The variability of life on Earth. The variety of plant and animal life in a particular habitat.
What is a worldview?
A core of set assumptions and beliefs that guide a person's actions regarding the enviornment. It includes their beliefs about the value of nature, how resources should be used, and what is considered right or wrong in enviornmental matters.
What are the global commons?
The pool of natural resources that are not owned by any one country. An example includes oceans.
Identify the three types of tectonic plate movements
Divergent
Convergent
Transform
What type of system is the water cycle?
A closed system.
What formed the atmosphere?
Volconic eruptions that released gases over 5 billion years formed the atmosphere!
What are glaciers?
A system of flowing ice that forms through accumulation and recrystalisation of snow. It alters landforms through erosion.
Why is biodiversity important?
Promotes soil formation
Provision of resources
Maintain genetic diversity
Ecosystm balance
Maintains food chains
What is anthropocentrism?
Places human beings at the center of the universe and considers human interests and well-being as the most important factor. The enviornment is valued based on its utility.
What is the main tragedy of the commons?
What are the two types of weathering?
Mechanical and chemical
What is transpiration?
The process involves water moving through a plant and evaporating from tiny pores in the leaves.
What is a low-pressure system?
The type of pressure system associated with rising air, clouds, and rainfall and is common near the equator.
What are glacial and interglacial periods?
Glacial periods is when there are extensive ice sheets presents. Whereas, interglacial periods are warmer periods with less ice sheets present.
Why do billions of migratory animals move across the Earth?
Foraging opportunities, improve safety and increase reproductive outputs.
What is biocentrism and ecocentrism?
Biocentrism follows the belief that humans and all living organisms have rights. It recognises the intrinstic value of all living beings. Ecocentrism emphasises the intrinsic value of entire ecosystems, including both living and non-living elements.
What are the challenges with managing the Global Commons?
Lack of clear ownership (difficult to control/ hold people accountable)
Some nations often benefit fromt he commons without contributing to their protections or sustainable management.
Short term economic gain prioritized
Weak international agreements
Geopoltical tensions
Having resources to facilitate/ police management.
What is mechanical weathering
What does the water cycle link together?
The water cycle links terrestrial freshwater and marine ecosystems.
What is a high-pressure system?
ThThe pressure system that brings sinking air, clear skies, and dry weather often found 30 degrees north and south of the Equator.
What are glacial cycles?
A glacial cycle is when large ice sheets in the Northern Hemisphere grow and shrink over time. This causes glical periods and interglacial periods
Why does the humpback whale breed in the warmer waters in the North and migrate to the South later?
New born calfs do not have a thick layer of fat to protect them from the cold water. So, the breeding grounds are in warmer waters and migration to the colder waters occur later.
In 1730, more than 300 Bishnoi were killed while trying to protect trees. Their descendants have sought to carry on their legacy. What viewpoint does this follow?
Ecocentrism.
This area beyond any single nation's jursdiction is protected by international law and is crucial for regulating Earth's climate and supporting marine biodiversity.
High Seas
What is chemical weathering
The changing of composition of rocks, breaking them apart by dissolving particular elements or minerals. E.G Salty water, acidic water, oxidation.
What is a secondary consumer?
Animals that eat primary consumers (herbivores). Examples: Small fish, frogs.
This circulation cell is found near the Equator and features warm air rising, creating low pressure and heavy rainfaill in tropical regions.
Hadley Cells
What influences glacial periods?
The role of Milankovitch cycles (Earth's orbit), volcanoes, Atmospheric composition
Why is biodiversity important?
The loss of biodiversity will lead to the extinction and changes in migration of flora and fauna species casuing the detriment of the ecosystems. Supports all lifeforms in the world.
What is the key difference between biocentrism and ecocentrism?
Biocentrism is centred on all living organisms, whereas ecocentrism nature/ ecosystems are the centre.
This frozen region is considered a global common due to its importance in climate regulation, and its governed by a treaty that bans military activity and mineral mining.
Antartica
What is albedo and how does it impact the enviornment?
Albedo is the reflectivity of a surface - how much sunlight is reflected vs absorbed.
High albedo (light surfaces like ice and snow) reflect more sunlight.
Low albedo (dark surfaces like forests and oceans) absorb more heat.
It helps control how much solar energy is retained in the atmosphere, regulates glaciers and ice formation, affects ocrean currents and influences weathering and erosion rates.
What is Net Primary Productivity? Why is it important?
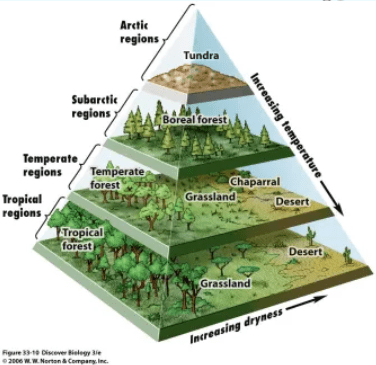
The amount of energy left in plants after they use some for growth and survival and it shows how much energy is avilable to animals in the food chain. (Higher levels of biodiversity which allows self-correction in environments)It is important because it leads to higher biodiversity and resilience in ecosystems.
The circulation cell operates near the poles, where cold, dense air sinks, creating high pressure and very dry cold conditions.
Polar Cells
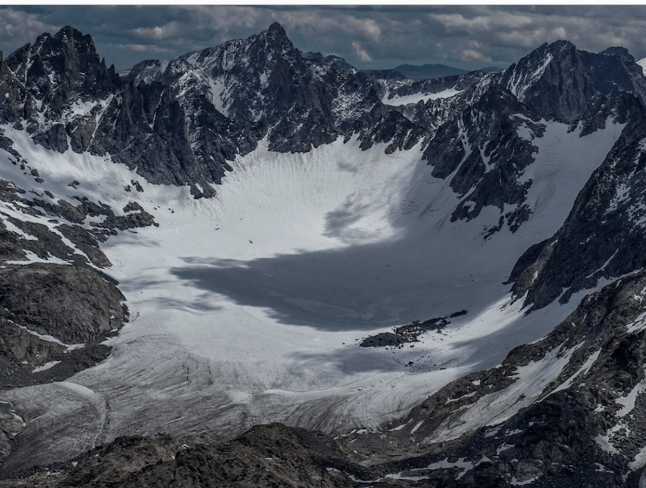 What glacier am I?
What glacier am I?
Mountain