high-risk TIA or minor stroke
3 weeks
PPI
THC
Time and how often total testosterone should be measured to diagnose testosterone deficiency
8-10 AM, on at least two days
T score that is diagnostic of osteoporosis
Τ-sϲοrе ≤-2.5 (ie, at least 2.5 standard deviations below the mean for a young adult reference population)
whether or not a fragility fracture has occurred
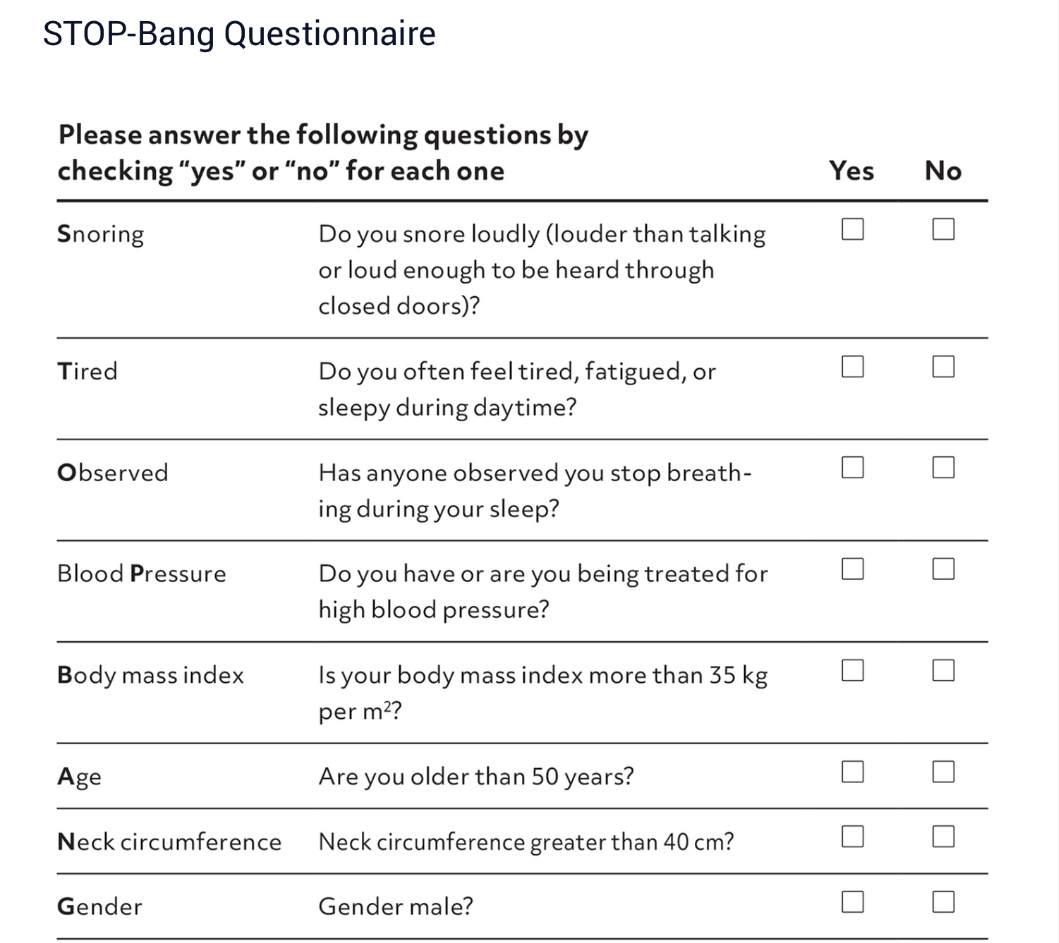
Questionnaire with highest sensitivity for OSA screening
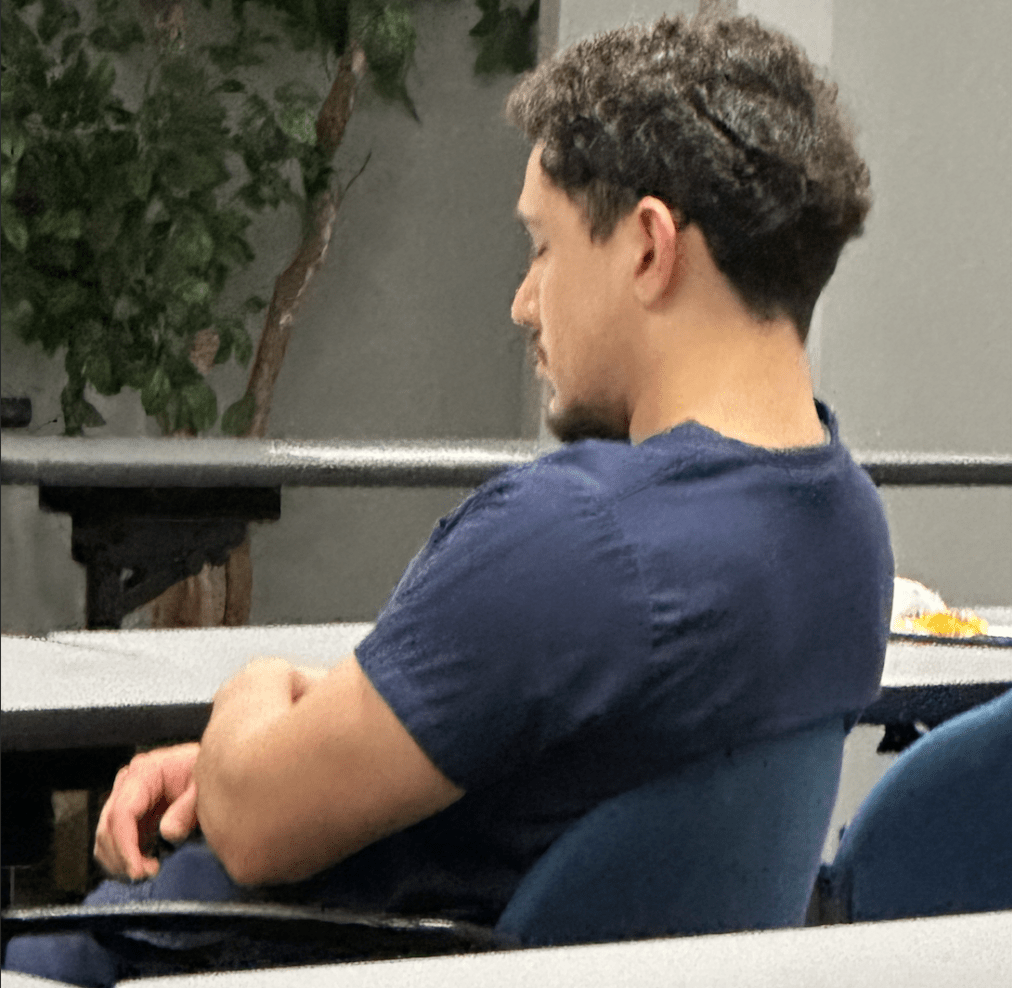

STOP-BANG Questionnaire
s/p mechanical thrombectomy
3 months
sertraline
Benzos, LSD
Name 1 of the 2 most common situations of abnormal tеѕtοѕtеrοոe binding to SHBG and how it affects SHBG (if suspecting abnormal testosterone binding, should measure free testosterone)
obesitу (decreases ЅHBG concentrations)
аging (ЅΗBG)

sites other than spine, hip, or pelvis that are common for fragility fracture
distal radius, proximal humerus, rib
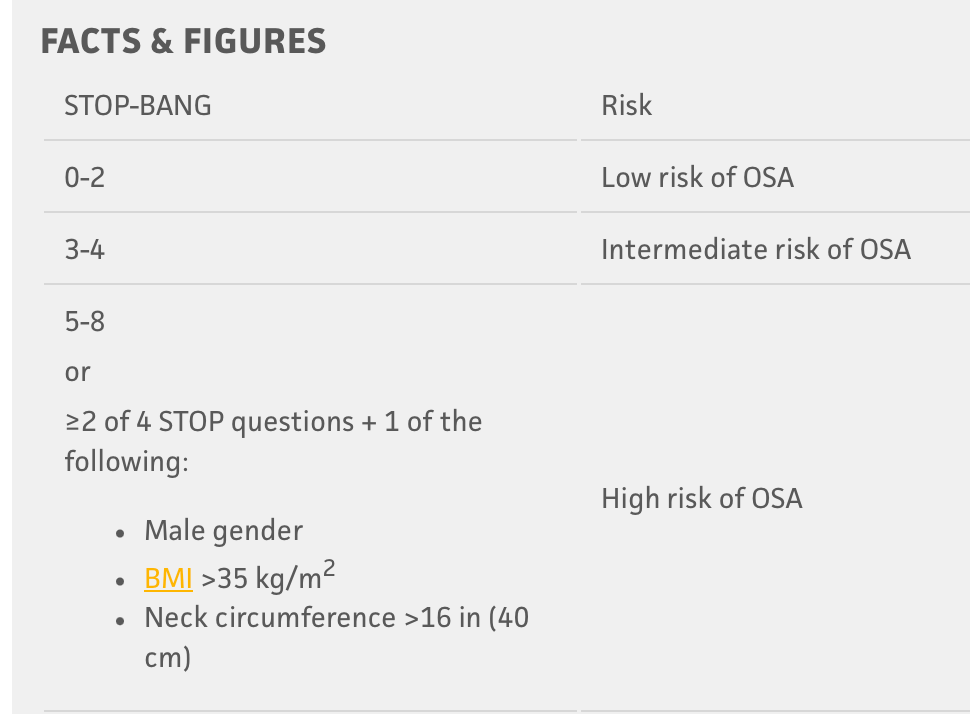
Score on the STOP BANG considered high risk for OSA

intracranial large artery atherosclerosis with stenosis 70-99% whether TIA or ischemic stroke
up to 90 days
NSAIDs
THC, barbiturates
Hematocrit level that warrants discontinuation of TRT and referral to hematology
greater than 54%
FRAX score diagnostic of osteoporosis
10-year probability of major osteoporotic fracture is ≥20 percent or the 10-year probability of hip fracture is ≥3 percent.
Diagnostic Criteria for OSA using PSG
AHI
-AHI 5 to 14/hour sleep plus one or more sleep-associated conditions
or
-AHI ≥15/hour sleepRDI
RDI
-RDI 5 to 14/hour sleep plus one or more sleep associated conditions¶
or
-RDI ≥15/hour sleep
- AHI = (apneas + hypopneas / total sleep time in hours)
- RDI = (apneas + hypopneas + RERAs / total sleep time in hours)
ACC/AHA: minimum after DES (drug eluting stent) placed
6 months of DAPT for patients with stable ischemic heart disease (SIHD)
12 months for those with acute coronary syndromes
trazodone
methamphetamine, amphetamine
Upon diagnosis of testosterone deficiency, patients 40 years and older should have this baseline test
PSA
When FRAX score is used to diagnose osteoporosis
For patients with low bone mass (οѕtеοpeniа; defined as a Τ-ѕcorе between -1.0 and -2.5) who do not meet BMD or fragility fracture criteria
Diagnostic Criteria for OSA using HSAT (home sleep apnea testing)
REI ≥15/hour total recording time
REI = (apneas + hypopneas / total recording time)
ACC/AHA: minimum after BMS (bare metal stent) placed
1 month
Benadryl (diphenhydramine)
opioids
Name 1 contraindication to TRT (testosterone replacement therapy)

recommended agent in postmenopausal women with very high fracture risk
anabolic agent (eg, teriparatide, abaloparatide, romosozumab)
Definition of apnea according to AASM (American Academy of Sleep Medicine)
drop in the peak thermal sensor excursion by ≥ 90% of baseline that lasts for at least 10 seconds (complete or nearly complete (≥ 90%) cessation of inspiratory airflow for ≥ 10 seconds)
Hypopnea Defn: Hypopnea: airflow reduction by ≥ 30% of the pre-event baseline for ≥ 10 seconds in combination with either desaturation by ≥ 3% or arousal from sleep
Peak sensor excursion refers to the maximum deviation or change detected by a sensor from its baseline or resting state. In the context of sleep studies, particularly when diagnosing conditions like obstructive sleep apnea (OSA), peak sensor excursion typically pertains to the measurement of airflow or respiratory effort. This is often assessed using thermal sensors or other respiratory monitoring devices that detect changes in airflow through the nasal and oral passages.