Main source of energy for Earth?
What is the Sun?
Strong winds in the upper troposphere that move weather systems and transport cold or warm air to a region.
What is "the jet stream"?
These are some of the most significant green house gases (name at least 4).
What are carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4), water vapor (H2O), Nitrous oxide (N2O), and ground level ozone (O3)?
As a result of increased levels of GHG's trapping more heat, atmospheric temperatures on our planet have already risen by this amount relative to preindustrial levels.
What is 1.5 degrees Celsius (3.7 degrees Farenheit)?
194 nations and the European Union have signed this commitment to reduce carbon emissions to zero by 2050 in order to limit global warming to 2 degrees Celsius and avert the most severe impacts of climate change.
What is the Paris Climate Agreement?
Most of the energy from the sun comes from these two parts of the EM spectrum.
What is Visible and (near or shortwave) infrared
The primary source of energy that powers hurricanes.
What is ocean heat.
Gases such as CO2 allow shortwave sunlight to enter while absorbing and re-emitting some of the longwave heat radiation emitted by the warm surface. Without this the earth would be an uninhabitable ice ball. Over a periods of hundreds of thousands of years it has undergone slow changes as CO2 levels in earth's atmospheres stayed at levels between 180 and 280 ppm and the earth cycled between glacial and interglacial period.
Natural Greenhouse Effect
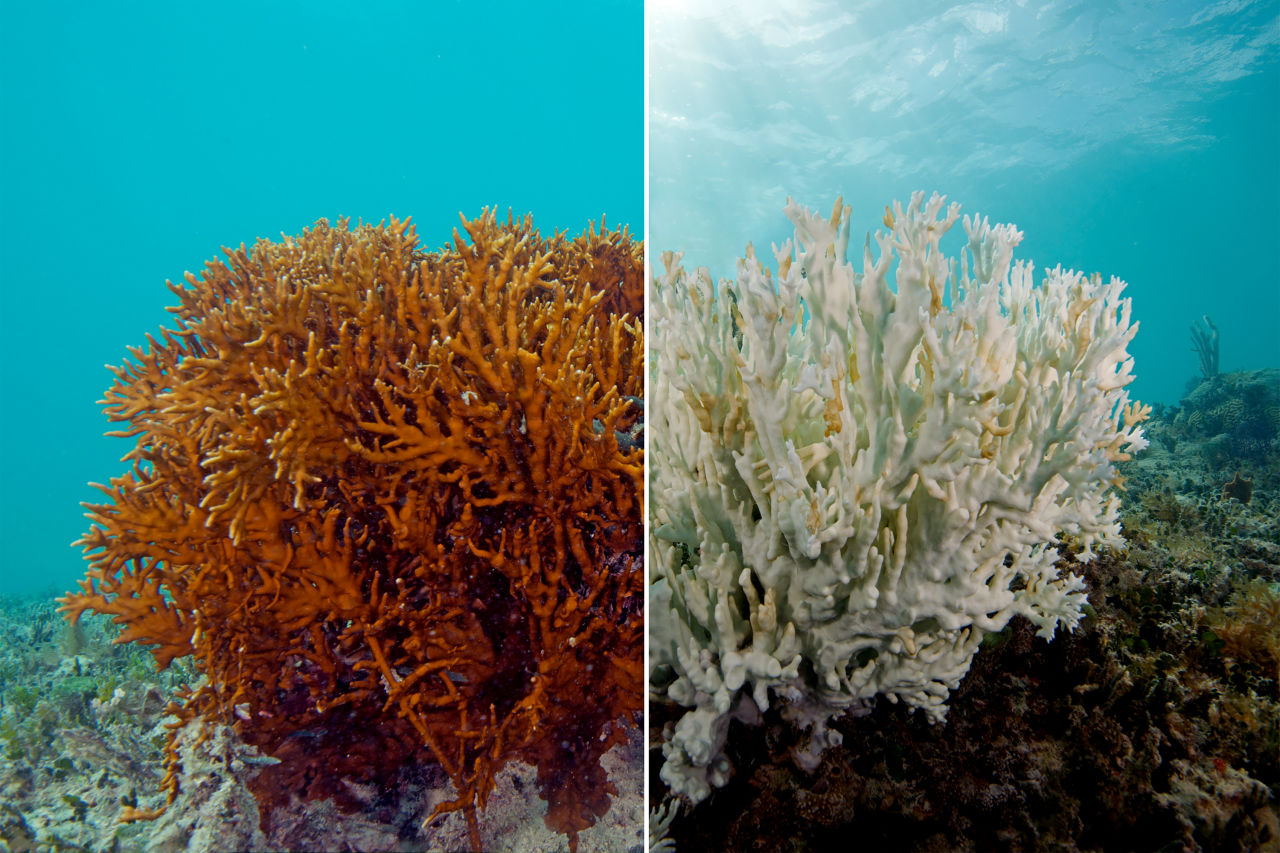

The picture on the right illustrates this phenomenon which results from increased acidity due to excess carbon dioxide that is absorbed by the oceans.
What is "coral bleaching"?
These attempts to remove carbon from the air or oceans are currently expensive and would need to be massively scaled up before having a significant impact of GHG levels.
What are carbon capture and storage (CCS) or carbon capture and utilization (CCU)?
Percentage of sunlight hitting the earth that is reflected back into space.
What is "albedo".
Heat is carried away from earth's surface when H2O evaporates, rises upward, and experiences this to form the liquid water droplets in clouds.
What is condensation?
The increased ability of the atmosphere to trap heat resulting from humans releasing CO2 into the atmosphere. In the last 150 years the burning of fossil fuels changes of land use has increased atmospheric CO2 levels from 288 ppm to 425 ppm and temperatures have already risen by about 1.5 degrees Celsius (nearly 3 degrees Farenheit)
What is "enhanced" greenhouse effect or anthropogenic (human caused) global warming?
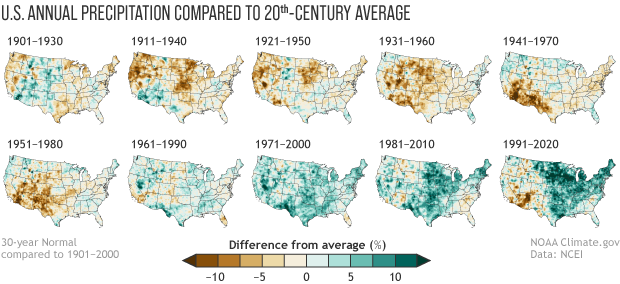 These maps which show increasing amounts of rain and river flooding in north east US and more dry weather and droughts in the southwest are examples of this.
These maps which show increasing amounts of rain and river flooding in north east US and more dry weather and droughts in the southwest are examples of this.
What are the regional impacts of climate change on rainfall?
Reaching this by 2050 is important to limit warming to around 2 degrees Celsius to avoid the most severe impacts of climate change.
What is "net-zero emissions"?
Energy is transported from the surface to higher up in the atmosphere when air warms, expands, and rises.
What is "convection"?
This acronym describes the potential energy associated with warm air that "wants" to rise upward. It can be though of as the available fuel for sever weather.
What is "CAPE"? (Convective available potential energy)
The main thing that is pushing the earth's energy budget out of balance is the burning of fossil fuels and other human activities increases the amount of GHG's in the atmosphere. This has resulted in trapping more long wave radiation before it escapes to space.
What is the primary climate "forcing" that is affecting the balance of energy entering and leaving the earth/atmosphere system? (Other forcings include "global dimming" which refers to the blocking of sunlight by aerosols, small particles suspended in the air. These have a net cooling effect)
While other factors may also contribute to the upward trend shown in the graph there is a broad consensus among experts that climate change has increased the devastation caused by wildfires.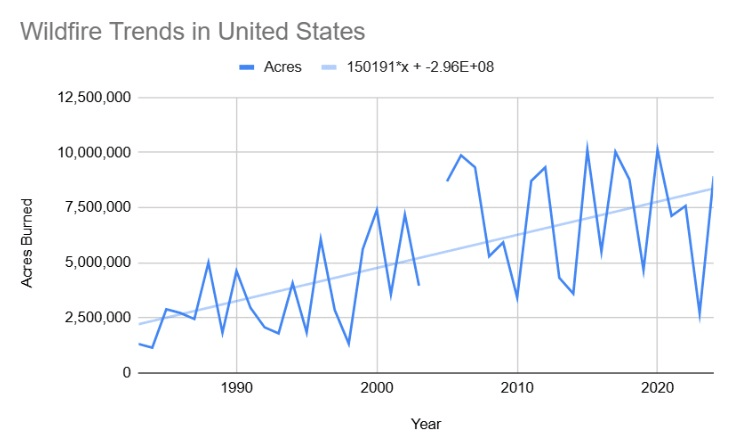
This controversial geoengineering proposal would purposefully pump aerosols into the atmosphere to block sunlight from reaching the surface.
What is "solar radiation management".
Name given to the steady rise of atmosphere and ocean temperatures which is happening because the earth is currently absorbing more energy each second than the amount radiated back into space (roughly 1.5 W/m^2)
What is "global warming"?
The air in the troposphere generally gets warmer the closer it is to the surface due to this type of heating resulting from collisions of slower moving molecules with faster molecules at the air-surface boundary.
What is conduction?
1. Less light reflects when sea ice melts. 2. More long wave radiation is trapped because warm air hold more water vapor. 3. More long wave radiation is trapped because methane is released from thawing permafrost. 4. Oceans can't absorb CO2 as effectively as the water warms.
What are four examples of positive feedback loops? (They are considered "positive" feedbacks because they amplify the warming that is already)
These graphs show a steady increase of the frequency, duration, and intensity of heat waves during recent decades.
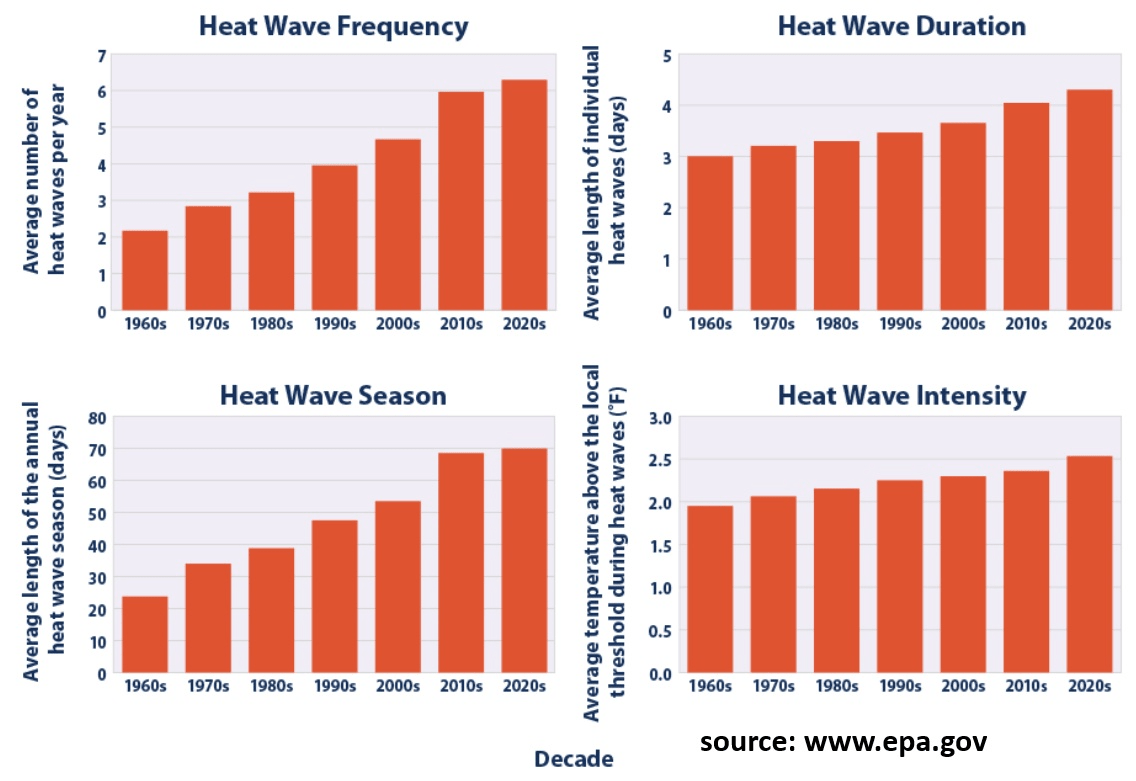
How has climate change affected the frequency, severity, and duration of heat waves in the U.S.?
1. Seawalls to protect coastal communities from flooding and storm surge. 2. Water management to ensure enough fresh water is available for agriculture and and consumption. 3. Drought resistant crops. 4. Investing in energy infrastructure to prepare for more renewables and more severe weather.
What are four examples of resilience strategies to deal with current and future impacts of climate change?
What is "the urban heat island effect"?
A large, long lived, low pressure region near Earth's Poles which circulates cold air in a counterclockwise pattern. Periodically it can split into multiple weaker cells which causes changes to the path of the jet stream.
What is a "polar vortex"?
Most of atmosphere consists of nitrogen (N2) and oxygen (O2) but these do not interact strongly with either the short wave radiation from the sun, nor the long wave heat radiation from the earth.
Hurricanes may become stronger and more frequent because warmer oceans provide more "fuel" to power these massive storms.
How does climate change affect hurricanes?
Examples of this type of strategy which seek to rapidly reduce net GHG emissions and avoid the worst impacts of climate change include: reforestation, increasing the power generation capacity of renewables like wind and solar, and carbon taxes which could provide a financial incentive to move away from fossil fuels and and fund green initiatives.
What are "mitigation strategies"?