Triaxial diagram
Leads I, II, and III joined at the middle
A normal PR Interval
0.12 - 0.20 seconds

Asystole
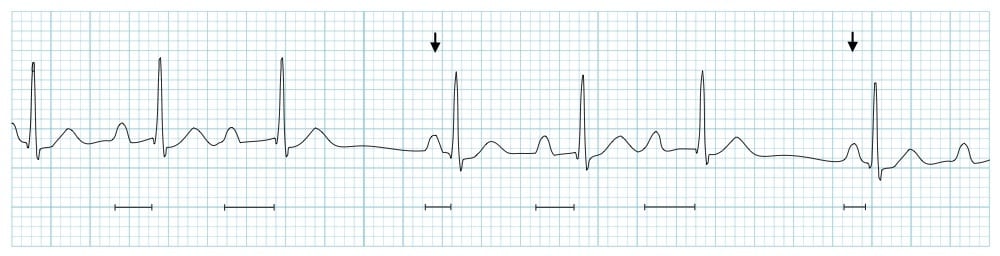
Wenckebach
Flight or Fight
Sympathetic nervous system
The six leads placed on the patients chest
Precordial Leads
What you count to determine Heart Rate
R to R Interval

Ventricular Tachycardia

SR with 1st AV block
S2, the second heart sound, reflects the closure of these
Aortic & pulmonic valve
V1 is placed here
Fourth Intercostal space, right sternal boarder
Represents ventricular repolarization on the ECG
T wave

Trigeminy

2:1 Heart Block
Returns deoxygenated blood to the right atrium from the lower chest and abdomen
Inferior Vena Cava
Used for accessing rhythms with wide QRS complexes, and can pinpoint abnormalities in ventricular conduction
MCL
The flat line between the T wave of one beat and the P wave of the next beat
Basline / isoelectric line

Agonal

3rd Degree Heart Block
The outermost layer of the heart
Epicardium
Einthoven's Law
Lead I + Lead III + Lead II
In this period, a strong stimulus will result in depolarization
Relative refractory period

Ventricular Fibrillation

2nd degree type II, Mobitz II
This separates the right and left ventricle
Interventricular septum