All of the non-living things in an ecosystem.
What are abiotic factors?
When both organisms benefit from the other.
What is mutualism?
Organisms that use the sun's energy to make their food.
What are producers?

The approximate largest population that species 1 reached.
What is 175,000 organisms?
Organisms that eat only plants.
What are herbivores?
A group of organisms of the same species.
What is a population?
The relationship where one animal hunts and eats another animal of a different species.
What is predator/prey?
A series of events in which one organism eats another and obtains energy.
What is a food chain?
 The year that species 2 reached their carrying capacity.
The year that species 2 reached their carrying capacity.
What is year 7?
Carnivores that feed on dead organisms.
What are scavengers?
The largest number of individuals an area can support.
What is carrying capacity?
When one organism benefits while the other is being harmed.
What is parasitism?
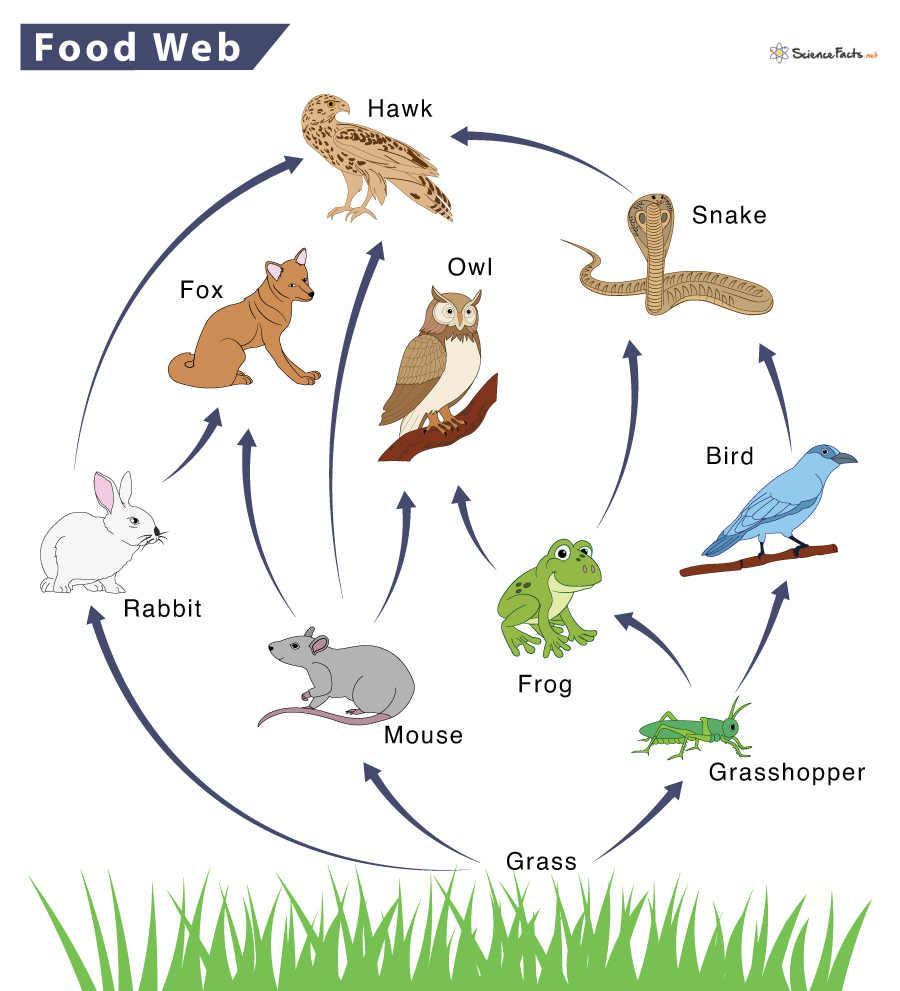
The organisms that eat a mouse.
What are foxes, owls, and hawks?

The symbiotic relationship most likely represented by this graph.
What is mutualism?
Organisms that break down wastes and dead organisms.
What are decomposers?
The two major events that will cause a population to decrease.
What is death and emigration?
When one organism benefits and the other is neither benefited or harmed.
What is commensalism?

The trophic level of snails in this energy pyramid.
What is primary consumer?

The carrying capacity of both species in the graph.
What is 40,000 organisms?
Multiple populations of organisms of different species.
What are communities?
The number of individuals in an area of a specific size.
What is population density?
A close and long-term biological interaction between two different species.
What is symbiosis?
The trophic level that eats secondary consumers.
What are tertiary consumers?

The symbiotic relationship most likely represented by this graph.
What is parasitism?
Abiotic and biotic parts of an ecosystem that cause a population to stop growing or decrease.
What are limiting factors?