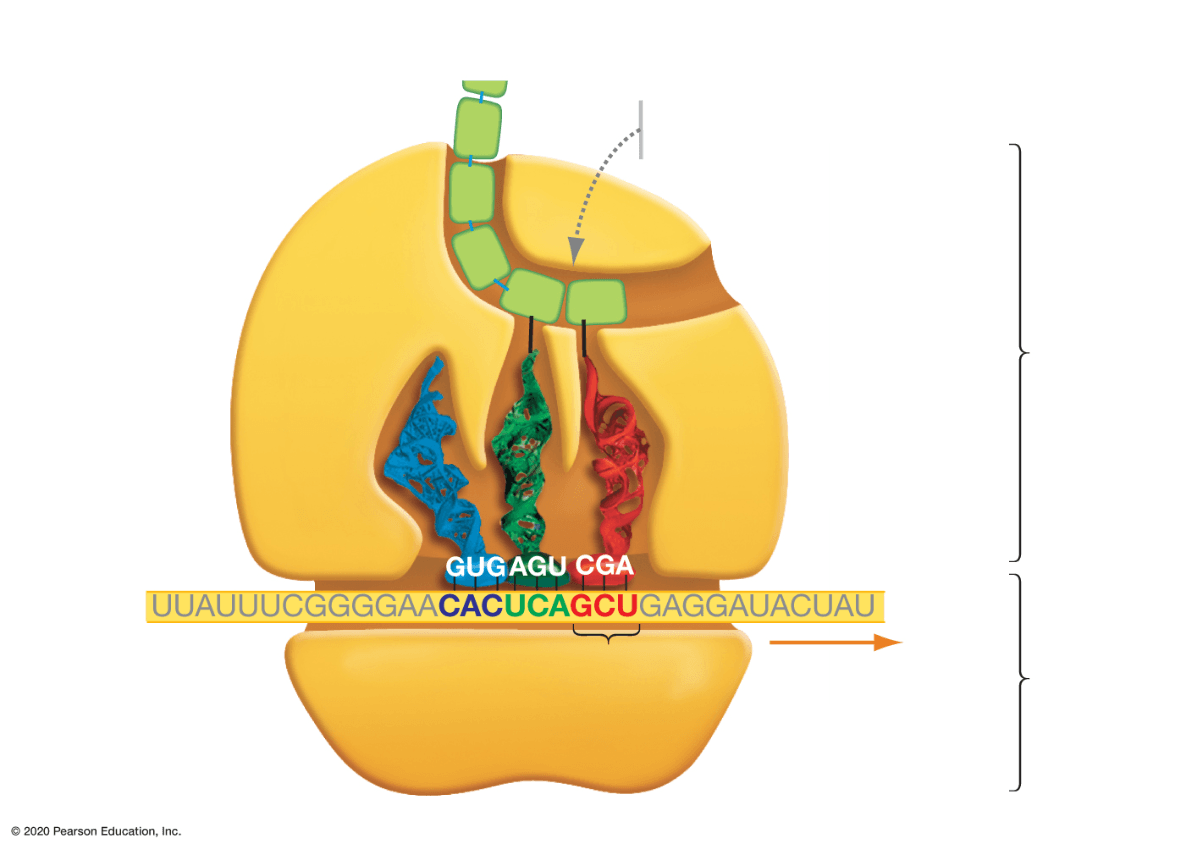
This process is called ____.
What is translation?
The end of the DNA where the phosphate group is located.
What is the 5' end?
The energy to form phosphodiester linkage comes from the _______ of the two phosphate groups.
What is hydrolysis?
Sequence in promoter region that transcription factors bind to.
What is a TATA box?
What is an anticodon?
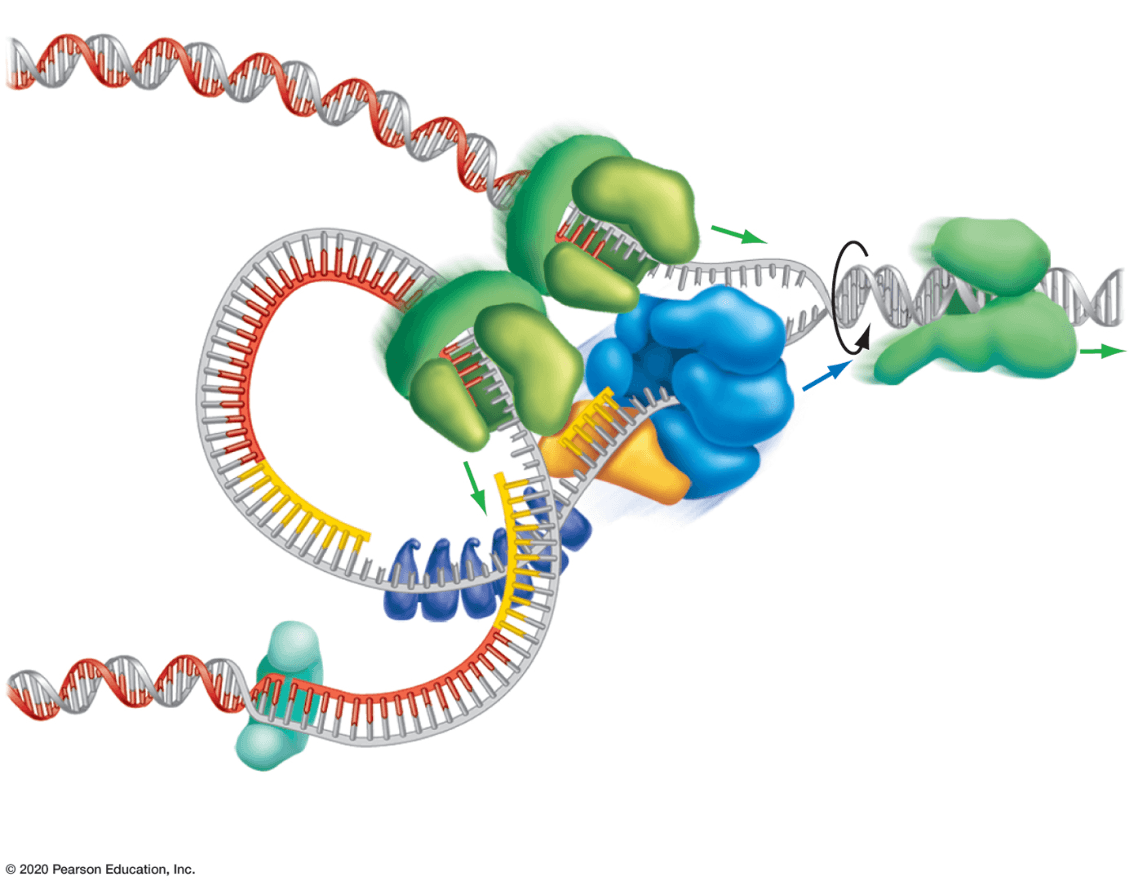 This process is called ____.
This process is called ____.
What is DNA replication?
Where a new phosphate group binds.
What is the 3' end?
Short sections of DNA formed at the time of discontinuous synthesis of the lagging strand during replication of DNA.
What are Okazaki Fragments?
Region where RNA polymerase falls off.
What is the terminator region?
Occurs in order for a protein to become fully functional.
What is post-translational modification?
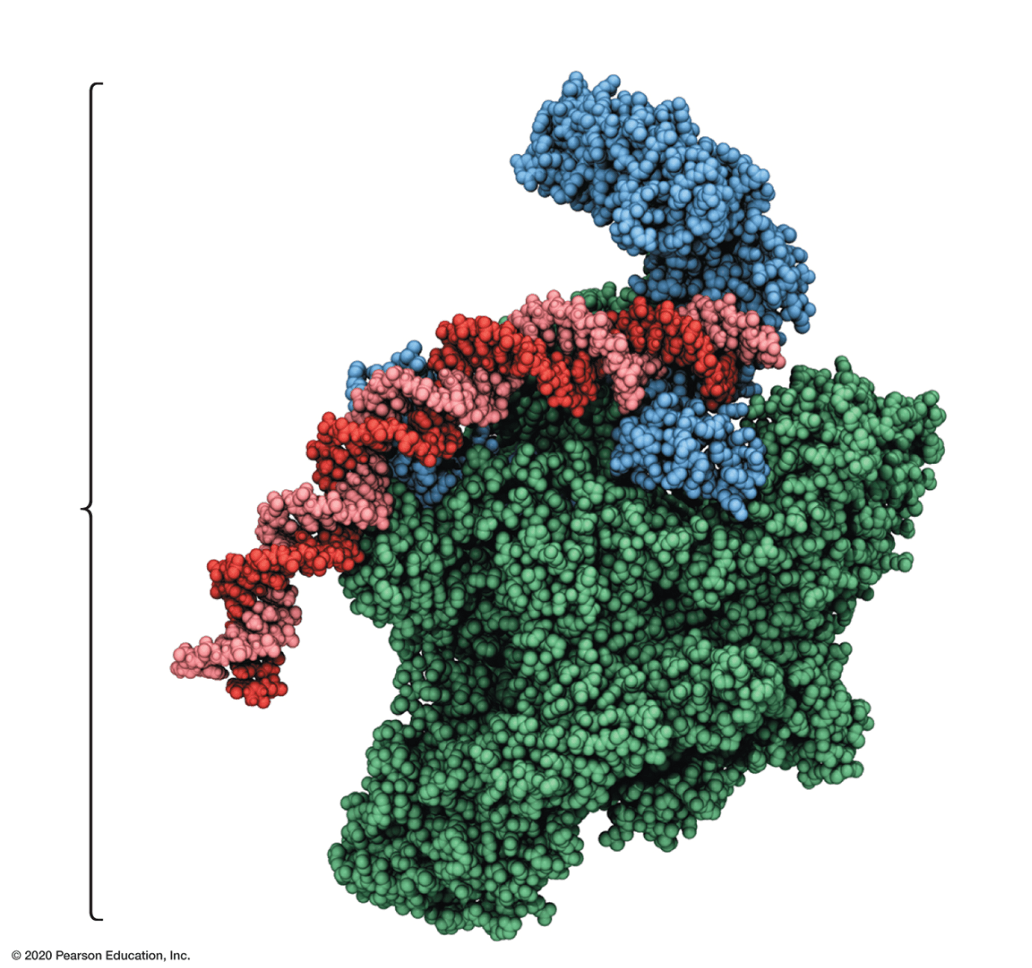 Found in bacteria and plays a role in transcription.
Found in bacteria and plays a role in transcription.
What is a holoenzyme?