What is economics?
study of the allocation of scarce resources
Define imports vs exports
Imports: goods produced abroad and sold domestically
Exports: goods produced domestically and sold abroad
What is the law of demand? What is the law of supply?
Law of demand: other things being equal, the quantity demanded of a good falls when the price of the good rises, the quantity demanded of a good rises when the price of the good falls
Law of supply: other things being equal, the quantity supplied of a good will fall when the price of the good rises, the supply demanded of a good rises when the price of a good falls
What is price gouging?
Price gouging: “laws to prevent high prices for essential goods in short supply in a crisis would raise social welfare”
What is elasticity?
T/F Elasticity of demand will always be positive
measure of how much buyers and seller respond to changes in market conditions, measure of the responsiveness of Qd or Qs to a change in one of its determinants
false
T/F a price floor is the legal maximum on the price at which a good can be sold
F (that's a price ceiling)
Create a PPF and describe efficiency, inefficiency, and infeasible.
Efficient: economy is getting all it can from the scarce resources available (points on PPF)
Inefficient levels of production: points inside the PPF
Not feasible: points outside the PPF
T/F the opportunity cost lies between the two price of trades
False: the price of trade lies between the two opportunity costs
Which of these scenarios would result in a shift along the demand curve?
a) number of buyers changes from 15 to 20 when the produce goes viral
b) everyone's income decreases because of a massive layoff
c) more people decide to use Spotify instead of CDs and Spotify lowers their monthly payment
d) the government decides to heavily tax a related good and that price increases by 35%
c) the only thing that causes a movement along a curve (supply or demand) is the price of the good itself
Create two graphic examples of shortage and surplus
surplus: the quantity supplied is greater than the quantity demanded
shortage: the quantity supplied is less than the quantity demanded
All else equal, the more slowly the value of purchasing additional units of a good decreases
a) the steeper is that good's demand curve
b) the flatter is that good's demand curve
b)
define binding and non-binding
Non-binding: price floor set below equilibrium
Binding: price floor set above equilibrium
T/F: All economic models are correct.
False - all economic models are incorrect because economics is formed upon assumptions
Define market, sellers, and buyers
Market: a group of buyers and seller of a particular good or service
The buyers: determine the demand for the product
The sellers: determine the supply of the product
Sketch what happens when:
a) increase in # of buyers
b) you purchase a normal good after another big promotion at work
demand shifts right
What is the process of applying the supply/demand model to a question?
Decide if the event shifts the supply or the demand curve (or both)
Decide in which direction the curve shifts
Compare the new equilibrium with the initial one
Describe very inelastic v very elastic
Very inelastic: quantity demanded responds little to price changes
Very elastic: quantity demanded responds strongly to price changes
A. Is not affected because below equilibrium
B. Binding price floor that results in a surplus of 8 donuts
Is this a positive or a normative sentence: "A decrease in the interest rate will lead to an increase in consumer spending."
positive - factual statement that can be tested and validated or refuted with data.
When is trade not beneficial?
Countries are the same level of opportunity cost (does not matter if one single country has the best absolute advantage)
Opportunity cost is the biggest evaluating factor
If the dollar-price of soda falls from US $3 per bottle to US $2 per bottle,
a) the price of beer implicitly rises
b) the price of beer does not change
c) the price of beer implicitly falls.
a) substitutes
Which of the following statements are true?
i. An equilibrium price in a market is the price that all consumers are willing and able to pay.
ii. An equilibrium price in a market is the price at which there is no excess supply or demand.
iii. An equilibrium price in a market is the price at which people are "happy" consuming the equilibrium quantity.
ii
Using these two formulas:
Calculate percentage changes: (end value - start value)/start value * 100
Midpoint method: (end value - start value) / midpoint *100
If P = $400, Qd = $10,600
If P = $600, Qd = $8,400
a) Use the midpoint method to calculate percentage change in price
b) Use the midpoint method to calculate percentage change in quantity
c) Calculate the price elasticity of demand
a) [(600-400)/500]*100 = 40%
b) [(8400 - 10600)/9500]*100 = -23.16%
c) 23.16/40 = 0.58
What are 4 price ceiling effects?
A shortage arises
Sellers must ration scarce goods among potential buyers
Long lines (inefficient, wasting buyers’ time)
Bias of sellers (inefficient and unfair)
There are ten economics principles. Give me four.
Principle 1: people face tradeoffs
Principle 2: the cost of something is what you give up to get it (opportunity cost)
Principle 3: rational people think at the margin
Principle 4: people respond to incentives
Principle 5: trade can make everyone better off
Principle 6: markets are usually a good way to organize economic activity
Principle 7: governments can sometimes improve market outcomes
Principle 8: a country’s standard of living depends on its ability to produce goods and services
Principle 9: prices rise when the government prints too much money
Principle 10: society faces a short run tradeoff between inflation and unemployment
What happens when a country specializes in the goods in which it has a comparative advantage? 3 outcomes...
Total production in all countries is higher
The world’s ‘economic pie’ is bigger
All countries can gain from trade
Explain these topics:
normal v inferior goods
substitutes v complementary goods
Normal good: other things being equal, as income increase, increase in demand, shifts demand curve to the right
Inferior good: other things being equal, as income increase, demand stays the same
Substitutes: two goods are substitutes if an increase in the price of one leads to an increase in the demand for the other
Complementary goods: an increase in the price of one leads to a decrease in the demand for other
According to this table:
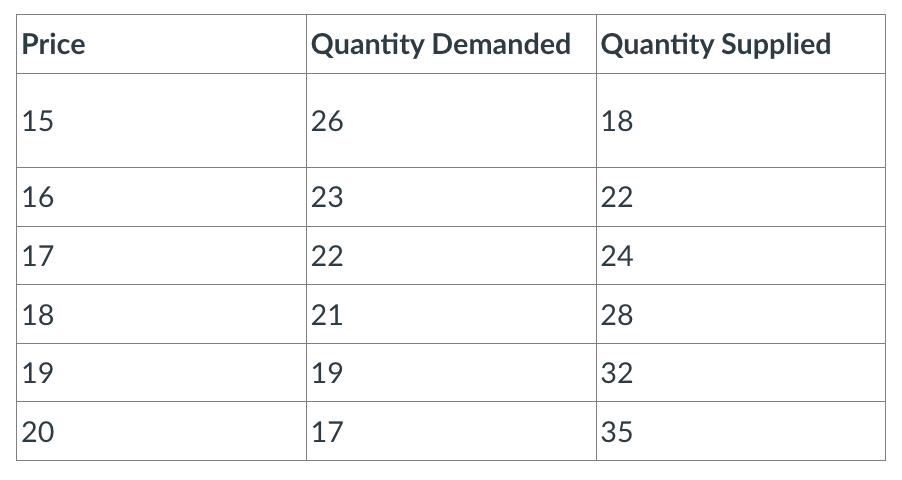
a) At a price of $18, unsatisfied sellers will put downward pressure on the price.
b) Consumers will react to a decrease in price from $19 to $17 by decreasing the quantity demanded by 3 units.
c) At a price of $18, there is a surplus of 7 units of the good.
d) None of the other options are true.
e) At a price of $19, there is a shortage of 13 units of the good.
c)
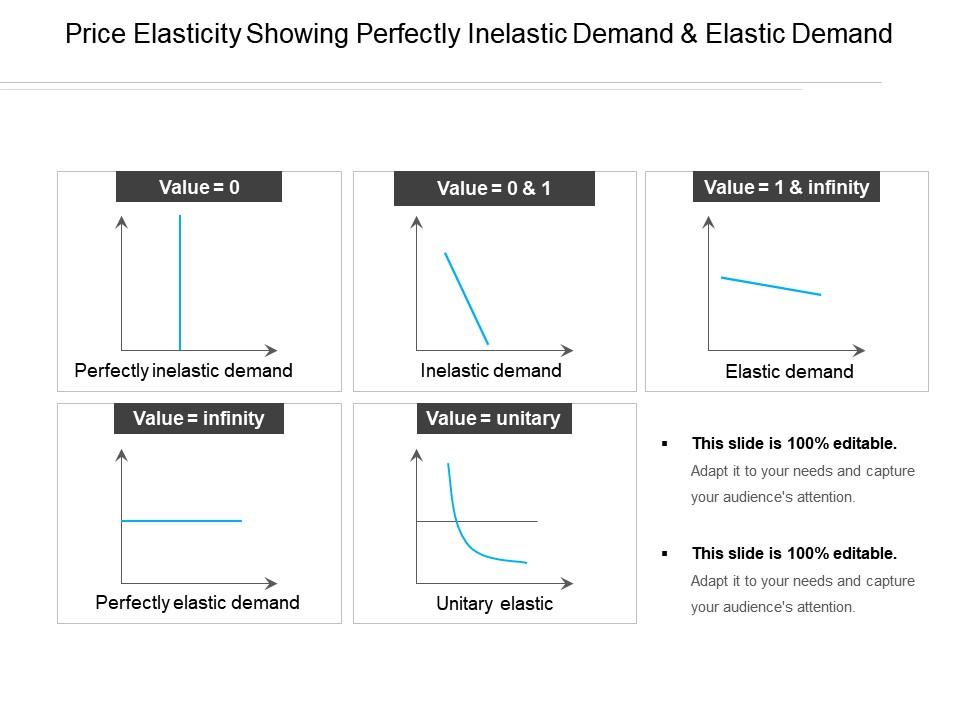
Draw these scenarios:
a) Demand is elastic
b) Demand is inelastic
c) Demand has unit elasticity
d) Demand is perfectly inelastic
e) Demand is perfectly elastic
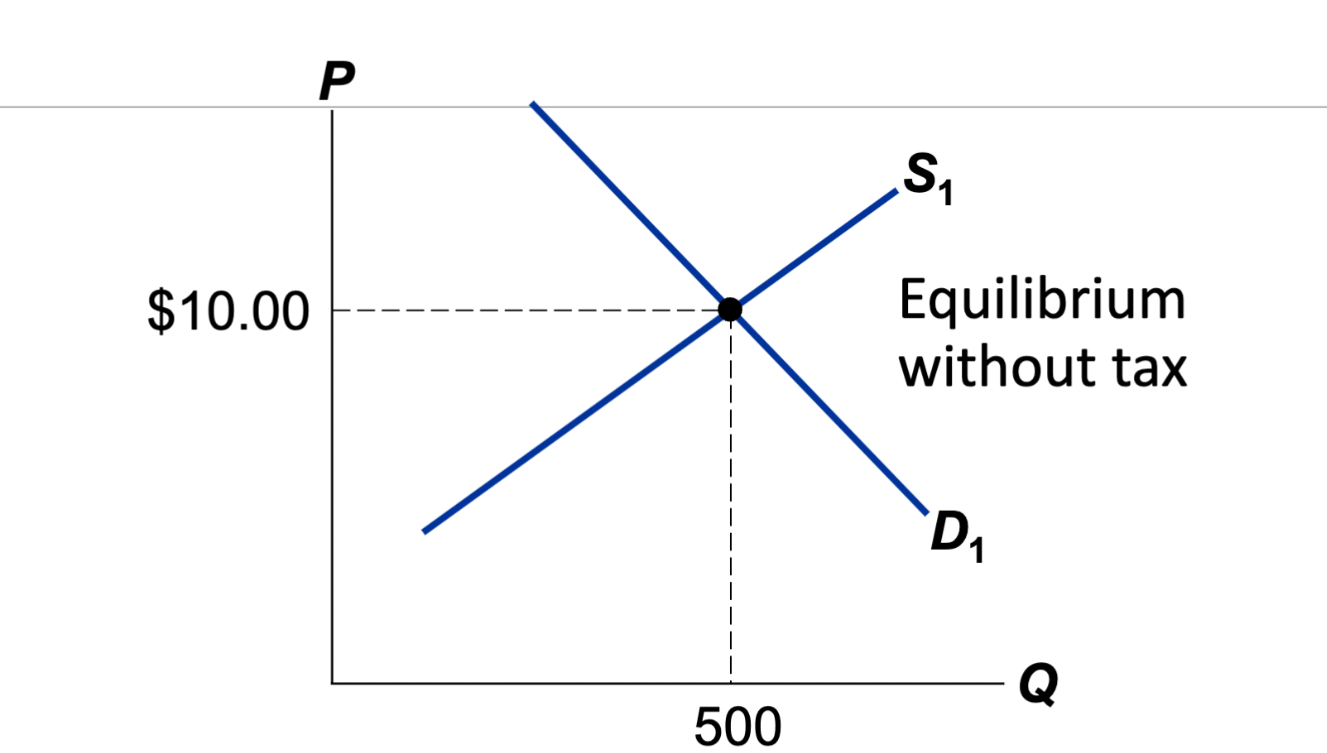
Impose a $1.50 tax on buyers. Draw the new market.