The Septal leads are part of the 6 Precordial leads. What are these 2 leads called and where are they placed on the chest?
What is V1 and V2.
V1 right sternal border, 4th ICS.
V2 left sternal border, 4th ICS.
You do a 12-lead ECG of a 45 year old female presenting with epigastric discomfort, lethargy and diaphoresis. The ECG shows ST elevation in precordial leads V1 through V6. What type of MI is she having? Which coronary artery is affected? What are a few complications?
Anterolateral MI.
Left anterior Descending, circumflex
Cardiogenic shock
Vfib, Vtach pulseless
Fast Narrow heart rhythm >150
what medication is appropriate?
Adenosine 6mg ,12mg and cardiovert
Your patient is having an inferior MI. VSS You are getting ready to transport when you notice she is in 3rd degree AV block. What do I do?
Notify MD. Get help apply pads to patient.
Assess patient's vs, ABC's, Neuro status.
if unstable transcutaneously pace.
What medication do we initially give for V-Fib and what is the dosage and frequency?
Epinephrine 1mg 1:10,000
Every 3-5 minutes
Why do we do 12-lead ECG's?
Multiple Reasons: observe electrical conduction through the heart, look for ischemia,injury, infarction, electrolyte imbalance, pericarditis,and because we get them on everyone with heart
You do a 12-lead ECG of a 60 year old female presenting with epigastric discomfort, lethargy and diaphoresis. The ECG shows ST elevation in I, AVL, V5, V6
What type of MI is she having? What coronary artery is affected? What are some complications?
Lateral MI Circumflex artery
Cardiogenic shock, LVHF, pulseless vtach, vfib
The heart rate on the monitor is 32 there are more P waves than QRS complexes. What rhythm is this?
Third degree heart block
Your patient is having an anterolateral MI. The patient begins to have runs of 12 beat VT followed by multifocal PVC's. What should you do?
Notify the MD. Get help.
Make sure pads are on correctly prepare to defibrillate if necessary.
Assess ABC's, neuro status
Prepare and amiodarone infusion
What anti arrhythmic is given for Ventricular fibrillation?
Amiodarone 300mg IVP
The 12 lead ECG shows ST-segment elevation what is the best treatment for this patient?
Reperfusion therapy coronary angioplasty with stent placement
You do a 12-lead ECG of a 60 year old female presenting with epigastric discomfort, lethargy and diaphoresis. The ECG shows ST elevation in V1, V2.
What type of MI is she having?
Which coronary artery is affected? What are some of the complications.
Septal MI
LAD
Cardiogenic shock, LVHF, Vtach pulseless, Vfib
The PR interval is greater than .20. What rhythm am I?
First degree A-V block
You have started your patient on nitro sublingual for chest pain 8/10. After the first dose the patient becomes hypotensive and diaphoretic. What should you do?
Notify the MD.
Assess ABC's make sure IV access is working.
Repeat ECG anticipate ivf order.
Do not give more nitro.
I have a fast wide complex tachycardia. My heart rate is 180, BP 100/60. What rhythm and what medication will I get?
Ventricular Tachycardia
Amiodarone 150mg over 10 mins
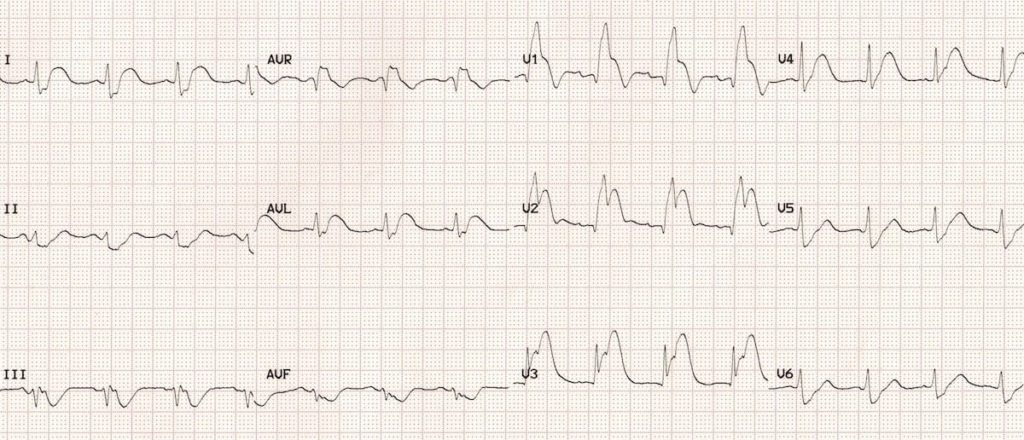
Anterior MI
You do a 12-lead ECG of a 65 year old male presenting with jaw pain radiation to the left shoulder and arm. On assessment you note an elevated JVD, normal lung sounds, and hypotension.The ECG shows ST elevation in II, III, AVF. What type of MI is he having? Which coronary artery is affected? What are some of the complications.
What other ECG may you consider?
Inferior MI right ventricle
Right coronary artery
complications hypotension, atrial arrythmias, preload dependent.
Right sided ECG look at RV3, RV4,RV5,RV6
PR interval remains constant but has a non-conducted P wave. There is no lengthening but does have dropped beats
Second degree type II
Your patient is having a anterolateral MI. Vitals are stable when leaving the ED. On your way to the elevator you notice your patient becomes unresponsive and the monitor shows Vfib. What do you do?
Check for unresponsiveness, check pads, follow ACLS protocol and shock the patient. Bag the patient and begin CPR.
What are the H's and T's
Hypovolemia, Hypoxia, Hydrogen Ion, Hypo/Hyper kalemia, Hypothermia
Tension pneuothorax, Tamponade, toxins, Thrombosis pulmonary/coronary
The five step procedure for ECG analysis.
What is rate, rhythm, P waves, PR intervals, and QRS complex?
You do a 12-lead ECG of a 45 year old male presenting with severe sternal chest pressure for 3 hours. The ECG shows ST depression and tall T waves in V1, V2.
What type of MI is he having? What type of ECG might you want to do?
Which coronary artery is affected? What are some of the complications.
Posterior MI
Posterior ECG
Coronary artery circumflex or RCA
Complications Cardiogenic shock LVHF, Vtach, Vfib
A uniformed rhythm wide QRS >.12. May or may not have a pulse.
Ventricular Fibrillation
Your patient has been diagnosed with hyperkalemia. The orders call for insulin, D50, and calcium.
What is given first and why?
What is calcium. Helps the heart to beat normally by binding to the troponin complex to make the heart cell squeeze together.
How many times does your heart beat a day?
50,000 - 130,000