Studies ways in which drugs move through the body
Pharmacokenetics
Atropine is a competitive antagonist of muscarinic acetylcholine receptors. It causes Increased Heart Rate, Dry Mouth, Large pupils, Urinary Retention, Constipation, & Extreme Confusion.
What is the drug action, therapeutic effects, side effects, and drug effects in this case?
Drug action: Atropine
Drug effects: all of its causes
Therapeutic effects: Increased Heart Rate
Side effects: Dry Mouth, Large pupils, Urinary Retention, Constipation, & Extreme Confusion
What does ED50, TD50, LD50, and TI represent?
ED50: half of the maximal dose
TD50: half of the 100% toxic dose
LD50: half of the 100% lethal dose
TI: margin of safety
R-of-A: Oral (enternal "gut" administration)
Advantage and disadvantage?
Advantage: easy to administer
Disadvantage: first-past metabolism by the liver (some is metabolized before it reaches bloodstream)
Irregular blood plasma level influenced by metabolism slow onset
R-of-A: Intraperitoneal
Advantage /Disadvantage?
Advantage: useful in research, variable metabolism, absorption, and distribution but can be as fast as IV
Disadvantage: not common in humans, but used in research
Define ADME
Absorption
Distribution
Metabolism
Elimination
What is the MAIN difference between Therapeutic Effects and Side Effects?
In TE, the drug-receptor interaction produces DESIRED physical or behavioral effects
whereas,
in SE, all drugs effects OTHER THAN DESIRED changes
Why is the purple line more potent?
Purple is more potent because it takes a lower concentration to have the same effect as green.
Rightward Shift = More Potent
R-of-A: Rectal (enteral "gut" administration)
Advantage and Disadvantage?
Advantage: Convenient if subject is vomiting, bypasses first pass metabolism
Disadvantage: less pleasant than oral, irregular blood plasma level, onset is difficult to predict
R-of-A: Intravenous
Advantage /Disadvantage?
Advantage: little to no initial metabolism, very quick distribution and onset
Disadvantage: difficult to administer, risk of infection, overdose, and is difficult to reverse
What is Pharmacodynamics?
What is the definition of Half-life and what is its formula?
Hint: WE use this to determine dosing for drugs that exhibit first-order kinetics (non-saturable elimination).
The amount of time it takes to eliminate half of a dose of the drug from the body.
t1/2= (0.7 x VD) / CL
-VD is the drugs volume of distribution VD = L/kg
-CL is the (constant) clearance of the drug CL = (L/h)/kg
What is a ligand?
What is an example of a biological ligand and a mimic of that ligand?
Biological ligand – Norepinephrine
Mimic - Clonidine
Lock & Key Fit & Mimics :
R-of-A: Transdermal (nicotine patches)
Advantage and Disadvantage?
Advantage: easy to administer, bypasses first metabolism, controlled and sustained delivery, influenced by blood supply to site of administration
Disadvantage: can irritate the skin
R-of-A: Inhalation
Advantage /Disadvantage?
Advantage: easy to administer, no initial metabolism, very quick (seconds), lungs are rich in capillaries and the blood that leaves the lungs goes straight to the brain
Disadvantage: might irritate nasal passages and damages lungs
The specific molecular changes produced by a drug when it binds to a particular target site
Drug Action
What is the difference between Antagonist & Agonist drugs effects?
Antagonist drugs have compounds that interfere with or inhibits the physiological action or another
whereas,
Agonist drugs have compounds that bind to a receptor and activate the receptor to produce a biological response
How does lipid-soluble drugs move across the cell membrane?
Passive diffusion
Lipid soluble drugs move from higher to lower concentrations called a concentration gradient
R-of-A: Intramuscular
Advantage /Disadvantage?
Advantage: can self-administer (epipens), destroy at site or by lymph, slow, even absorption over time ~ 10 to 30 mins.
can adjust using oil or coinjections, influenced by blood supply
Disadvantage: Less convenient than transdermal, can cause irritation and muscle discomfort
R-of-A: Topical
Advantage /Disadvantage?
Advantage:easy to administer (utilizes mucous membranes), bypasses first pass metabolism, can be quickly taken up by the blood, intranasal moves straight into the blood and bypasses blood brain barrier
Disadvantage: most drgus have a high molecular weight and are poorly lipid soluble, so they are not absorbed by the skin or mucous membranes
What is the difference between Specific Drug Effects and Non-Specific Drug Effects?
Specific drug effects focuses on the physical and biochemical interaction of a drug with its target sites, whereas Non-specific Drug Effect focuses on drug effects unique to the characteristics of the individual
What is the difference First & Zero order kinetics?
What is Half-life?
1st order: drugs are cleared from blood at an exponential rate
Zero order: clearance is at a constant rate regardless of drug concentration
e.g Alcohol; when you have more alcohol molecules than enzymes to break it down
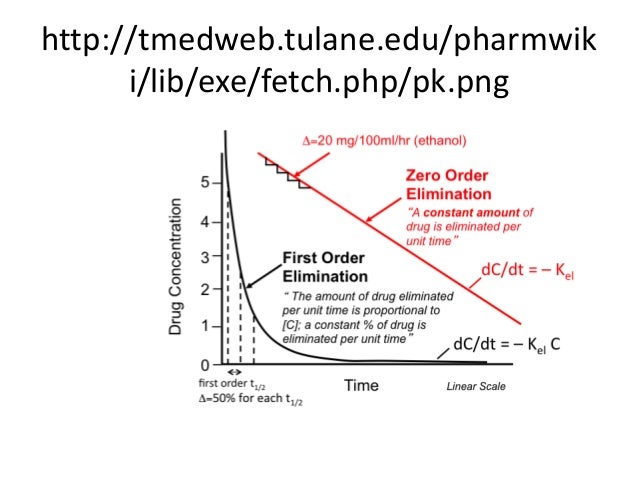 Half-life is the amount of time it takes to clear 50% of the drug from the blood
Half-life is the amount of time it takes to clear 50% of the drug from the blood
What is the half-life of THC, Cocaine, Prozac, and Aleve?
Cocaine:
THC:
Aleve:
Prozac:
R-of-A: Subcutaneous
Advantage /Disadvantage?
Advantage: destroy at site or by lymph, slow and prolonged absorption, influenced by blood supply favored for chronic conditions and botox
Disadvantage: still involves needles (shorter needle), only small volume can be injected
R-of-A: Special injection methods
Advantage /Disadvantage?
Advantage: only small amount needed, administered directly to active site
Disadvantage: can raise blood pressure, can lead to serious nerve damage/ side effects if administered incorrectly
