atrial
contraction
Flutter
Fib
Failure
AFIB
TX
Normal SA node rate?
Primary or Secondary?
60-100 beats/min
primary (sinoatrial)
what is premature atrial contraction (PAC)?
Extra HB that occurs in atrial chambers contracting too early
"skips a beat" 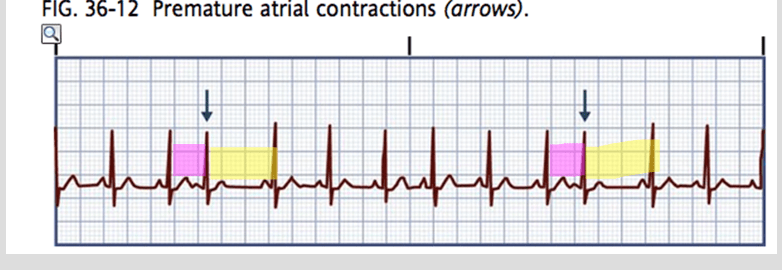
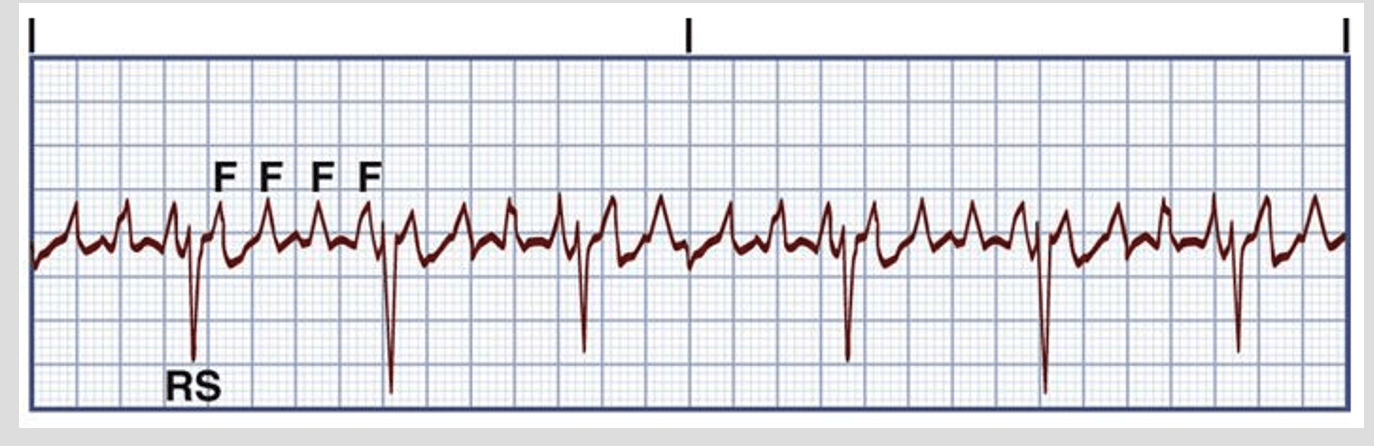
what is atrial flutter?
upper chambers (atriums) beat rapidly but in a regular rhythm
Decreases cardiac output bc of ineffective atrial contractions
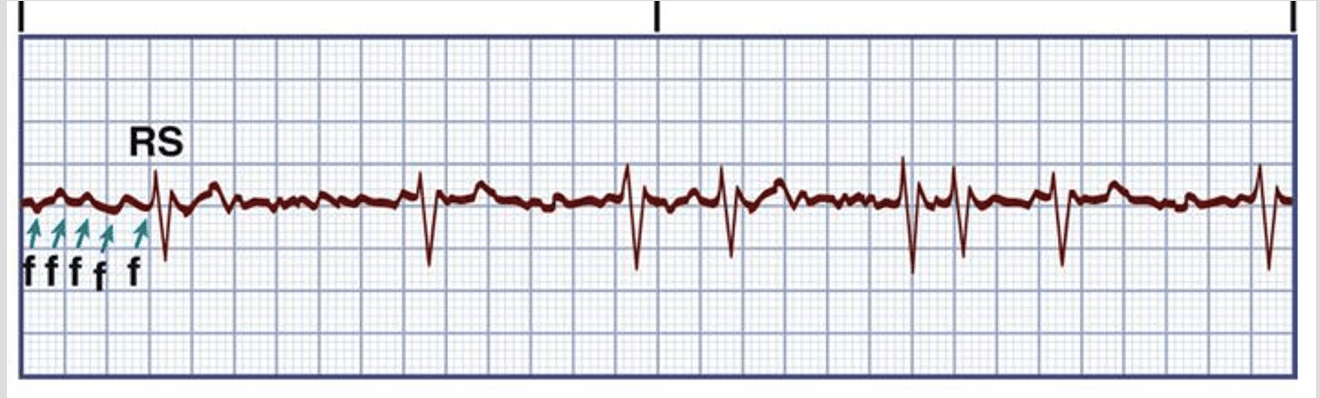
what is atrial fibrillation?
upper chambers (atriums) beat rapidly but in a irregular and chaotic rhythm (in LT atria)
ventricular filling (diastolic)
or
Ventricular ejection (systolic)
Diltiazem classification
calcium channel blocker
Normal AV node rate?
Primary or secondary?
40-60 beats/min
Secondary (atrioventricular)
what causes PAC?
stress, fatigue, caffeine, tobacco, alcohol, hypoxia, electrolyte imbalance, disease states
what is a radiofrequency catheter ablation?
burns and destroys tissue causing arrhythmias
What is synchronized cardioversion?
A counter shock using a cardioversion machine on the R wave of the QRS complex of ECG.
What is Ejection fraction?
Amount of blood pumped by ventricles with each beat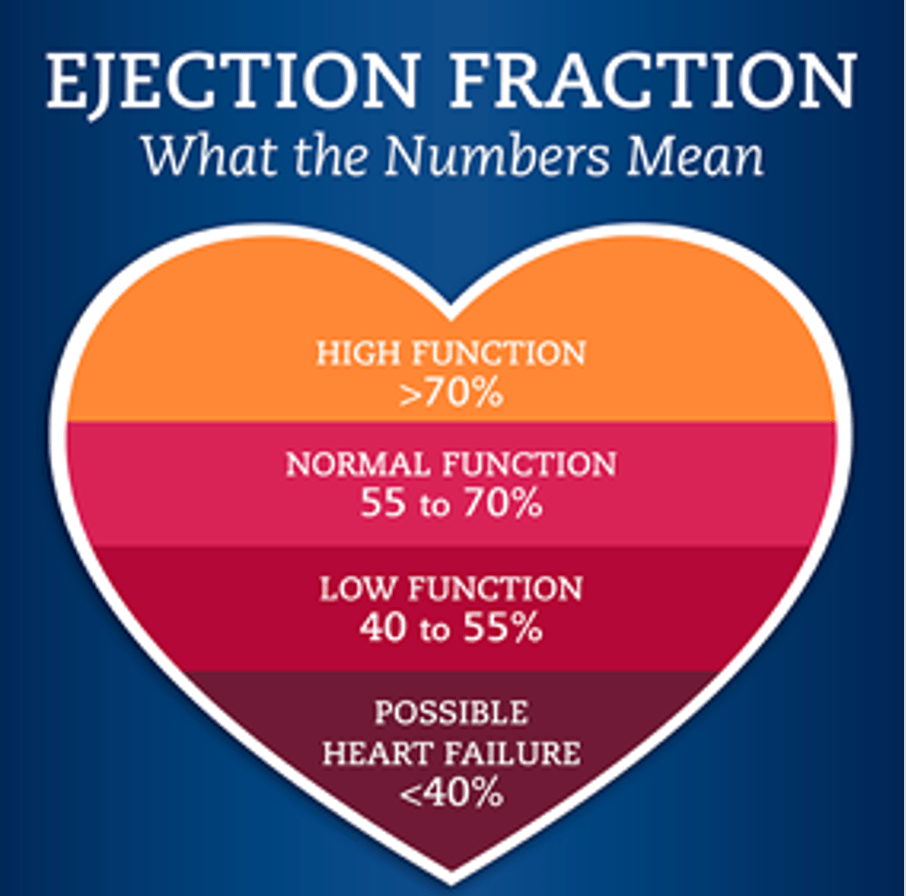
Metoprolol
beta blocker
what is the rate of His-Purkinje fibers?
20-40 beats/min
what are complications of PAC?
A-flutter & A-Fib
what is the rhythm regularity and BPM?
What kind of formation does it make on ECG?
regular, fast rhythm, 200-350 BPM
Sawtooth formation
Too many P wave formations
what is the rhythm regularity and BPM?
What kind of formation does it make on ECG?
Iiregular, fast rhythm, 350-600 BPM
no distinct formation
No discernable P-waves
Why does HF occur?
when the heart muscle is unable to pump effectively by ...
Inadequate cardiac output
Insufficient blood supply/O2 to organs/tissues
Myocardial hypertrophy
Pulmonary/systemic congestion
Amiodarone
anti-dysrhythmic
what electrolytes affect the heart?
what are the lab values?
Na+ (136-145)
Ca (9.0-10.5)
K+ (3.5-5.0)
medication(s) to administer?
Beta blocker
reduces the extra beats and mellows heart
Less severe or more severe?
less severe
most ppl can live in a flutter
less or more severe?
More severe as it is harder to treat compared to Aflutter
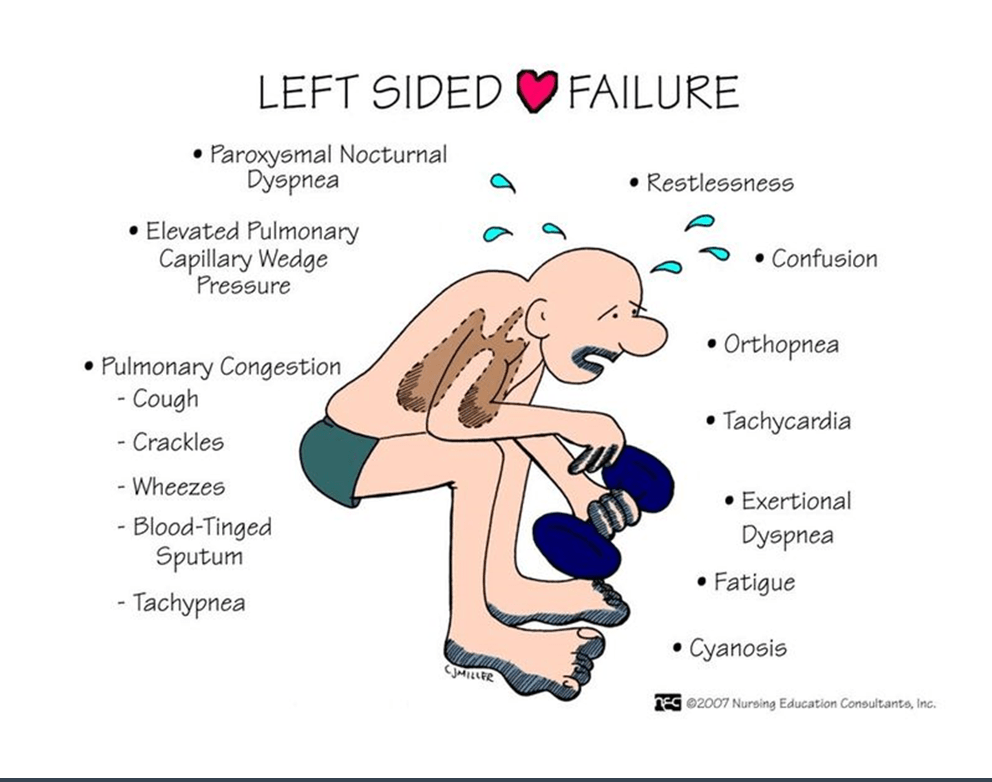
What is LT HF? what organs does it affect?
What does LT HF look like?
Blood backing up into LT atrium and pulmonary veins BC LT vent is not pumping properly.
Lungs, Kidneys, Liver
Digoxin
digitalis glycoside
* controls rate and rhythm
*used on Afib
what are the atrial dysrhythmias? (2)
Atrial flutter
Atrial Fibrillation
What is hypertrophy?
The increase in muscle mass and heart wall thickness
What are normal BNP levels?
What are normal Ejection fraction levels?
Normal BNP= <100 pg/mL
*Greater than 100 pg/mL = HF *
Normal EF = 55-75%
*less than <40% = RT HF*
what are therapeutic serum digoxin levels to prevent digoxin toxicity?
0.8-2.0 ng/mL
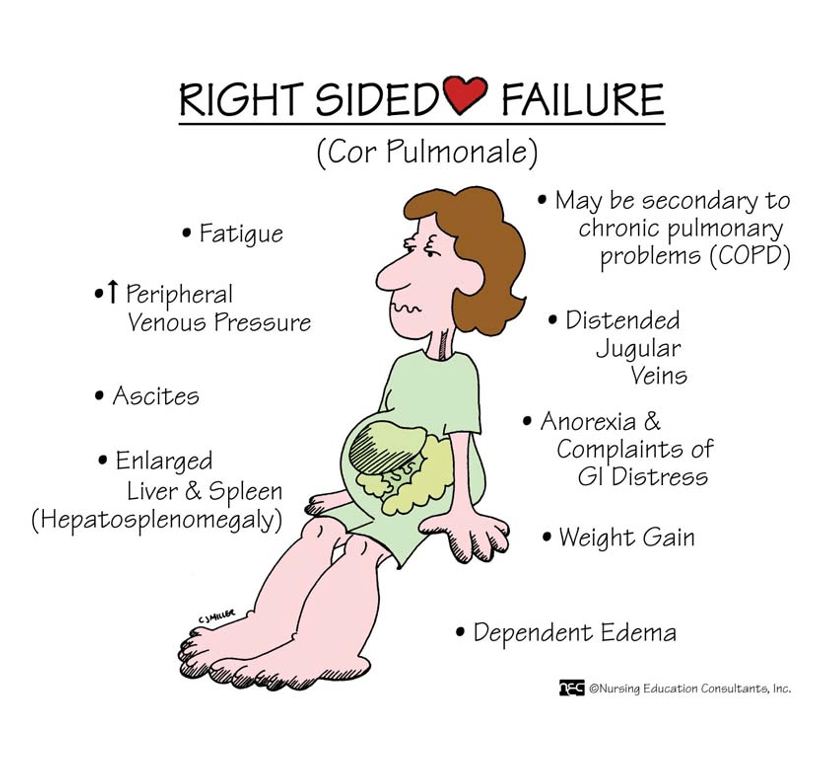
What is RT HF? what organs does it affect?
What does RT HF look like?
RT vent does not pump effectively, fluid backs up into systemic venous system causing fluid to fill into body tissue and organs.
Cor pulmonale, hepatomegaly, ascites and KF
anticoagulant brand names
warfarin
apixaban
rivaroxaban
coumadin
elaquis
xarelto