Most commonly reported vector-borne disease in the US
Lyme disease (accept Borrelia burgdorferi)
Test to distinguish exogenous from endogenous hyperinsulinemia
Plasma C-peptide
Most likely GERD-related esophageal diagnosis
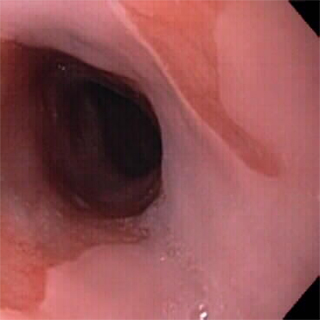
Barrett esophagus
A metalloproteinase that is deficient in TTP
ADAMTS 13
Vasculitic disorder characterized by chronic rhinosinusitis, asthma, and prominent peripheral blood eosinophilia
Churg-Strauss syndrome (allergic angiitis and granulomatosis)
Common antecedent event of jugular vein suppurative thrombophlebitis
Acute pharyngitis (accept tonsillitis; peritonsilar abscess; Fusobacterium infection)
Initial drug therapy for pituitary apoplexy
Hydrocortisone (accept steroids)
Liver disease most closely associated with anti-LKM antibody
Autoimmune hepatitis
Intervention that decreases recurrent stroke in sickle cell disease
Exchange transfusion
Stage of sleep during which hypoventilation is most prominent
REM (accept rapid eye movement)
Adjuvant treatment for tuberculosis meningitis
Dexamethasone (accept steroid, glucocorticoid, corticosteroid)
Adrenal incidentaloma threshold size suspicious for malignancy
> 4 cm
Diagnosis for diastase resistant, PAS-staining foamy macrophages and villous atrophy
Whipple disease
Cause of splenomegaly and hepatomegaly in myelofibrosis (myeloid metaplasia)
Extramedullary hematopoiesis
Liver disorder associated with platypnea and orthodeoxia
Hepatopulmonary syndrome
Isolation precautions for disseminated varicella-zoster virus infection
Airborne and contact
Most likely mechanism of disabling hypoglycemia after gastric bypass surgery
Beta islet hypertrophy (accept beta cell hypertrophy and pancreatic nesidioblastosis)
Commonly prescribed drug class for portal hypertension that is associated with worse prognosis in patients who develop spontaneous bacterial peritonitis
Beta-blocker
Hereditary bleeding disease accounting for findings
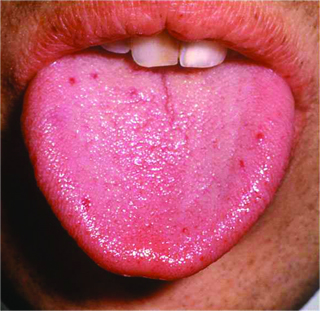
Hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasias (Osler-Weber-Rendu)
Fleischner criteria for timing of next imaging study for incidentally discovered 3 mm pulmonary nodule in high risk patient
12 months
name 2 of the 3 most common laboratory abnormalities in patients with human ehrlichia diseases
Leukopenia, thrombocytopenia, elevated aminotransferases
Syndrome characterized by the combination of autoimmune adrenal insufficiency with other autoimmune endocrine disorders
Polyglandular autoimmune syndrome type 2 (accept polyglandular autoimmune syndrome)
Receipt of a blood transfusion prior to this date is a risk factor for hepatitis C infection
1992
Diagnosis accounting for absence CD55 and CD59 on red cells and granulocytes
Paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria
Best test to differentiate sleep apnea from obesity hypoventilation syndrome
Daytime (awake) ABG (accept PCO2)