The earth has 20 _________________ under Earth's surface that move toward, past, or against each other
tectonic plates
What are the 3 different processes that change the surface of Earth?
Weathering, Erosion, and Deposition
List 5 different types of landforms we have talked about in class this unit
answers may vary
mountains, volcanoes, islands, river deltas, canyons, plateaus, glaciers, valleys, sandunes, etc.
Identify the human technology in the photo
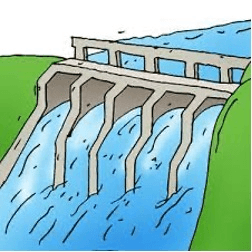
dam
What is a crack in Earth's surface called?
a fault
Because tectonic plates are slowly but constantly moving beneath the surface of earth
Define weathering, erosion, and deposition
weathering is the process that breaks down rock material
erosion is the process that moves broken rock material from place to place
deposition is the process when broken rock materials settles down in a new place
Identify the Landform in the photo below.
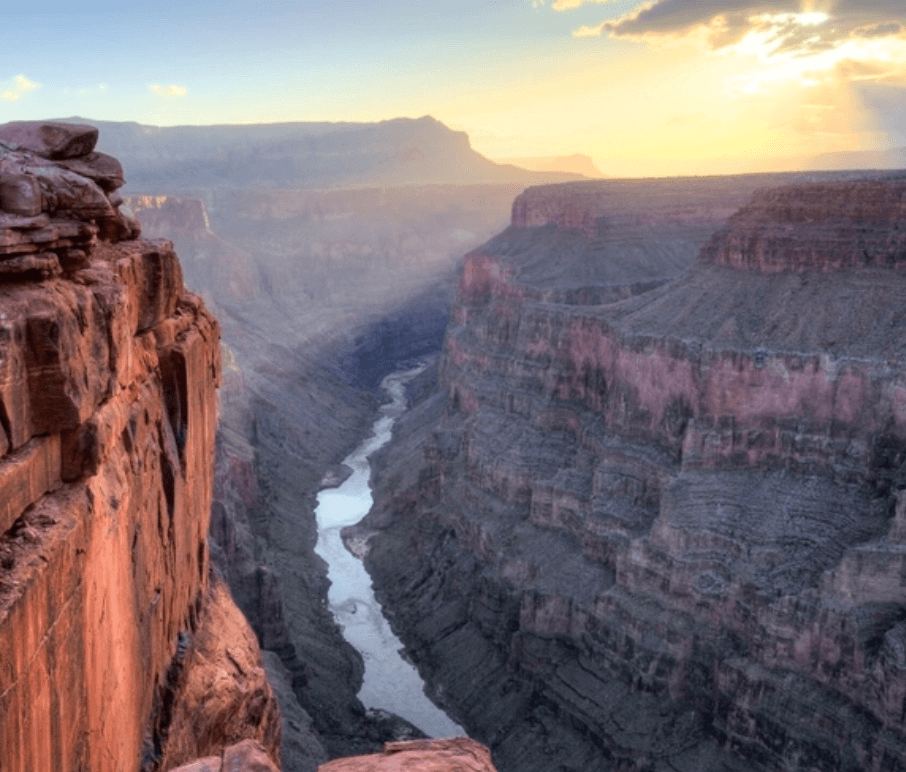

canyon
 Identify the human technology in the photo
Identify the human technology in the photo
jetty
Describe what processes are happening in the photo below
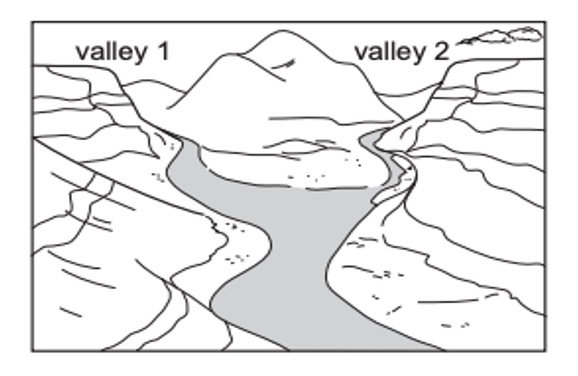
The 2 valleys are slowly being carved out from weathering and erosion by the moving river.
List each of the 4 types of plate boundaries and explain how they each move.
Convergent - moving towards each other
Divergent - moving away from each other
Transform - sliding past each other
Subduction - one sliding under the other
Describe how rivers cause weathering, erosion, and deposition over time
Rivers are powerful movements of water and over time can break down rocks and land at the bottom of the river. Rivers then move those rock pieces as they flow. Finally, rivers deposit the rock pieces or sediment at the opening or mouth of the river.
Identify the Landform in the photo below.
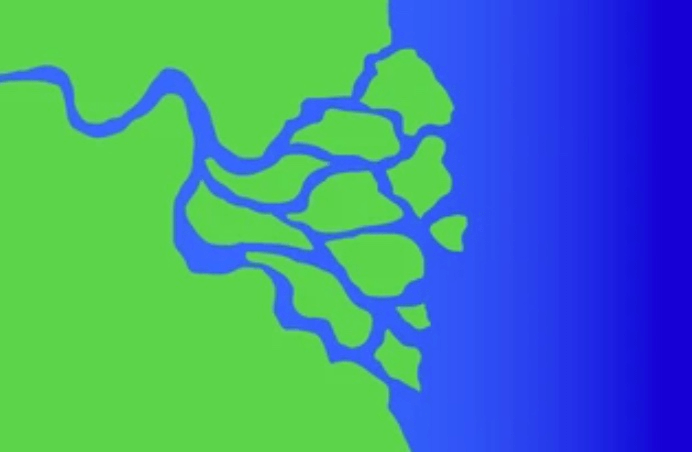
river delta
Identify the human technology in the photo
beach restoration
Describe what sediment is and list 1 example of it
Sediment is broken down pieces of rock or land.
Examples: Dirt, sand, clay, pebbles, gravel, etc.
Label each of the layers of Earth
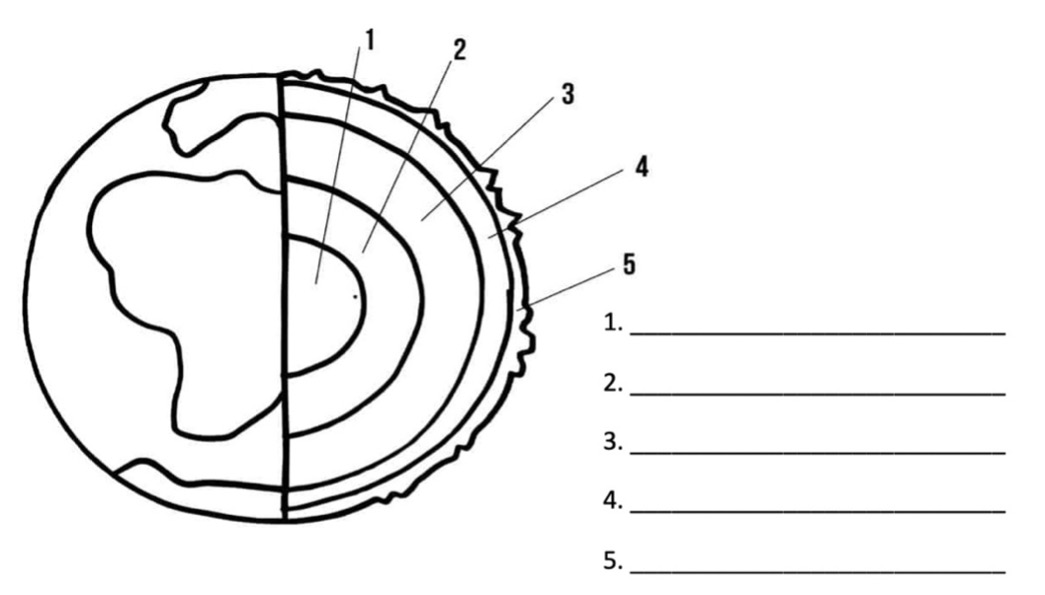
1 - Inner Core
2 - Outer Core
3 - Lower Mantle
4 - Upper Mantle
5 - Crust
This rock has been weathered down by frost wedging. Look at the picture and describe what frost wedging weathering is. 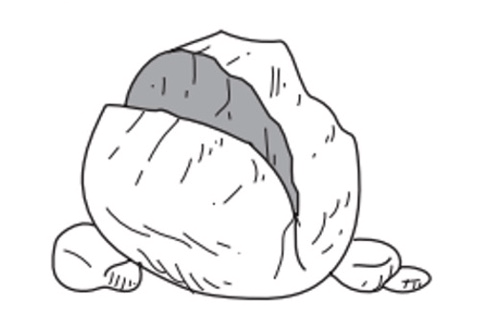
Frost wedging is when water seeps into rocks, then freezes and expands, and finally melts. This process happens over and over again until the rock begins to break apart.
Identify the Landform in the photo below.
sand dunes
List 3 different ways that human technology can prevent flooding
storm drains, dams, levees
Explain why Hurricane Katrina was so devastating to the city of New Orleans?
Hurricane Katrina was a bad hurricane but the reason it destroyed New Orleans was because the levees broke.
List each of the 4 types of plate boundaries and explain what their movements cause
Convergent - push up mountains and new land
Divergent - pulls apart to let magma escape from under Earth's surface, creating new land
Transform - slide past each other creating earthquakes; does NOT create new land
Subduction - one plate slides under the other pushing land upward further inland
What process is happening in the 2 pictures. Explain how you know. 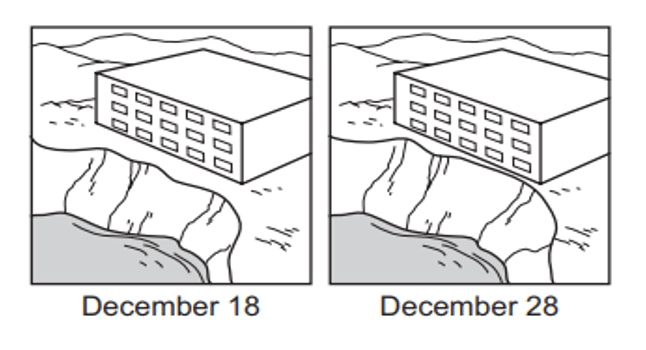
Weathering and Erosion by water.
Waves break down the land over time and the water washed rock pieces away.
Identify the Landform in the photo below.
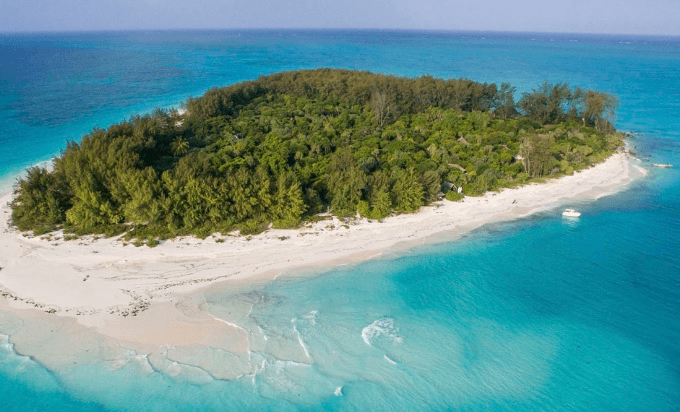

island
Describe what a seismograph does
A seismograph measures the movement of the earth and can specifically determine the magnitude of an earthquake
Explain how volcanos are both constructive and destructive
Constructive - when magma comes out of volcanoes it eventually hardens into new land, building up mountains or even islands
Destructive - volcanoes detroy the earth with their eruptions of hot lava and ash, dirt, and soot.