This term describes the natural, gradual, and predictable sequence of changes that occur in an ecosystem over time.
Ecological succession
This term describes when an ecosystem is forming for the first time.
Primary succession
What do the arrows in a food web tell you?
The direction that the energy is flowing.
What is biodiversity?
The variety of organisms living in an ecosystem
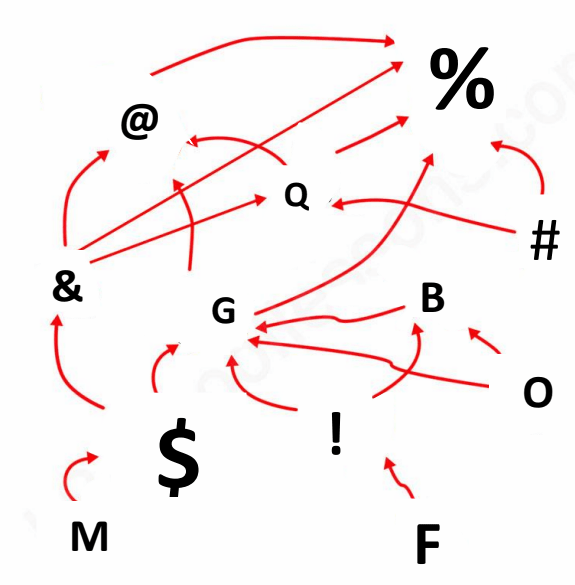 Name the producers in this food web
Name the producers in this food web
M, F, O and #
What must remain intact for secondary succession to occur? Why?
The soil, because the plants need it in order to start growing again right away.
Explain what secondary succession is.
When an ecosystem comes back after being destroyed (the soil must remain intact).
Whenever an organisms eats another organism, how much of the energy is passed on?
10%
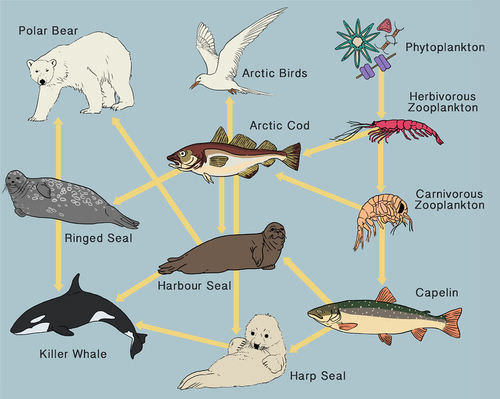
Phytoplankton
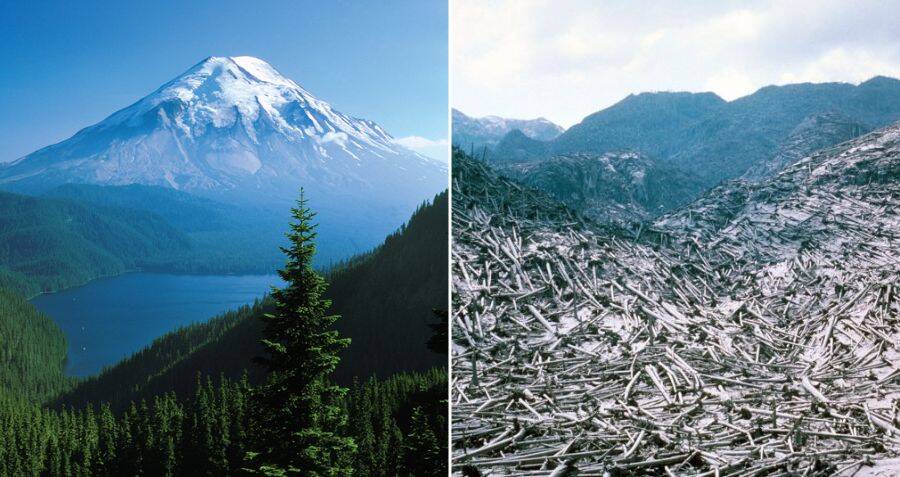


The photos above show Mount St. Helens before and after its explosive eruption, then they show the same patch of forest throughout different years following the eruption. Explain what this is an example of, and how/why it is happening. (Hint the grey stuff is ash NOT lava/rocks).
This is an example of secondary succession. The forest ecosystem was destroyed by the eruption, but the soil remained intact, so the ecosystem was able to grow back. It is growing back quickly because the soil was already deep/nutrient-rich.
Name 2 ways that primary succession can start AND 2 ways that secondary succession can start.
Primary succession: Glaciers scraping off ecosystems/dirt & new rock from lava from volcanic eruptions.
secondary succession: (possible answers include...) Forest fires, tornadoes, hurricanes, volcanic eruptions, etc (anything that wipes out the ecosystem but leaves the soil intact.
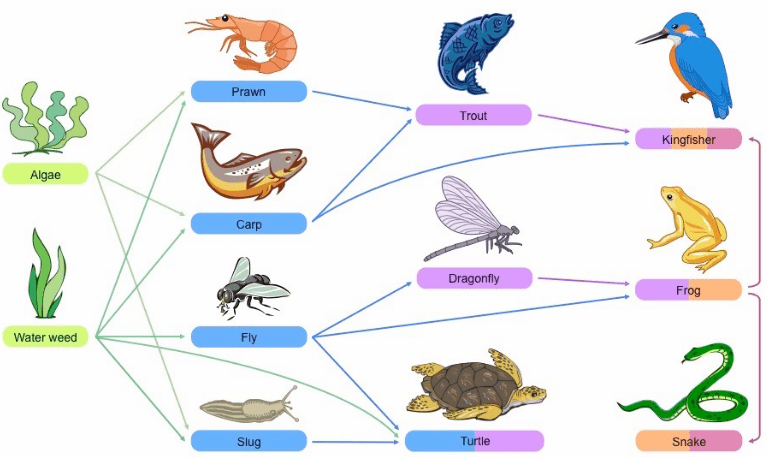
Name 1 producer, 2 primary consumers, and 2 tertiary consumers, and 2 quaternary consumer
Multiple right answers
What is sustainability? And explain what decides the sustainability of an ecosystem?
The ability of an ecosystem to survive/keep going. The more biodiversity an ecosystem has the more sustainable it is.
Organize the cards in correct sequence:
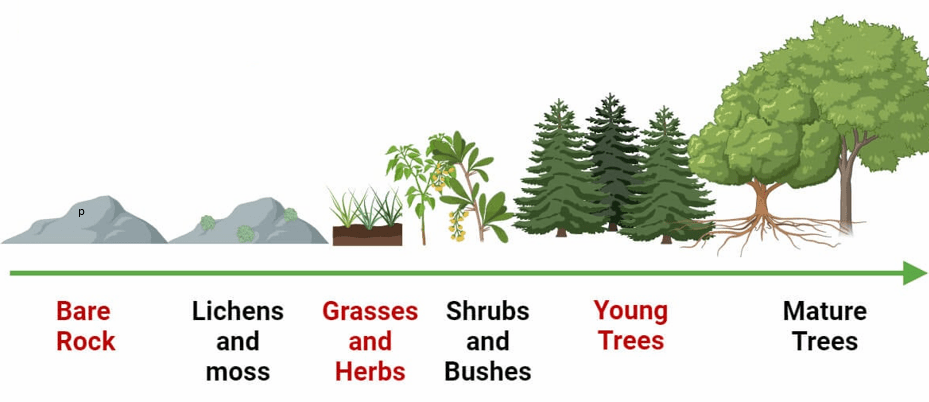
Organize the cards in the correct sequence:

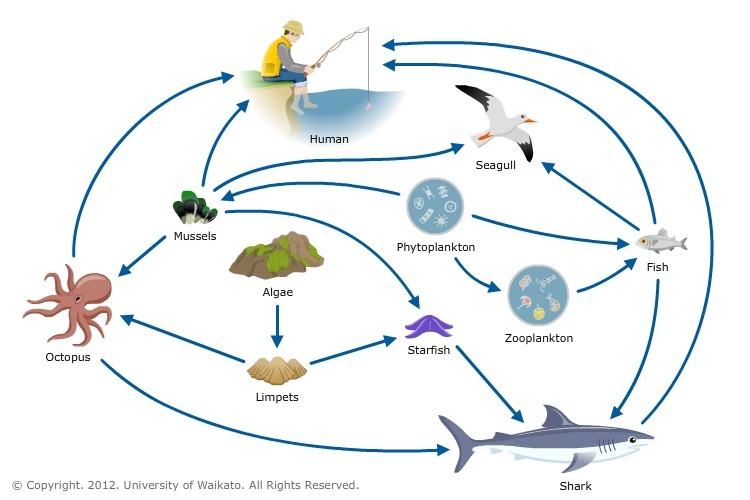
Who is/are the producer(s) in this ecosystem?
Phytoplankton & Algae
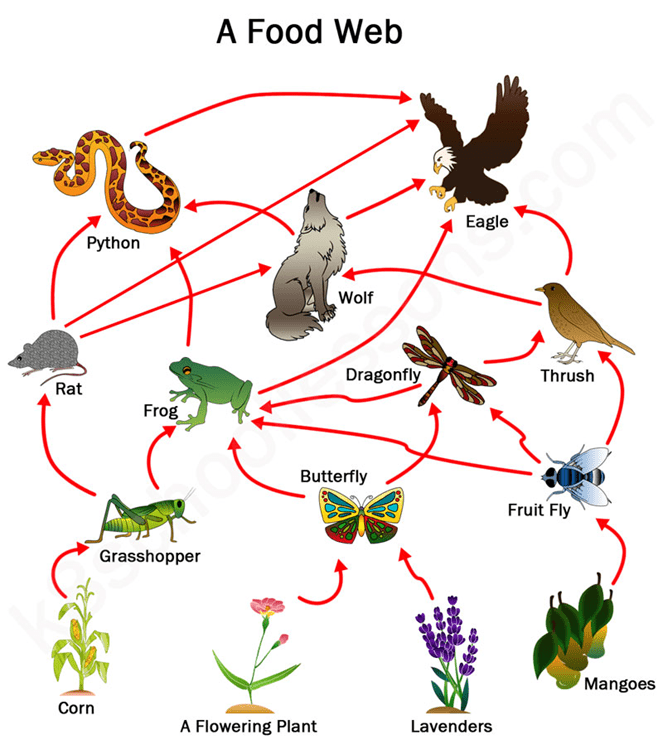
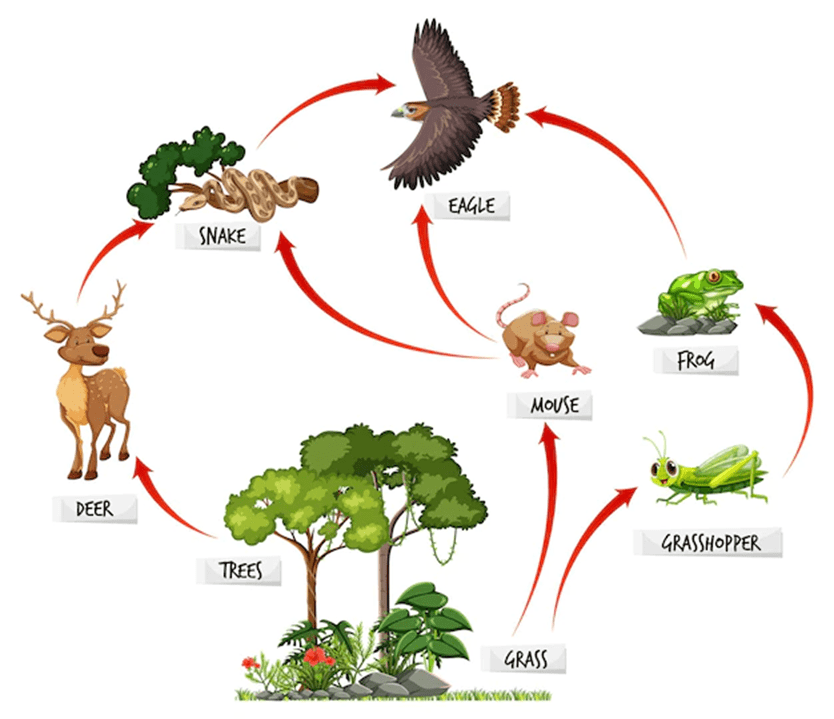
Which of these food webs is more sustainable AND why?
The 1st one because it has more producers and more organisms overall.
During primary succession, are large plant's (such as oak trees) seeds waiting for soil to get deep enough before they try to grow? Explain why/why not?
No, they are constantly trying to grow in the soil all the time, but if the soil is not deep enough the tree will die before it gets fully grow due to lack of nutrients/soil depth.
Explain in detail who the plants are waiting on during primary succession, AND who the animals are waiting on.
Plants are waiting on the mosses/lichens to create enough soil for them to grow their roots deep enough into to survive. Animals are waiting on there to be enough plants for food and shelter.
If a carrot produces 1,500 Kilocalories of energy through photosynthesis, then a rabbit eats that carrot, then a fox eats that rabbit, then a coyote eats that fox, how much of the original 1,500 kilocalories does the coyote receive?
1.5 kilocalories.
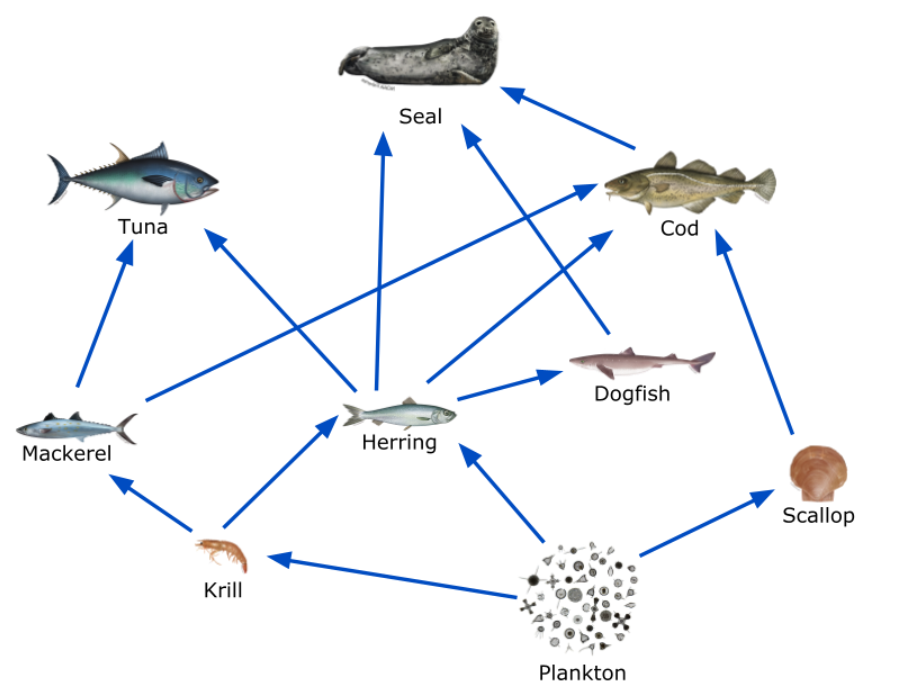
Which secondary or higher level consumer would have the greatest impact if it were overfished to near extinction? AND WHY?
Herring, because it is the prey of 4 different organisms that depend on it for energy.