True or false: seismic waves travel in all directions from the focus
true
What is point B?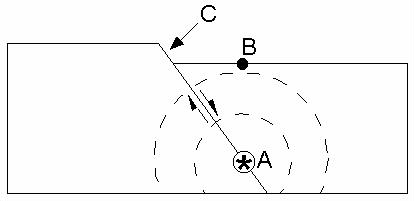
Epicenter
List 2 negative effects of volcanoes
-tsunamis
-ash clouds
-volcanic bombs
What is magma?
molten rock that is still below earth's crust
Using the Moment Magnitude scale, what is the highest magnitude an earthquake could reach?
10 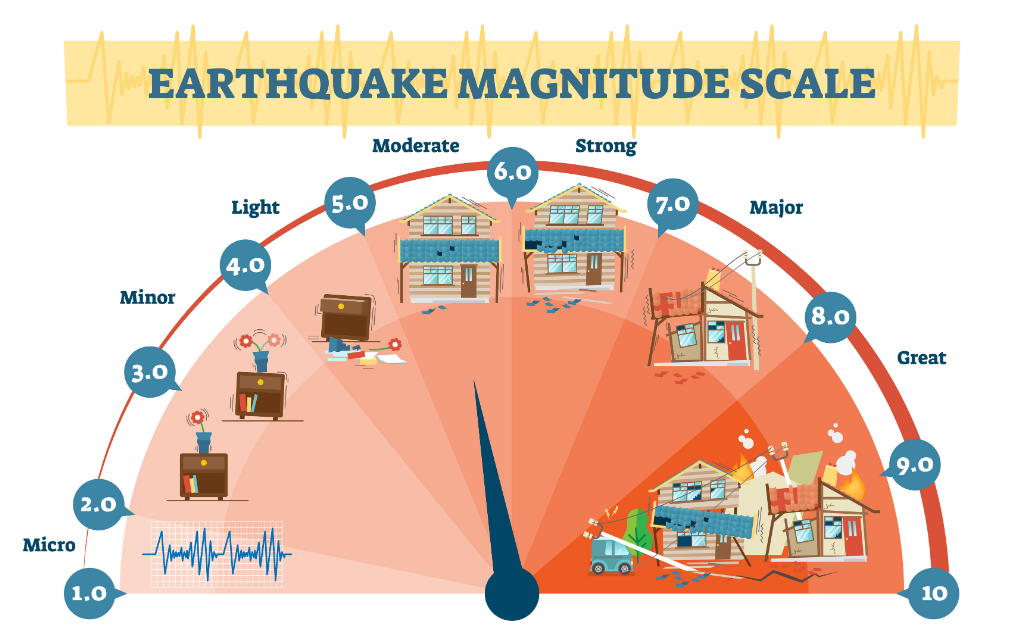




What is the name of the instrument that records the energy of earthquake vibrations
seismograph
What is point A?
Focus
List 2 positive benefits to volcanoes
- fertile soil
-land formation (makes islands, etc)
-raw materials (diamonds, metals)
-geothermal energy (warms the earth)
What is the conduit?
pipe that carries magma from the magma chamber to the vent
What is aftershock?
the smaller earthquakes that follow a larger one
These are vibrations that travel throughout the earth and are caused by earthquakes and volcanic eruption
seismic waves
What is point C? 
Fault
Describe a composite volcano
cone with steep sides that curve inward
very explosive
Come up and point to the magma chamber
bottom
What kind of volcano has lava with a high viscosity
composite
How are Primary Waves and Secondary Waves different?
P Waves: faster, travels through solids, liquids, and gases
S Waves: slower, only travels through solids
What is the focus?
the point below earth's surface where earthquake starts
Describe a shield volcano
shallow volcanoes with large, gently sloping sides
Come up and point to the conduit 
middle
What causes a volcano?
When one crustal plate moves under the other
What causes an earthquake?
When tectonic plates shift position
What is the epicenter?
location on EARTH where an earthquake is felt; above the focus
Describe a Cinder Cone volcano
made of small rock particles or cinders
fragments around vent form a cone with steep sides
Come up and point to the vent

top
What is viscosity?
how think or think a liquid is