This is the ultimate source of energy in any ecosystem
What is the sun?
This type of dispersion pattern is commonly see in plant species around the world
What is random dispersion?
This type of succession begins with only bare rock
What is primary succession?
This nutrient cycle does not utilize an atmospheric reservoir
What is the phosphorus cycle?
This term means rain that is has a lower pH than normal
What is acid rain (precipitation)?
This rule states that 90% of energy is lost each time energy from up a food chain/web
What is the 10% rule?
This term means the maximum amount of a population one ecosystem can tolerate
What is carrying capacity?
This is the name of species who contribute to the beginning of a new ecosystem (ex. lichen and moss)
What are pioneer species?
This energy cycle is dependent on bacteria "fixing" gaseous nitrogen so that plants can take ammonia into their roots
What is the nitrogen cycle?
This term means a resource that takes hundreds to thousands of years to replenish
What is a nonrenewable resource?
This organism can be described as a heterotrophic, secondary and tertiary consumer
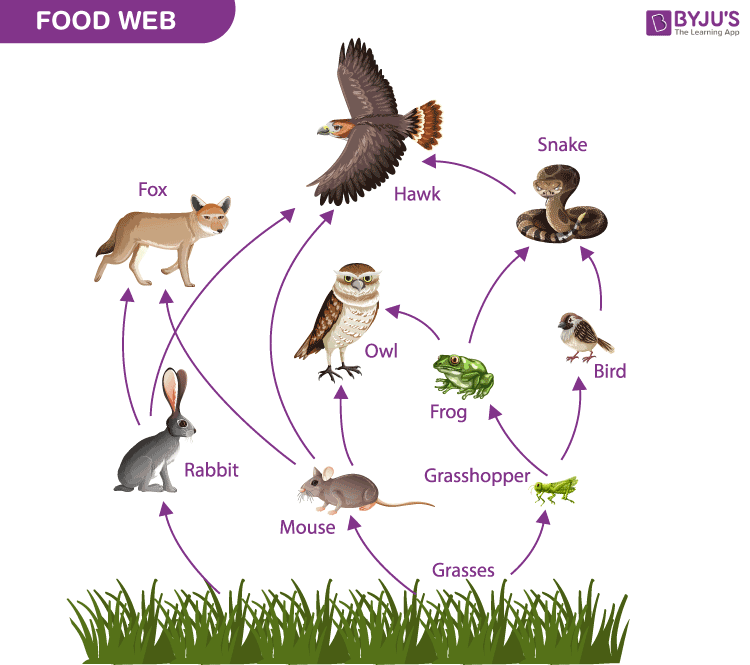
What is the owl?
Fires, earthquakes, droughts, etc. could be considered this type of limiting factor
What are density-independent limiting factors?
This biome typically has extreme ranges of temperatures between day and night; very little precipitation over very long periods of time
What are deserts?
These two processes actively move carbon between chloroplasts and mitochondria
What are photosynthesis and cellular respiration?
The burning of these contributes to increases in carbon dioxide in the atmosphere, indirectly stimulating global warming
What are fossil fuels?
This term means that one organism is benefitted while another is unaffected
What is commensalism?
This type of growth model is typically shaped like the letter 'J' and is present in ecosystems that have no disease, massive amount of food and water, and plentiful space
What is exponential growth?
This biome maintains warm to hot temperatures throughout the year; abundance of precipitation; enormous biodiversity
What are tropical rainforests?
This is the equation for photosynthesis
What is sunlight + water + carbon dioxide yields glucose + oxygen?
Deforestation is an activity that humans engage in that destroys trees in ecosystems. Increases in deforestation will lead to an increase of this gas in the atmosphere.
What is carbon dioxide?
This term means every type of living thing in an ecosystem
What is a community?
This term means that populations at the top of the food chain will be affected by pollutants in an area more than producers/primary consumers (ex. bald eagle population and DDT pesticide)
What is biological magnification?
This biome is known for seasonal changes; average precipitation which could include rain in the spring, summer, and fall with snow in the winter; this is the biome that we live in
What are temperate deciduous forests?
These two nutrient cycles are directly contribute to eutrophication in water systems
What are the nitrogen and phosphorus cycles?
This term means resources from organisms (typically animals) are harvested for economic gain so frequently that is leads to a severe decrease in the animal population (ex. poaching rhinos or elephants for ivory, killing whales for oils, etc.)
What is overexploitation?