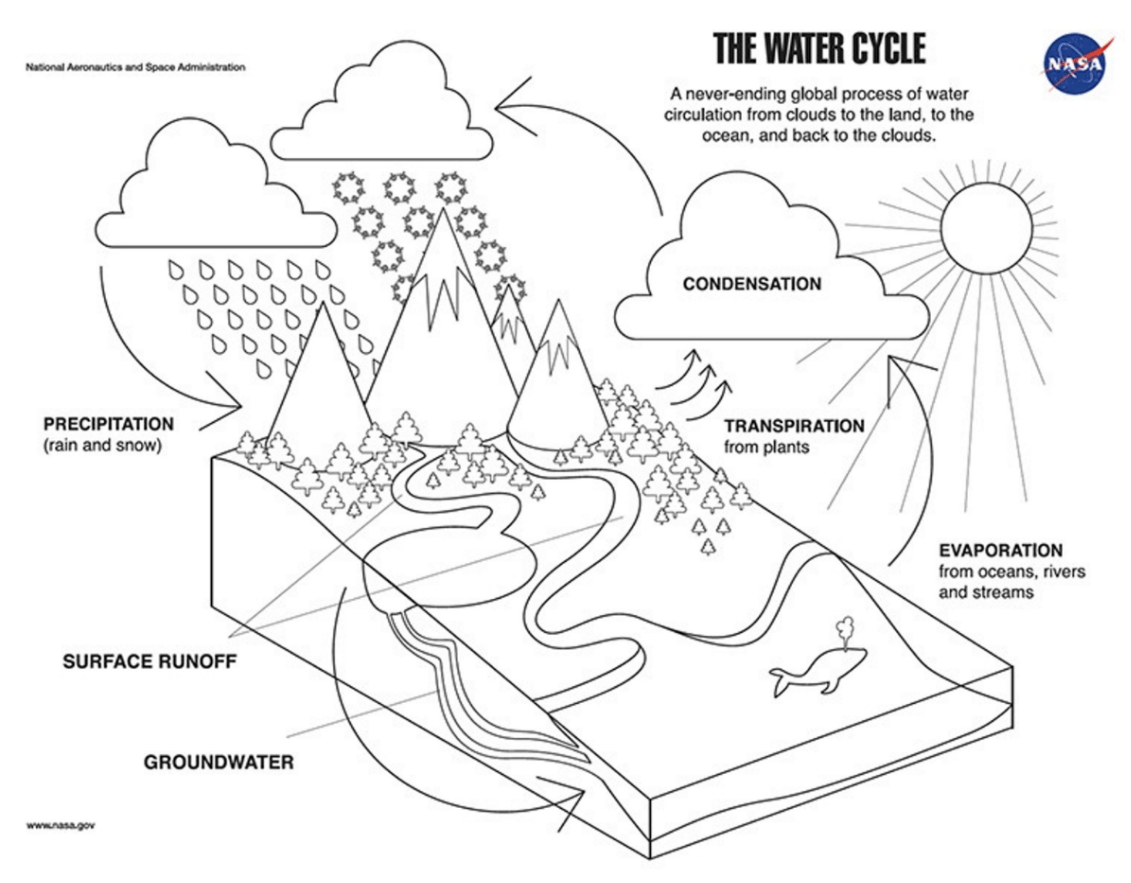
The driving force of the water cycle
What is
the sun
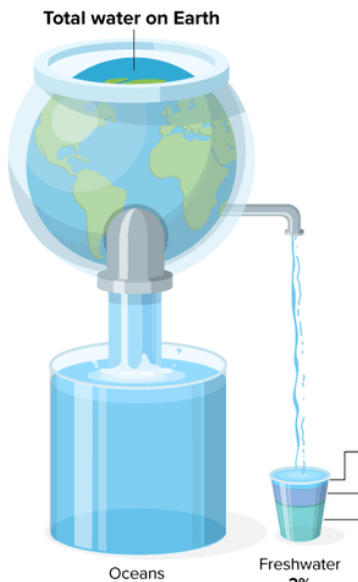
The percentage of water on Earth that is saltwater
What is
97%
 Type of ocean current formed by wind and the Earth's rotation
Type of ocean current formed by wind and the Earth's rotation
What are
surface currents
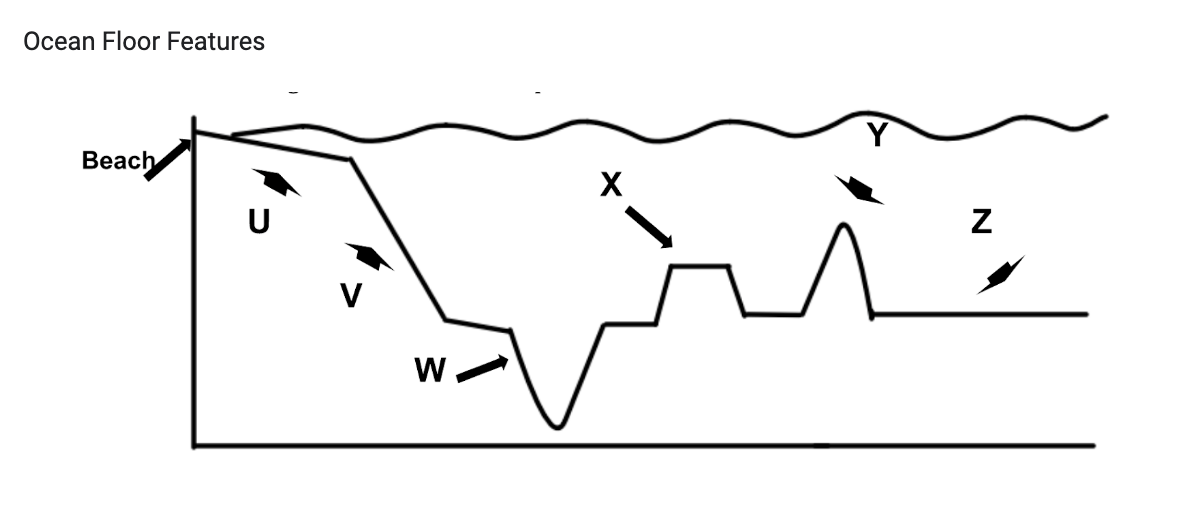
Give the letter and name of ocean floor feature:
The area of the ocean floor feature you are standing on when you step into the ocean from the shore line
What is
U: continental shelf

The water source that has the biggest impact on the water cycle and our weather
What is
the ocean
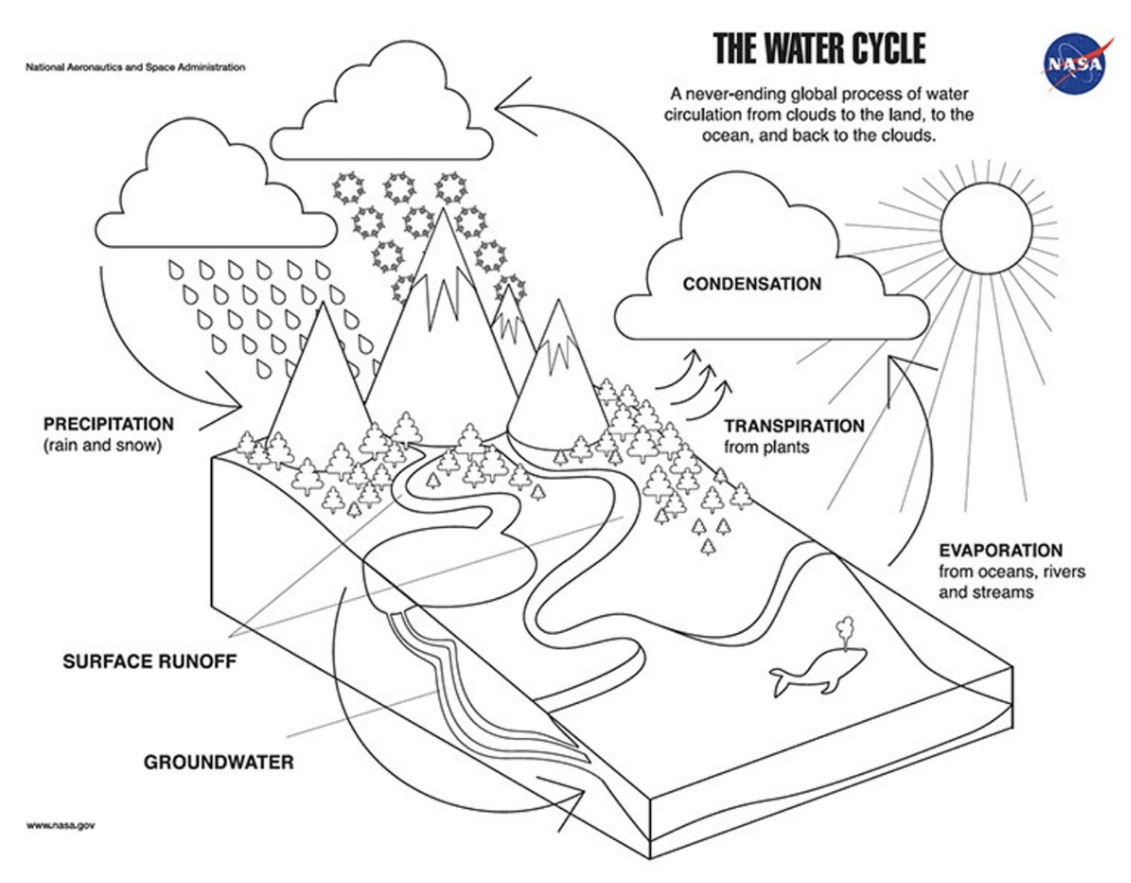
What is the process in the water cycle that changes liquid water from oceans, rivers, lakes, etc to a gas
What is
evaporation

The percentage of freshwater on Earth that is EASILY accessible
What is
less than 1%

Type of ocean current formed by differences in density (temperature & salinity)
What are
deep sea currents

Give the letter and name of ocean floor feature:
A flat-topped underwater mountain
What is
X: guyot
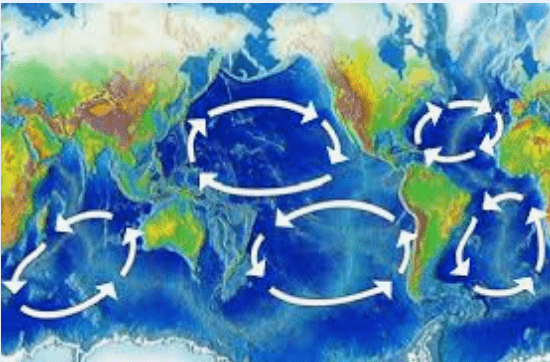
What type of current forms the Pacific Garbage Patch and how does it move?
What is
a gyre- it moves in a circular pattern

What is the process in the water cycle when water vapor cools in the atmosphere and turns back into a liquid, forming clouds
What is
condensation

The order of freshwater source amounts on Earth from MOST to LEAST
What is
glaciers & ice caps, groundwater, rivers/lakes/streams, atmosphere

Tides are caused by
What is
the gravitational pull between the moon and the Earth

Give the letter and name of ocean floor feature:
The flattest part of the ocean floor
What is
Z: abyssal plain

It is important to be good stewards of our freshwater because
What is
We only have access to less than 1% of freshwater and our rivers, lakes, and streams are becoming polluted or drying up due to climate change

The process in the water cycle when a cloud becomes full of liquid water and falls from the sky as rain or snow
What is
precipitation

We get most of our drinking water from
What is
rivers/lakes/streams

Most ocean waves are caused by
What is
the transfer of wind energy

Give letter and name of ocean floor feature:
The steep drop from the edge of the continent to the ocean floor
What is
V: continental slope
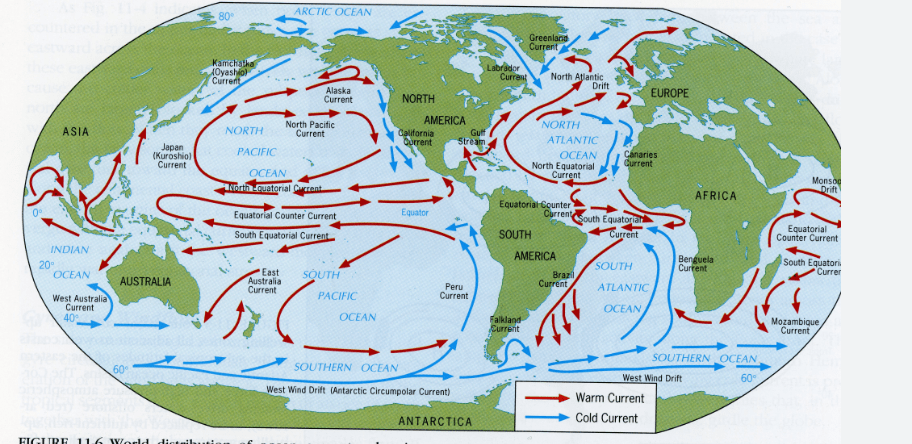
Cold, salty water sinks below warm, salty water because
What is
cold water is more dense (the molecules are more packed together) than warm water
or
differences in density

The process in the water cycle when water from plants and trees enter the atmosphere as water vapor
What is
transipiration

Percentage of Earth's surface that is covered in water
What is
70%
 Moves warm, salty water from the equator and cold, salty water from the poles, transferring heat all around the globe
Moves warm, salty water from the equator and cold, salty water from the poles, transferring heat all around the globe
What is
the Global Conveyor Belt

Deep narrow cuts into the ocean floor formed at subduction zones
What is
W: trench
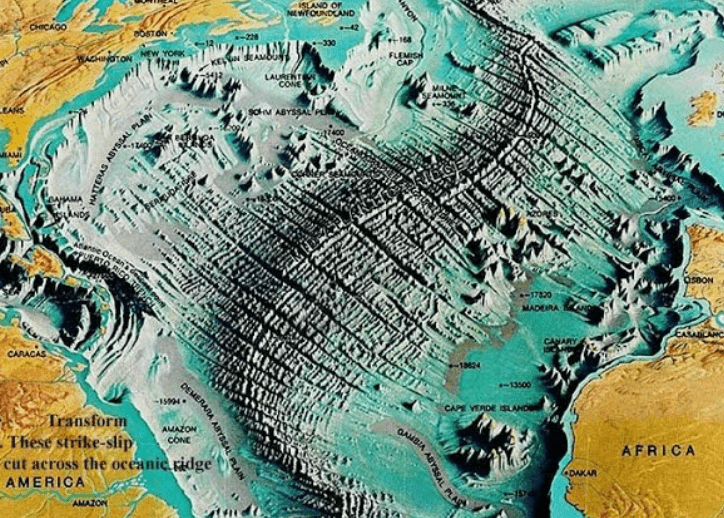 Underwater mountain chains and the boundary type in which they form
Underwater mountain chains and the boundary type in which they form
What is
mid-ocean ridges at divergent boundaries