What is DLP and what type of control is it?
What is Data loss prevention (DLP) and technical control
What is a cold site?
A cold site typically doesn’t have any equipment or work areas set up—it’s essentially just empty floor space waiting for the organization to move in if necessary.
What is SaaS?
What is Software as a service (SaaS) allows a customer to essentially lease software, such as applications and databases, thus enabling rapid rollout to the greater user community.
What is a Community Cloud?
Community clouds are created when two or more organizations create a mutual cloud.
What are the reuse of code security concerns?
Reuse of code that contains weak cipher suites and implementations, often incorporated to better integrate with legacy software, can introduce inherent weaknesses into your new project.
What is one common type of exercise, which involved parties sitting around a table and stepping through a scenario to discern weaknesses in the plan?
What is a tabletop exercise
What are the three states of data?
What is: At rest
- In transit/motion
- In processing/use
What is a Hot Site?
A hot site has all the amenities—floor space, utilities, workspace, and fully mission-capable equipment—required to switch business processing from the primary site to the recovery site, with little interruption.
What is IaaS?
What is Infrastructure as a service (IaaS) provides the ability to quickly stand up virtual machines, storage devices, and other infrastructure that would otherwise require the purchase of physical devices.
What is a Hybrid Cloud?
Hybrid clouds combine two or more different types of clouds (such as private and community) to perform specific tasks not easily completed through one standard solution. For example, an organization could utilize a community cloud for its greater workforce but segment a portion of its most sensitive data to a private cloud managed internally.
What is Obfuscation/camouflage with Secure Coding Techniques?
The nature of interpreted code is that the system must read it as quickly as possible. There are ways to obfuscate or camouflage code, on the other hand, so that it’s extremely difficult to read.
An organization’s __________ must also contain information planning for the succession of key employees.
What is Incident Response Plan
What is Tokenization?
Tokenization is the process of turning meaningful data, such as an account number, into a random string of characters called a token that has no meaningful value if breached. Tokens serve as a reference to the original data, but cannot be used to guess those values. That’s because, unlike encryption, tokenization does not use a mathematical process to transform sensitive information into a token. There is no key or algorithm, that can be used to derive the original data for a token. Instead, tokenization uses a database, called a token vault, which stores the relationship between the sensitive value and the token
What are Honeyfiles?
A honey file is a fake file located on a network file share. Honey files are designed to detect attackers who are accessing and potentially removing data from your network. Attackers will often find a file share on a network, zip the contents of the share into a folder, and dump the data for offline analysis.
What type of cloud service is this?
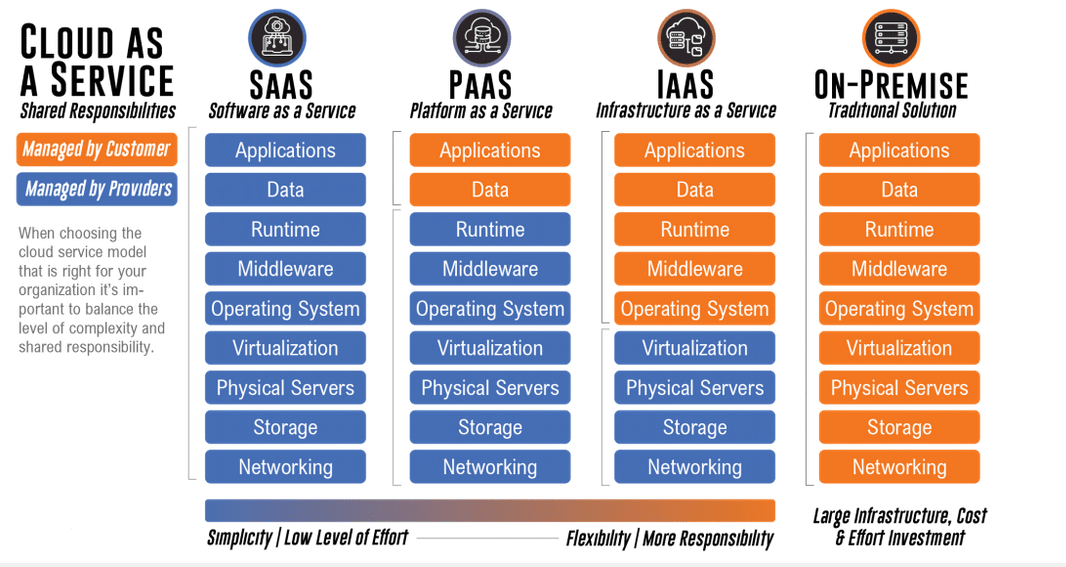
What types of cloud services
What is a Private Cloud?
Private clouds are available only to the organization and can be managed either internally by the organization or externally by a third party.
What are Server-side vs. client-side Secure coding technique concerns?
Client-side validation can respond to the user more quickly because the feedback can be generated almost instantaneously as you get a result.
The server side is generally considered more secure because the server doesn’t show its code to the client.
Which of the following is not a step of the incident response process?
A. Eradication
B. Preparation
C. Formulation
D. Lessons learned
What is Formulation
What is the difference in encryption between code and encryption?

Code shuffles data. Encryption transforms data
What is a warm site?
A warm site not enough to run the full operations, but enough at least to get started while recovering the rest of the business to the recovery site. The organization may also install peripherals such as printers, scanners, and so on. Typically, this spare equipment likely wouldn’t be updated with the latest operating systems, patches, applications, or even transactional data the business needs to get going again.
What is PaaS?
Platform as a service (PaaS) provides the framework of an operating system and associated software required to perform a function (for example, the Linux operating system and components needed to run a web server).
What is an MSP?
Managed service providers (MSP), and managed security service providers (MSSPs) look to outsource everything, their IT services to their security services to save money and reduce risk. MSPs offer service level agreements (SLAs) with uptimes guaranteed, typically comply with certification bodies, and may have more experienced handling incident response and other critical processes than an in-house shop.
What is the design of a database to remove redundancies and improve integrity by simplifying the design.
What is Normalization or the design of a database to remove redundancies and improve integrity through simplifying the design.
What are the six steps of Incident response in order?

What is:
Preparation
Identification
Containment
Eradication
Recovery
Lessons Learned
What is the difference between a Hash and Encryption?
Encryption is a two-way process that packages data that can only be unpackaged with a key.
A hash is a one-way function used for integrity
What is a DNS sinkhole?
DNS Sinkholing is a mechanism aimed at protecting users by intercepting DNS request attempting to connect to known malicious or unwanted domains and returning a false, or rather controlled IP address. The controlled IP address points to a sinkhole server defined by the DNS sinkhole administrator.
What is XaaS
Anything as a service (XaaS): for a price, a user or company would want to use a computing system for can be delivered to them by a cloud service provider through the cloud infrastructure—typically through a thin client.
What is Edge computing?

Edge computing was developed to improve the response time of very bandwidth-intensive, speed-dependent activities such as streaming services by bringing the content to “edge devices” that are closer to the end users, reducing the amount of time the content takes to make its way from the provider to end users. In the same way, edge computing uses edge devices to improve response times for end users who are accessing data storage and other more traditional computing needs within an enterprise.
What technique is associated with the CIA Triad?
Confidentiality, Integrity, & Availablity
What is:
Confidentiality: Encryption
Integrity: Hash
Availablity: QoS
The MITER ATT&CK, Diamond Model, and Lockheed Martin Cyber Kill Chain are all what kind of frameworks?
What is an Attack Framework