Why are hospitalized patient is spending most of their time in bed prone to getting DVTs?
Immobility
The most common injectable medication for DVT prophylaxis in hospitalized patients
LMWH - works by binding to antithrombin III, a protein that inactivates clotting factors (mainly factor Xa) and prevents blood clots from forming
This triad describes the 3 major contributors to thrombosis
Virchow's triad
This is the most feared acute complication of a DVT
Pulmonary embolism
The first-line imaging study for suspected lower extremity DVT
Duplex ultrasound
Patients undergoing this type of surgery are particularly high-risk and routinely get prophylaxis
Orthopedic surgery - knee/hip replacements
An oral anticoagulant sometimes used for prophylaxis, especially in orthopedic surgery
Eliquis/Apixaban - works by inhibiting a clotting protein called Factor Xa, which reduces the blood's ability to clot
A long-haul flight increases DVT risk primarily due to this component of Virchow's triad
Venous stasis
This chronic condition, characterized by leg pain, swelling, and skin changes, occurs in up to 50% after a DVT
Post-thrombotic syndrome
This blood test has a high negative predictive value for ruling out DVT in low risk patients
D-dimer
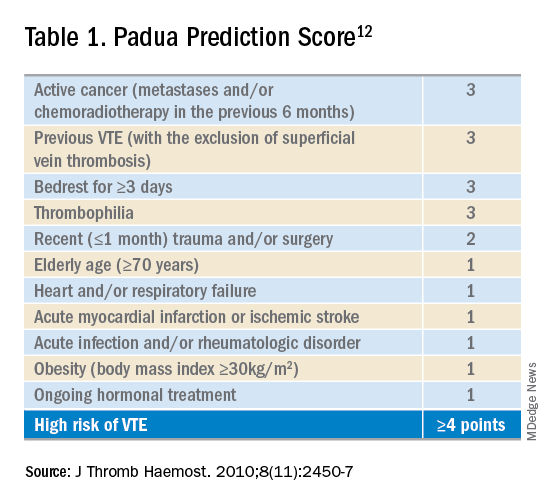
This scoring system can guide clinicians in deciding if a medical patient needs DVT prophylaxis
Padua prediction score
This form of heparin requires more frequent injections compared to LMWH
Unfractionated heparin - enhances the activity of antithrombin III, a naturally occurring protein that inhibits the clotting cascade. This prevents the formation of fibrin, the protein that makes up blood clots
This inherited condition involves a mutation of factor V, leading to resistance to activated protein C
Factor V Leiden
This finding on physical exam, swelling of 1 limb compared to the other, may indicate DVT but could also be due to this chronic condition
Chronic venous insufficiency
CT pulmonary angiography is the gold standard for diagnostic this complication of DVT
Pulmonary embolism
Cancer patients receiving chemotherapy have a risk roughly this many times higher than the general population
4-7x higher
This class of medications, once standard, is now less commonly used for prophylaxis because of narrow therapeutic windows and need for INR monitoring
Vitamin K antagonists - e.g. Warfarin
This pregnancy-related condition or increases DVT risk due to increased clotting factors and venous stasis
Hyper-coaguable state of pregnancy
This complication can lead to right heart strain in sudden cardiovascular collapse
Massive PE
This scoring system is widely used to estimate pretest probability of DVT
Well's score
Prophylaxis is indicated in hospitalized patients with at least 1 major or 2 minor risk factors in this widely used a model
Caprini risk assessment model

This direct thrombin inhibitor can be used for as prophylaxis in some orthopedic cases, though less commonly than factor Xa inhibitors
Dabigatran/Pradaxa
This rare paraneoplastic syndrome causes recurrent migratory thrombophlebitis
Trousseau's syndrome
Chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension (CTEPH) is a complication of unresolved emboli and presents with this primary symptom
Progressive exertional dyspnea
In patients where ultrasound is inconclusive, this invasive test can directly visualized venous obstruction
Venography