The general classification of a drain that drains fluid by suction.
What is a closed drain?
Or
What is an active drain?
The first goal of wound management.
What is infection control?
This part of a drain makes quantifying and monitoring wound fluid easy.
What is a collection device/fluid reservoir/collection bag/bottle/grenade/...?
In drain monitoring, you look out for these two general aspects.
What is function and what are complications?
Or what is fluid quality & quantity?
Another term for negative pressure.
What is suction/vacuum?
The type of drain that removes fluid by capillary action.
What is a passive drain/Penrose drain/open drain?
Alternative to an E-collar.
What is adequate pain relief, an inflatable neck collar/onesies?
The reason why active drains are called 'closed' drains.
What is negative pressure or suction (to remove the fluid)?
This practice minimises bacterial infections around drains.
What is aseptic technique?
The unit used for the sizing of drains, feeding tubes, and catheters.
What is French gauge = Fr
With this type, the fluid will drain out between the skin and the tube, not through the centre of the tube.
What is a Penrose drain?
A reason why fluid output in an active drain stops.
What is a kinked/clamped/obstructed tube?
The relative risk of ascending infection in active drains is ... then in passive drains.
What is lower?
4 signs of infection.
What are erythema, oedema, exudation, pain, pyrexia, swelling, lethargy/depression
The central cavity of a tubular drain.
What is lumen?
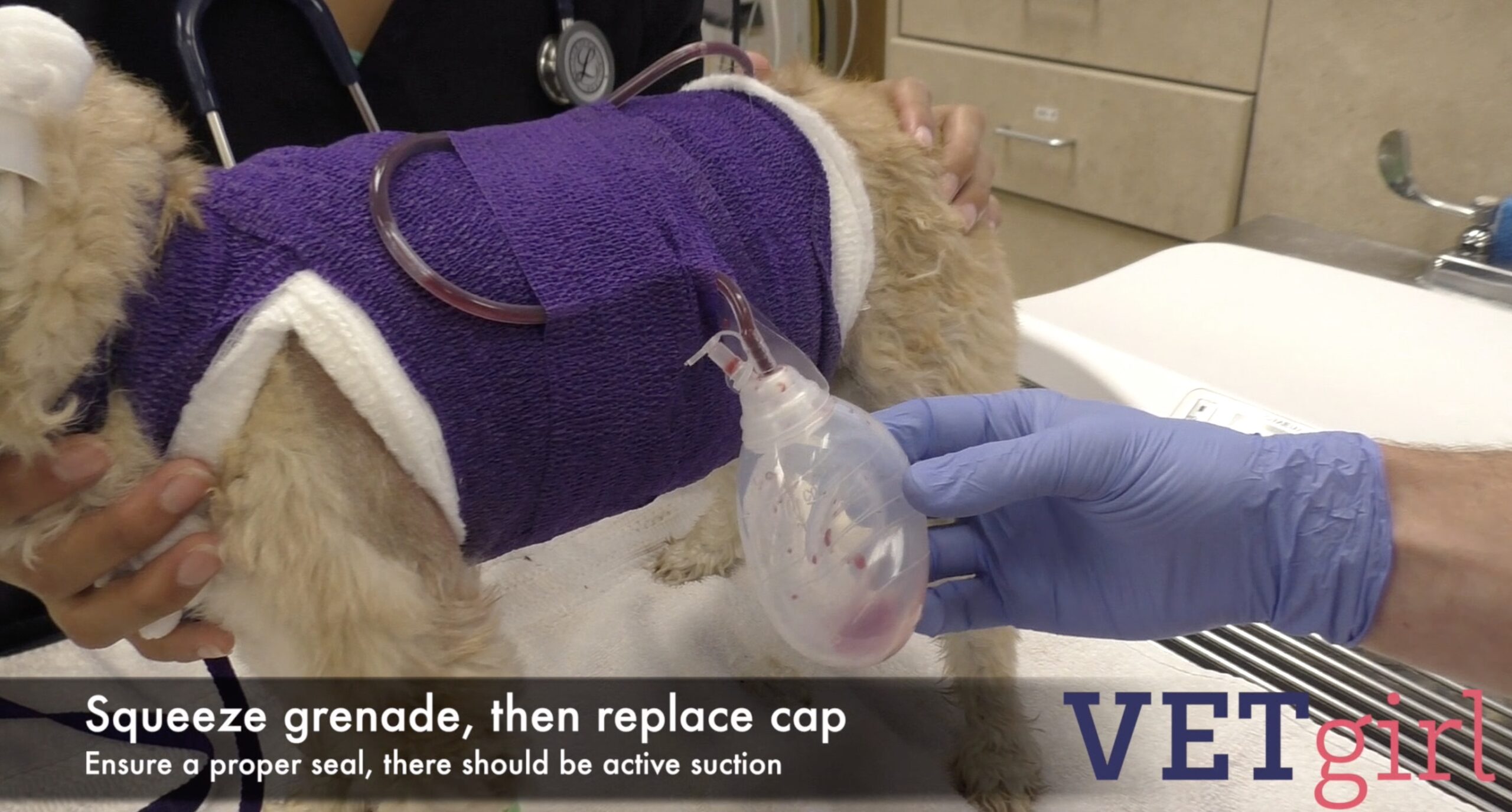
What is a Jackson Pratts drain?
Empty the grenade when...
What is whenever half full?
Two reasons why an active drain may not be able to establish negative pressure.
What is a loose connection, a leaky port or tube, open incision site, dislodged tube, obstruction, ...
The frequency you should check patients with active drains right after placement.
What is q1-2h?
An opening in the body that drains or tubes are passed through.
What is a stoma?
A drain material that causes a marked inflammatory response.
What is latex?
4 important points of homecare advice.
What is being instructed to keep the pet indoors to reduce infection risk/to keep running & jumping to a minimum to avoid strain on stoma site/post-GA care instructions if applicable/importance of effective avoidance of interference with the drain/bandaging advice if applicable/advice NOT to apply any non-prescribed topical treatments or give unprescribed medications/advice what visual checks are required/importance of timely follow-up appointments
Your clinic does not have a commercial closed suction drain like a Minivac Suction Set, a JP drain with a grenade, or a suction unit - but these items may be used to create a non-commercial closed suction dran.
What is a syringe or a butterfly catheter extension with a fenestrated tube and a vacutainer?
4 types of drain complications.
What is pain or discomfort/irritation or malfunction due to poor drain selection or placement/infection due to inappropriate handling, interference by patient/inefficient drainage/an active system not holding suction/incision dehiscence/premature removal?
What is elasticated net bandaging material?