What two words describe the structure of DNA?
double helix
Where does DNA replication occur in a eukaryotic cell?
nucleus
What base is found in RNA but not DNA? What base is not found in RNA?
Uracil is in RNA
Thymine is in DNA
Where does translation occur in a cell?
The ribosome!
Which is going to be more significant, a genetic mutation or chromosomal mutation?

Chromosomal Mutation
What are the four bases in DNA and how are they paired?
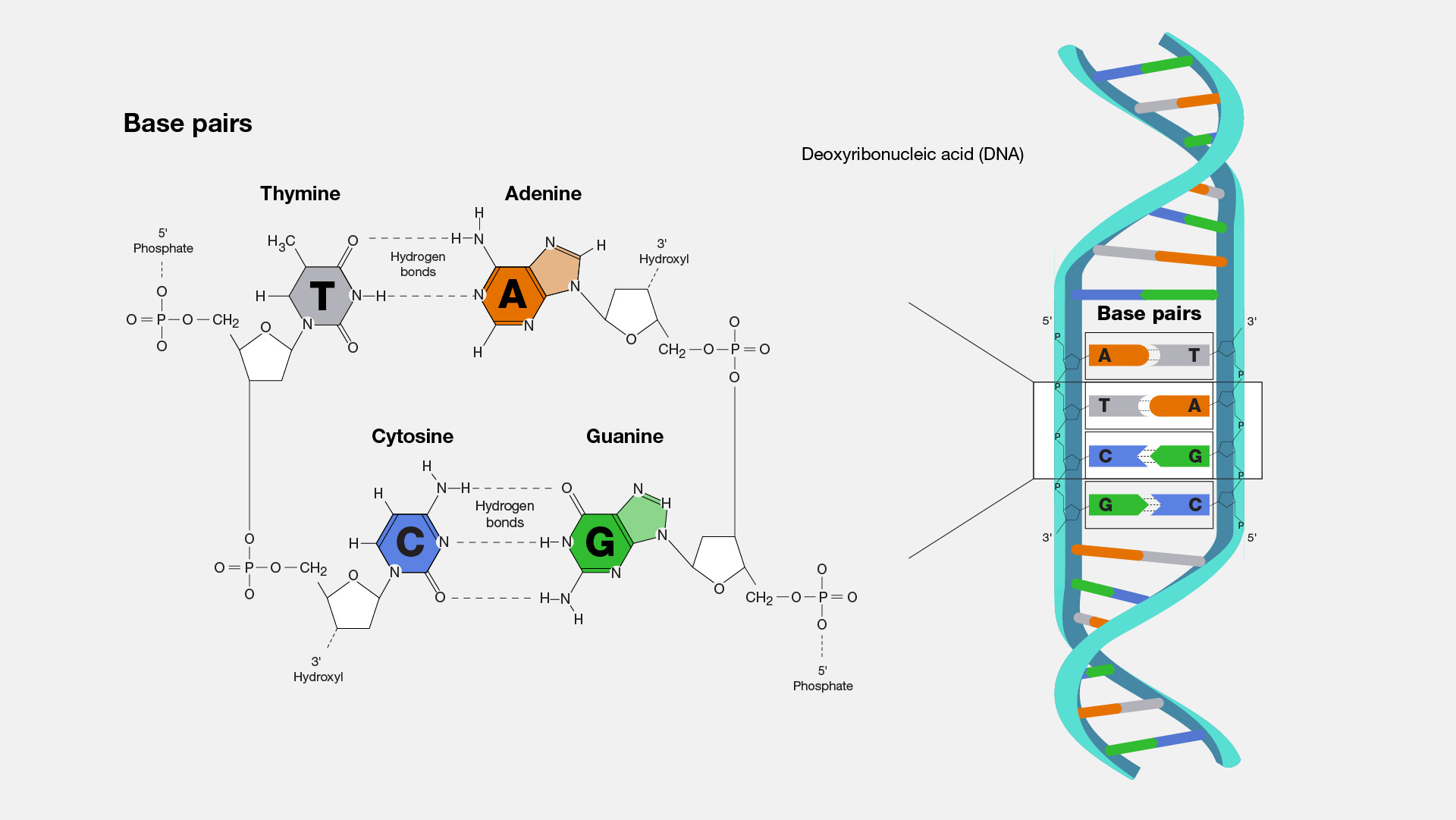
Adenine pairs with Thymine
Cytosine pairs with Guanine
What does it mean to say that DNA replication is semi-conservative?
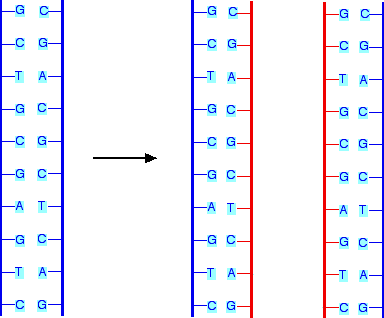
when it makes a new copy, each copy has one “old” strand and one “new” strand
What organelle does transcription occur in eukaryotic cells?
The nucleus

Translate the following:
GAG AUA CCG CAU UGG GCA UAG
Glu- Ile- Pro- His- Trp- Ala- Stop
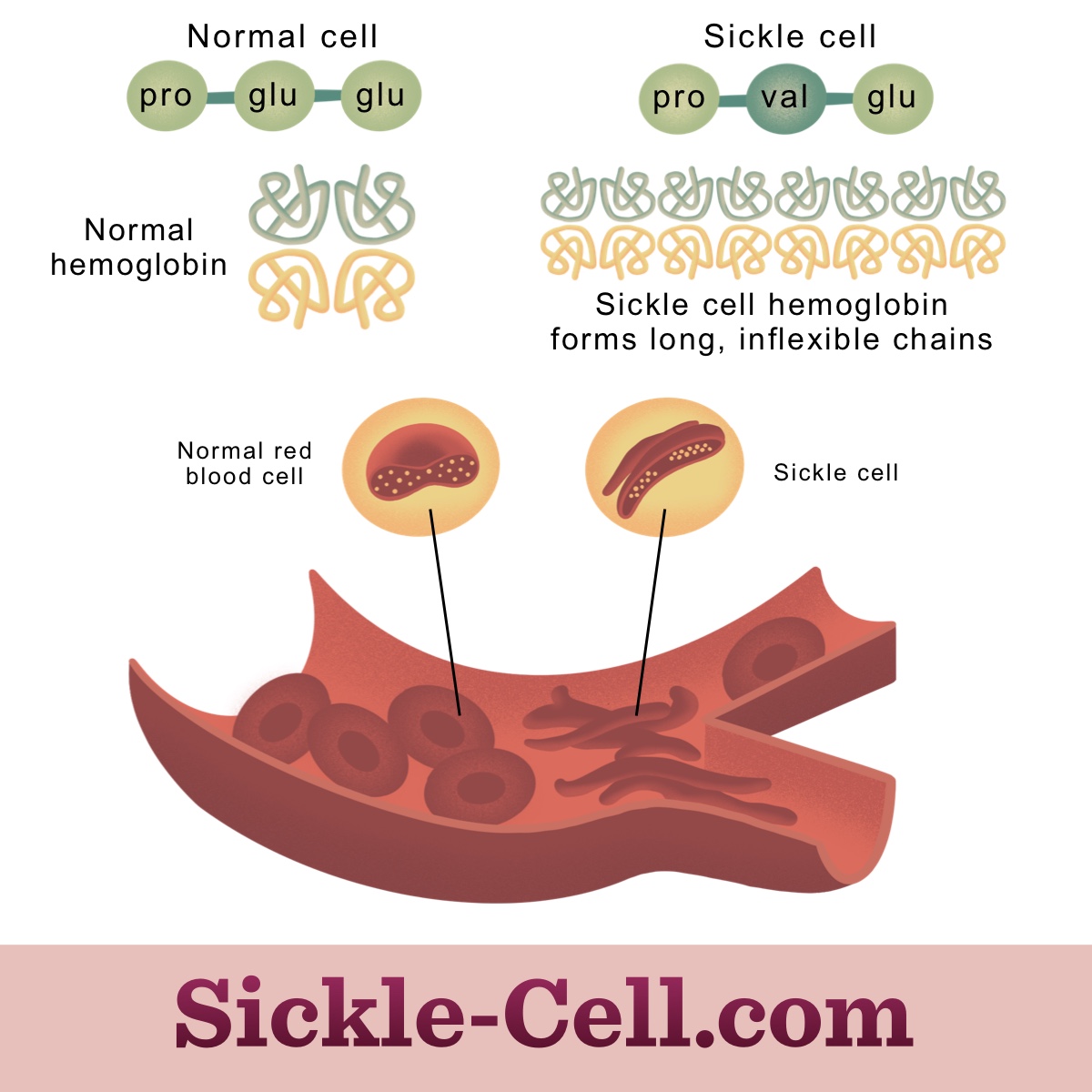
What specific example of a mutation did we look at in class? (hint: a genetic disease that affects a specific type of cell)
Sickle Cell Mutation
What are the complementary nucleotides for the following DNA sequence?
AGGCTGACCGTA
TCCGACTGGCAT
During what phase of the cell cycle does DNA replication occur?

S phase!
Transcribe the following DNA sequence.
CGGATAAGTCTTCGA
GCC UAU UCA GAA GCU
What is the start codon?
How many stop codons are there?

AUG
3
Which mutation is more likely to result in the production of a non- functioning protein -- a deletion or substitution?

Deletion because it is a frameshift mutation
What are the three parts of a DNA nucleotide? Must be specific.
What is the backbone of DNA made of?

Deoxyribose sugar, Nitrogenous Base, Phosphate Group
The backbone is made of the deoxyribose sugar and phosphate group
During DNA replication, what enzymes are involved and what do they do exactly?
Helicase separates the two strands of DNA.
DNA polymerase adds complementary nucleotides, and proofreads the DNA.
What are the three types of RNA and what are their functions?
messenger RNA carries instructions from a DNA in the nucleus to the cytoplasm (the message)
ribosomal RNA are part of what ribosomes are made of
transfer RNA brings specific amino acids that match the mRNA template
What is a codon?

3 consecutive nucleotides that "code" for a specific amino acid during translation
What type of mutation is shown below? be specific

substitution -- missense
What is the name of the scientist that took the first clear x-ray images of DNA, critical for the discovery of DNA structure, but never received a Nobel Prize for their work?
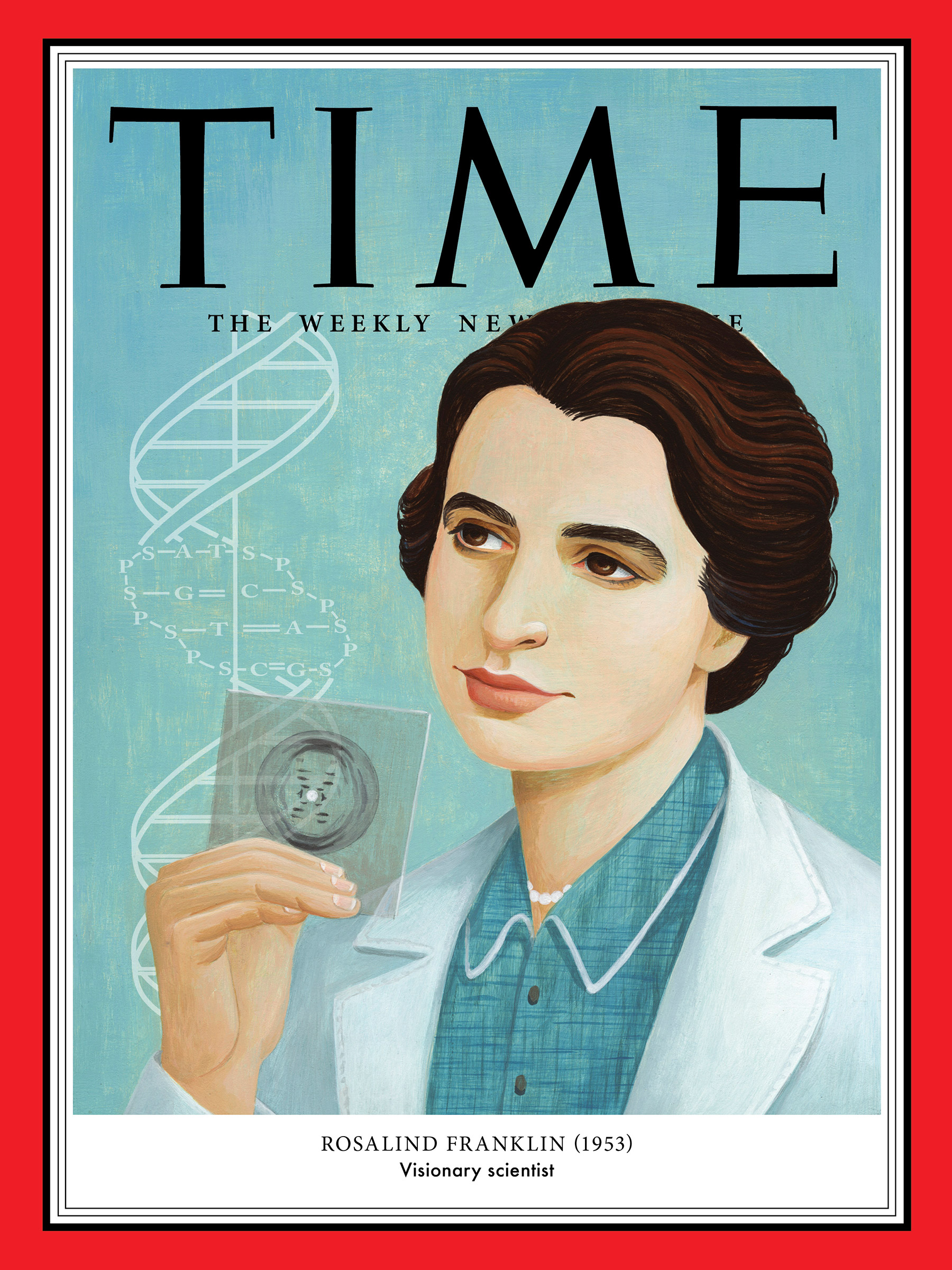

Rosalind Franklin
The sites where separation and replication occur on the DNA are called what?
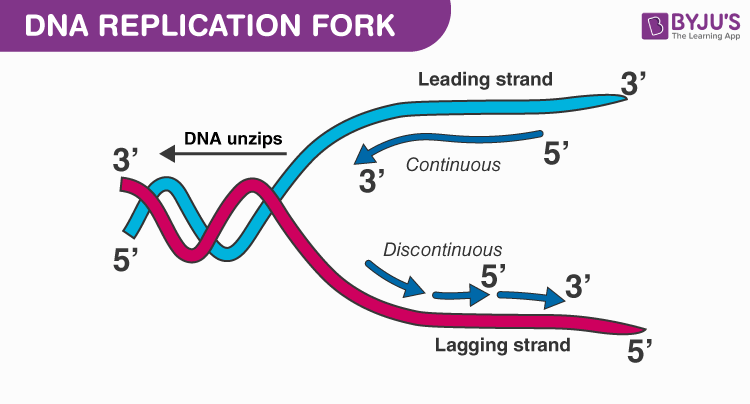
replication forks
What enzyme is responsible for transcription?
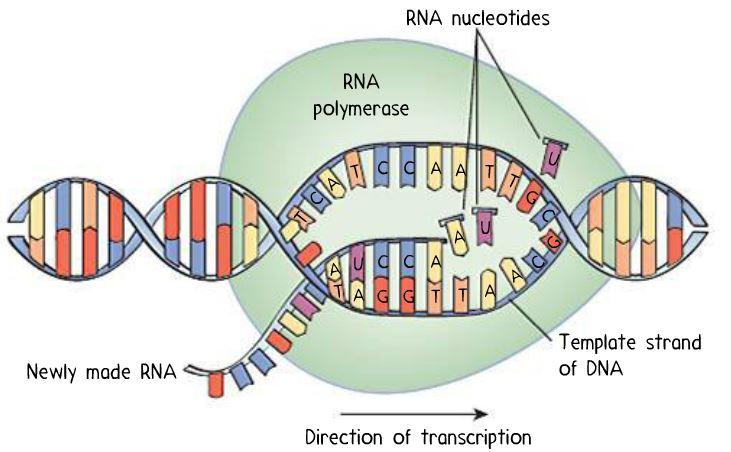
RNA Polymerase
The three steps of translation in order are:
initiation
elongation
termination
What type of mutation produces extra copies of parts of a chromosome (like in Down Syndrome)?
Duplication
