This is the proper order of the layers starting from the outside.
Crust --> Mantle --> Outer Core --> Inner Core
All of the crust and the upper mantle make up ...
Lithosphere
This is the definition of a boundary.
Where two plate tectonics meet in order to interact.
These are the two locations an earthquake forms at
focus - inside the earth
epicenter - directly above the focus on the surface of the earht
These are the three faults and the boundaries they are associated with.
reverse fault -- convergent
normal fault - divergent
strike slip fault - transform
This layer has convection currents that help shift plates around.
Mantle
The continents used to all fit into one super continent called ...
Pangaea
A description of the three boundaries
Convergent - collide
Divergent - pull a part
Transform - scrape past each other
These are the four main types of volcanoes
Cinder cone volcano
Composite volcano
Shield volcano
Hot spot volcano
This type of volcano forms quickly and will only erupt once in its lifetime.
Cinder cone
Describe what makes up each layer.
crust - rocks and soil
mantle - molten rocks
outer core - liquid nickel and iron
inner core - solid nickel and iron
This man identified that all our plates were once together through rock, fossil, and landform evidence.
Alfred Wegener
This zone is formed at every convergent boundary.
Double jeopardy for being able to describe what is occurring.
Subduction zone -- one plate is moving underneath the other
These are the differences between S and P waves.
S waves are longitudinal waves that occur second. They are slower and only move through solids.
P waves are transverse waves and occur first. They are the fastest and move through solids and liquids.
This is how we use seismic waves to figure out the earth layers:
S and P waves will both move out from the focus. S waves will stop at the outer core because it is liquid. P waves will travel through all the layers.
What are the two types of crust?
Double jeopardy if you can describe the two main differences between the two.
Oceanic and Continental
Oceanic is thinner but denser while continental is thicker and less desne.
This is the name of the theory that describes all our plates are in constant movement.
Continental Drift
These are the three types of stress and the boundary they are associated with
Compressional - convergent
Tensional - divergent
Shearing - transform
Label this picture
Ash cloud
Main Vent
Crater
Lava Flow
Strata
Side Vent
Magma Chamber
Describe what is occurring in this picture:
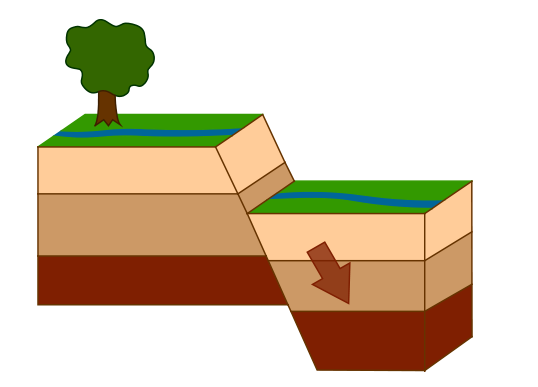
A normal fault: the hanging wall is sliding down and the footwall is sliding upwards. This causes the plates to be pulling away like at a divergent boundary.
What process makes the inner core different from the outer core?
The pressure and heat from all other layers makes the inner core solid while the outer core stays a liquid layer.
This process helped prove the theory that our plates are always moving.
Seafloor spreading
These are the two types of folds.
Anticline and syncline
Describe how an earthquake will occur.
At boundaries, stress is formed due to the plate movements. Rocks will begin to deform and produce faults. Pressure will start to build up until rocks snap at these faults.
Describe how new crust is formed and destroyed. Include why these processes are so important
New crust will be formed at divergent boundaries as magma rises up from the mantle and pushes outward. Crust will be destroyed at subduction zones from convergent boundaries and be grounded away at transform boundaries. We need all of this to occur in order to get landmasses and the Earth to be dynamic, always changing.