Soil forms from rock primarily through this process.
What is weathering?
A soil made of equal parts sand, silt, and clay.
The large pieces of Earth’s crust that move over time.
Tectonic plates
This plate boundary is MOST associated with the formation of new crust.
Divergent boundary
The envelope of gases surrounding Earth.
The atmosphere
The curving of wind and storms caused by Earth’s rotation.
Coriolis Effect
This soil particle feels gritty and drains water quickly.
Sand
This soil particle feels sticky when wet and holds the most water.
Clay
The semi-molten layer of Earth that tectonic plates float on.
The asthenosphere
These landforms can form when plates collide at a convergent boundary.
Mountains
The gas that makes up about 78% of Earth’s atmosphere.
Nitrogen
Circular wind patterns created by heating at the equator.
Weathering breaks rock down, while this process moves it.
Erosion
This type of weathering occurs when water freezes in cracks and expands.
Physical weathering
The movement of tectonic plates is driven by these currents in the mantle.
Convection currents
Plate tectonic movement helps explain the global distribution of these two features.
Earthquakes and volcanoes
Carbon dioxide, methane, and water vapor are examples of these heat-trapping gases.
Greenhouse gases
In the Northern Hemisphere, storms rotate in this direction.
Counterclockwise
This process binds sediment together using minerals dissolved in water.
Cementation
The smallest soil particle size is...
Clay
A boundary where two plates move toward each other.
A convergent boundary
A boundary where two plates slide past each other.
A transform boundary
The layer where meteors burn up due to friction.
The mesosphere
The part of Earth that receives the most direct sunlight year-round.
The equator
This organism produces acids and enzymes that help break down rock over time.
Lichen
On the soil texture triangle, sand percentages move in this direction.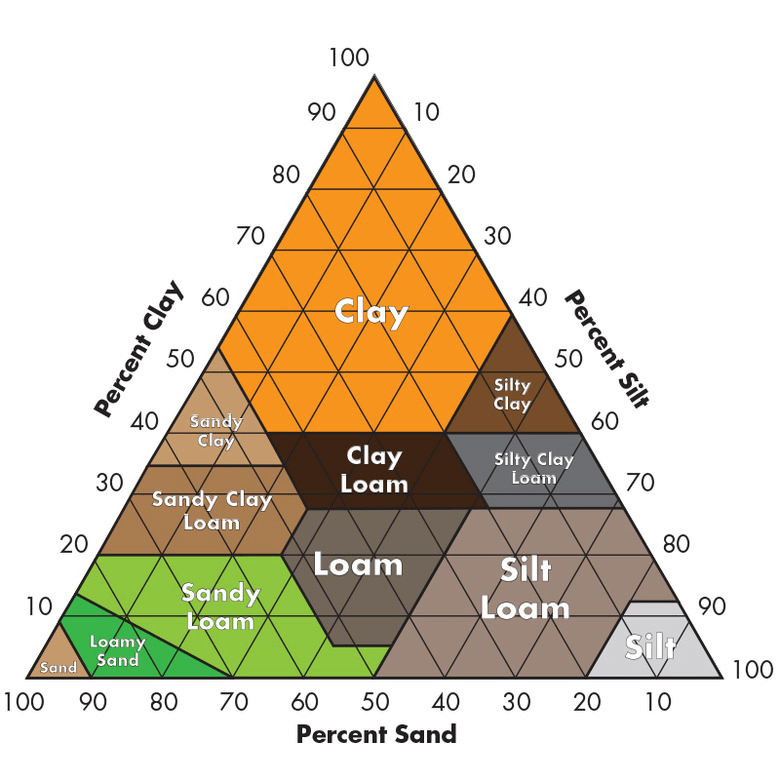
This process occurs when one tectonic plate is forced beneath another.
Subduction
Convection currents are caused by differences in __________.
Temperature
Air that is sinking is usually __________ and __________.
Cold and dense
Wind is the movement of air from areas of __________ pressure to __________ pressure.
High pressure to Low pressure