If Nike, an American corporation, produces sneakers in Thailand this would
A) count as part of US GDP since it is a US corporation.
B) count for both Thailand’s GDP and US GDP.
C) add to Thailand’s GDP but not US GDP.
D) add to neither US GDP nor Thailand’s GDP
C) Add to Thailand's GDP but not US GDP
The US Census Bureau conducts a survey on _____ households every month to calculate the unemployment rate.
60,000 households
Labor productivity equals
A) real GDP divided by the capital stock.
B) real GDP divided by the working-age population.
C) total wages divided by real GDP.
D) real GDP divided by aggregate labor hours.
D) real GDP divided by aggregate labor hours.
Which Federal Reserve Bank president is always on the Federal Open Market Committee?
A) New York.
B) Chicago.
C) St. Louis.
D) Boston.
A) New York
What is the equation for the money multiplier? What does it represent?
Money Multiplier = (𝐶ℎ𝑎𝑛𝑔𝑒 𝑖𝑛 𝑄𝑢𝑎𝑛𝑡𝑖𝑡𝑦 𝑜𝑓 𝑀𝑜𝑛𝑒𝑦) / (𝐶ℎ𝑎𝑛𝑔𝑒 𝑖𝑛 𝑀𝑜𝑛𝑒𝑡𝑎𝑟𝑦 𝐵𝑎𝑠𝑒)
The MM gives the multiple for the change in the quantity of money that results from a change in the monetary base. Measure of quantity of money in an economy within a certain period of time.
Suppose that you took out a $1000 loan in January and had to pay $75 in annual interest.
During the year, inflation was 6 percent. Which of the following statements is correct?
A) The nominal interest rate is 7.5 percent and the real interest rate is 1.5 percent.
B) The nominal interest rate is 7.5 percent and the real interest rate is 13.5 percent.
C) The real interest rate is 7.5 percent and the nominal interest rate is 1.5 percent.
D) The real interest rate is 6 percent and the nominal interest rate is 7.5 percent.
A) The nominal interest rate is 7.5 percent and the real interest rate is 1.5 percent.
Gross Private Domestic Investment, as defined in class, refers in part to the purchase of:
A) new capital goods.
B) stocks and bonds.
C) durable goods by consumers.
D) all of the above answers are correct.
A) New capital goods
What 3 groups of people are considered part of the working-age population?
Employed, Unemployed, Not in Labor Force
Suppose the economy is experiencing frictional unemployment of 1 percent of the labor force, structural unemployment of 3 percent of the labor force and cyclical unemployment of 4 percent of the labor force. What is the natural rate of unemployment?
A) 3 percent.
B) 5 percent.
C) 6 percent.
D) 7 percent.
E) none of the above.
E) None of the above.
Answer: 4 percent
((F + S)/labor force) x 100 = natural rate of unemployment
Define double coincidence of wants.
In order for an exchange of goods or services to occur in a barter, both sides must want the good or service that the other is offering. (Bartering is inefficient)
Real Money = ___ / ___
Real Money = Nominal Money / Price Level
The real interest rate
A) can never be negative.
B) is equal to the nominal interest rate plus the inflation rate.
C) is equal to the nominal interest rate minus the inflation rate.
D) is positively related to the inflation rate.
The real interest rate
C) is equal to the nominal interest rate minus the inflation rate.
The GDP deflator is
A) an index used to calculate inflation at the wholesale level.
B) the least used price index because it is so costly to calculate.
C) an index that measures real production.
D) a measure of the price level of goods and services included in GDP.
D) a measure of the price level of goods and services included in GDP.
Give the Unemployment Rate equation:
Unemployment Rate = (Number Unemployed/
Number Unemployed + Number Employed) 𝑥 100
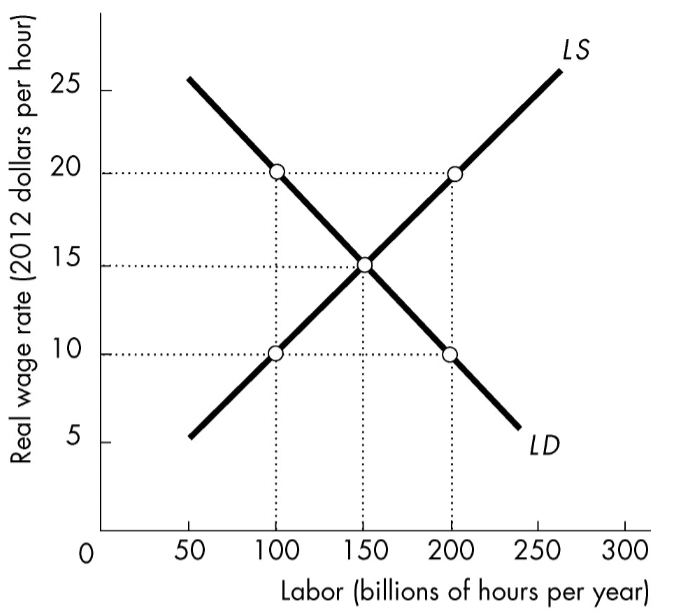
In the above figure, at a wage rate of $20 per hour
A) there is a shortage of labor.
B) there is a surplus of labor.
C) the labor supply curve will shift rightward.
D) the labor demand curve will shift rightward.
B) Surplus of labor
Quantity supplied is at 200, where as quantity demanded is at 100 when the the real wage rate is $20/hour. (Surplus of labor)
M2 consists of all of the following except:
A) Currency
B) Time deposits
C) Deposits with Money Market Mutual Funds
D) Savings Accounts
E) All of the above are part of M2
E) All of them are part of M2! (The primary money aggregate)
The goal of M2 is to capture the value of all liquid assets in the economy.
The quantity of real money that people choose to hold depends on which of the following?
I. The nominal interest rate.
II. The real interest rate.
III. The inflation rate.
A) I and II
B) II
C) I, II, and III
D) I and III
C) I, II, and III
If there is an increase in the real money supply, what changes will occur within other real variables?
ONLY a simple increase in the real money supply does not change other real variables.
Equation of Exchange:
𝑁𝑜𝑚𝑖𝑛𝑎𝑙 𝑀𝑜𝑛𝑒𝑦 𝑆𝑢𝑝𝑝𝑙𝑦 𝑥 𝑉𝑒𝑙𝑜𝑐𝑖𝑡𝑦 = ((𝑃𝑟𝑖𝑐𝑒 𝐿𝑒𝑣𝑒𝑙)/100) 𝑥 𝑅𝑒𝑎𝑙 𝐺𝐷𝑃
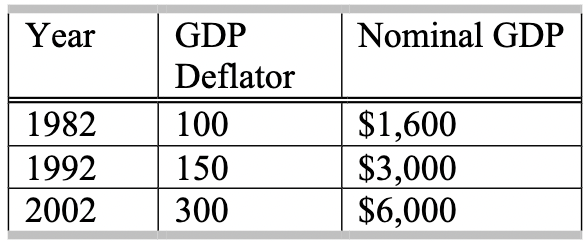
Using the information in the above table, which of the following is true concerning changes between 1982 and 1992?
A) Nominal and real GDP both increased.
B) Nominal GDP increased, but real GDP was unchanged.
C) Nominal GDP increased, but real GDP decreased.
D) None of the above statements are true.
A) Nominal and real GDP both increased.
Real GDP = (Nominal GDP/GDP Deflator) x 100
Therefore, both nominal and real gdp increased between these two years.
A recession causes a decrease in the demand for housing, resulting in substantial layoffs in
the construction industry. The people laid off are considered:
A) frictionally unemployed
B) structurally unemployed
C) seasonally unemployed
D) cyclically unemployed
D) cyclically unemployed
If the price level falls by 5 percent and workers' nominal wage rates remain constant, firms'
A) quantity of labor demanded will decrease.
B) quantity of labor demanded will increase.
C) supply of jobs will increase.
D) None of the above answers are correct.
A) quantity of labor demanded will decrease.
Price level refers to the price of goods and real wage rate = nominal wage rate - inflation rate. Given these facts, if nominal wages remain constant, so will the real wage rate. And if prices for goods & services fall, firms will want to save money and hire less (demand for labor falls).
If the Federal Reserve buys U.S. Treasury bonds through an open market operation,
A) the quantity of money will increase.
B) the nominal interest rate will rise.
C) bank reserves will decrease.
D) the real interest rate will rise.
A) the quantity of money will increase
The FED is conducting an open market purchase of a financial asset in order to increase the quantity of market in the economy.
Real money demand is ________ related to the nominal interest rate.
A) positively
B) negatively
C) not
D) None of the above answers is correct because the relationship between the demand for money
and the nominal interest rate changes with the inflation rate.
Real money demand is ________ related to the nominal interest rate.
B) negatively
What happens to real money supply and real money demand in the long-run?
The price level will tend to adjust to offset the increases in the nominal money supply, making real money supply equal to real money demand
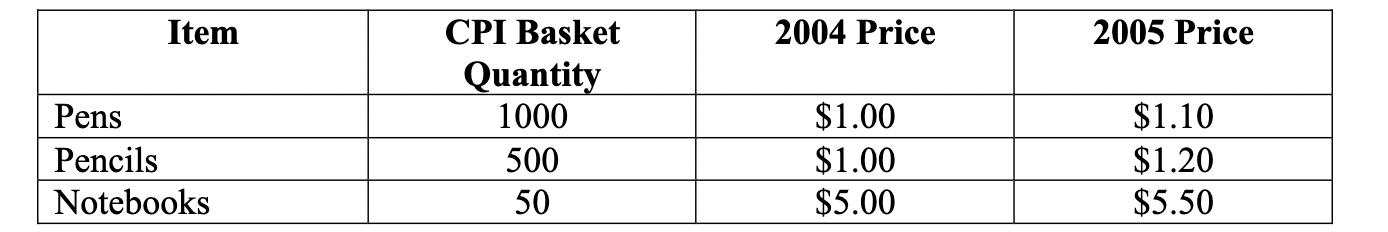
The information in the table above gives the CPI basket and prices used to construct the CPI for a small nation. Assuming that 2004 is the base year, what is the value of the CPI for 2005?
A) 112.9
B) 88.6
C) 225
D) 40
A) 112.9
Over longer periods of time, when the labor market has had time to adjust to equilibrium, the amount of employment will adjust toward ___ ______, and the unemployment rate will adjust toward the _____ ____ __ _______.
Full Employment & Natural Rate of Unemployment
When the economy moves into and out of recessions and expansions, the unemployment rate fluctuates away from the
A) level of potential real GDP.
B) structural unemployment rate.
C) cyclical unemployment.
D) frictional unemployment rate.
E) none of the above.
E) None of the above.
What happens to the funds that were paid to the FED during an open market sale?
The FED deletes them (trying to decrease money in economy).
If an economy has a Velocity of 3, then
A) the nominal money supply is 3 times real GDP.
B) in a year the average dollar is exchanged 3 times to purchase goods and services in GDP.
C) nominal GDP is 1/3 the size of the quantity of money.
D) the quantity of money is $3 for every dollar of GDP.
If an economy has a Velocity of 3, then
B) in a year the average dollar is exchanged 3 times to purchase goods and services in GDP.
How can we control the inflation rate in the long run? Why does this work?
We can control the inflation rate in the long run by regulating the long-run growth rate of the nominal money supply. This works because:
Inflation = (Growth in Nominal Money Supply) - (Growth in Potential rGDP)