Weather outside is very windy with lots of hail. Which spheres are in this example?
Atmosphere and Hydrosphere
I look out the window and notice lots of clouds in the sky. What conclusion can I make about the air pressure?
Low pressure since clouds were able to rise and form
What part of a water molecule has a partial positive charge? What part has a partial negative charge?
O is negative and H is positive
What is the term for a layer of rock or sediment that slows or prevents the movement of groundwater?
aquitard
Label the layers of the Earth:
Yellow- Inner Core --> SOLID, METAL
Orange - Outer Core --> LIQUID METAL
Red- Mantle --> LIQUID ROCK
Gray- Crust--> SOLID ROCK
What causes air pressure?
gravity
Fill in the blank. When warm air rises, it creates __________ pressure, and when cold air sinks, it creates __________ pressure.
Warm= Low
Cold = High
You pour water into a glass, and the water level rises slightly above the rim without spilling. The surface seems to hold together in a dome shape. What property of water is responsible for the water molecules holding together like this?
cohesion- WATER PLUS WATER
What is a spring in terms of groundwater?
When the water flows up from below ground to above ground
Which of the following layers of the Earth is liquid metal?
outer core
What is the Ozone layer?
A layer that helps protect us from the Sun’s radiation
Why did the warm red water stay on top of the cold blue water when it was stacked on top? In terms of density
Warm molecules are less dense and rise
You dip the tip of a paper towel into a small puddle of water. Slowly, the water begins to move upward through the towel. What property of water allows it to climb against gravity like this?
adhesion- WATER PLUS SOMETHING ELSE
What happens if an aquifer is used faster than it is replenished?
it runs dry
Name two oceanic and two continental plates
Continental Examples: Eurasian, North American
Oceanic Examples: Pacific, Nazca,
True or False: More solar radiation is reflected back into space than absorbed by the Earth.
In the "Magic Inflatable Balloon" demo, why does the balloon inflate in warm water? In terms of speed of molecules
Warm air molecules move faster and rise and spread out
Earth’s water is in many forms. Many of the forms are not usable for life. How much of Earth’s water is actually available for life?
2.5% IS FRESHWATER AND OF THAT 1.2% IS AVAILABLE TO US. THE REST IS TRAPPED AS ICE OR IN AQUIFERS
How does an artesian well bring water to the surface?
pressure pushes water up against gravity
Match each type of plate boundary with the landform it can create:
_______Convergent A. Fault lines
_______Divergent B. Mid Ocean Ridge
_______Transform C. Mountains
Convergent--> mountains
Divergent--> Mid Ocean Ridge
Transform --> fault lines
Match the description with the correct layer of the atmosphere:
A) Contains the ozone layer
B) Where weather happens
C) Location of the International Space Station
D) Most meteors burn up here
E) The "beyond," where outer space begins
A) Contains the ozone layer (STRATO)
B) Where weather happens (TROPO)
C) Location of the International Space Station (THERMO)
D) Most meteors burn up here (MESO)
E) The "beyond," where outer space begins (EXO)
Choose one: In areas of high pressure, air molecules are tightly packed or spread out.
Choose one: In areas of low pressure, air molecules move slow or fast.
tightly packed
fast
Label the hydrologic cycle:
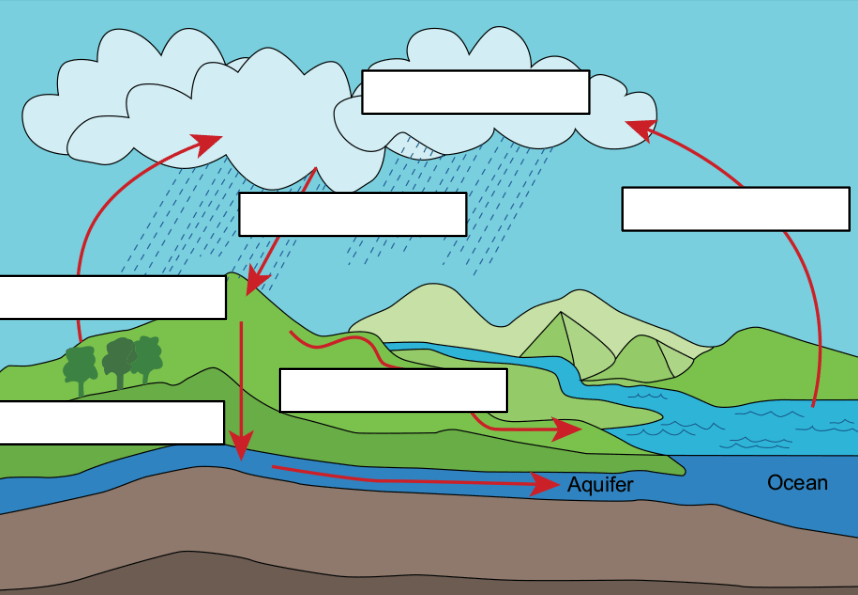
Clouds- CONDENSATION
Rain - PRECIPITATION
Water leaving ocean up - EVAPORATION
Plants Sweating- TRANSPIRATION
Water entering ground- INFILTRATION
Water flowing on top of ground into body of water - RUNOFF
How do confined aquifers recharge (refill) differently from unconfined aquifers?
Confined aquifers can take thousands to millions of year to recharge while unconfined recharge much faster
What is the asthenosphere, and where is it located?
A soft, semi-solid layer of the mantle beneath the lithosphere where convection occurs
How does the temperature change during the day and night in an inland city?
Heats up faster during the day and cools down a lot at night
Why is the atmosphere important for life on Earth?
Oxygen to let us breathe, ozone protects from harmful radiation, regulates temperature, provide water via water cycle, burns up meteors so they don't kill us
The area in which freshwater meets saltwater is called:
an estuary
Why is groundwater considered an essential resource for agricultural use?
-Consistent supply of water for crops
-Ground water is unaffected by droughts and is easily accessed via wells
How does convection in the mantle move the lithosphere?
Heat from core rises and when it cools it cycles down moving the tectonic plates
In The Day After Tomorrow, what caused the sudden change in climate?
Disruption of ocean currents from melting ice
A) Massive algae bloom (growth)
B) Surface water runoff carries extra nutrients
C) Sunlight is blocked from deeper water
D) Increased carbon dioxide causes pH to drop, leading to acidification
E) Water becomes very low in oxygen and plants/fish die
B
A
C
E
D
Describe how aquifers store water. Discuss permeability and porosity.
Aquifers store water in spaces between rocks and soil underground.
Porosity is how many tiny holes or spaces there are to hold water.
Permeability is how easily water can flow through those spaces.
If a rock has high porosity and high permeability, it can store and move a lot of water.
Name the two types of crust involved in plate boundaries and describe how they interact at a subduction zone.
Oceanic goes under continental
Label: Unconfined aquifer, unsaturated zone, water table, aquitard, artesian well
Unconfined: 6
Confined: 5
Unsaturated: 3
Saturated: 1 and 6
Water table: 4
Pump well: 7 and 8
Artesian well: 9 (see pressure pushing water out)
Aquitard: 2
-Identify the fault line pictured:
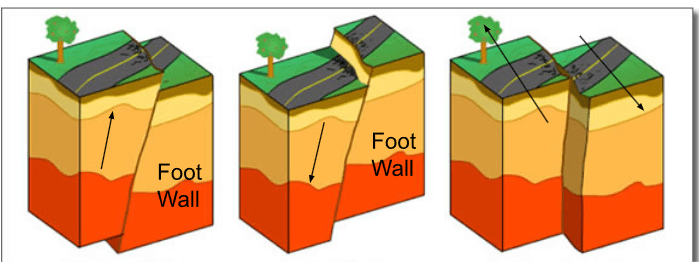
1- reverse
2- normal
3- strike slip