SPEED ROUND
What is a biotic factor?
A living factor within an ecosystem.
SPEED ROUND
Which biogeochemical cycles directly involve the atmosphere?
Water cycle, carbon cycle, and nitrogen cycle
SPEED ROUND
Explain the difference between a habitat and a niche.
A habitat is where a species lives, while a niche is the role that the species plays in the ecosystem.
Explain the differences between primary and secondary succession.
Primary succession: Takes place after a volcanic eruption, a glacier melting, strip mining, or a landslide; changes rocks into soil; takes a long time
Secondary succession: Takes place after a natural disaster, fire, or human activity; changes soil into small plants; takes less time
SPEED ROUND
What is an example of a chemical that is subject to biomagnification?
DDT
SPEED ROUND
Which of these are not levels of organization?
population, grouping, community, biome, organism
grouping & biome
Fill in the blanks: nitrogen-fixing bacteria, also called _____, changes _____ gas into useable _____ (same as second blank) for plants. This substance is used by plants as a _____ in the soil.
Legumes, nitrogen, nutrient
SPEED ROUND
What are the advantages and disadvantages of uniform population distribution?
Advantage: Organisms live at a specific distance away from each other
Disadvantage: Causes competition between species over territory
SPEED ROUND
What are the four spheres and what do they contain?
Atmosphere: air above water/solid surfaces
Biosphere: all living things
Geosphere: Earth's rocks, land, & seafloor
Hydrosphere: All of Earth's water and ice
SPEED ROUND
List three causes of water pollution.
Potential answers:
- Oil spills
- Agricultural runoff
- Garbage
- Factory runoff
Sharks are natural predators of stingrays, which eat arthropods. Given this, explain why sharks are a keystone species.
If sharks were removed from the ecosystem, stingrays would have no predators to keep their population down and would therefore reproduce rapidly. More stingrays would eat more arthropods, causing the arthropods to go extinct. Because of this, the stingrays have no food source, and they would go extinct as well.
Fill in the blanks:
The carbon cycle shows the circular pathway of carbon on Earth. In the _____, carbon is released in the form of _____ gas. This gas is released by __________. _____ take in this gas from the air and use it for _____, where then the gas is transferred to the roots of the plants where root _____ takes place. When organisms die, _____ break down dead matter and return carbon to the soil. This carbon accumulates underground, and is then extracted by humans for use as fuel.
- Atmosphere
- Carbon dioxide (CO2)
- Humans, volcanic activity (any plausible answers accepted here)
- Plants
- Photosynthesis
- Respiration
Is a hurricane a density dependent limiting factor? Why or why not?
No, a hurricane is a density independent limiting factor. Hurricanes will not have a greater chance of occurring depending on the density of a population.
List some organisms found in a taiga biome.
- Caribou
- Bears
- Wolves
- Owls
- Lynx
- Coniferous trees
A couple of frogs at a local pond grow extra legs.
- What can the frogs be classified as?
- What is this event indicative of?
- Indicator species
- Pollution or environmental change
Consider this food web.
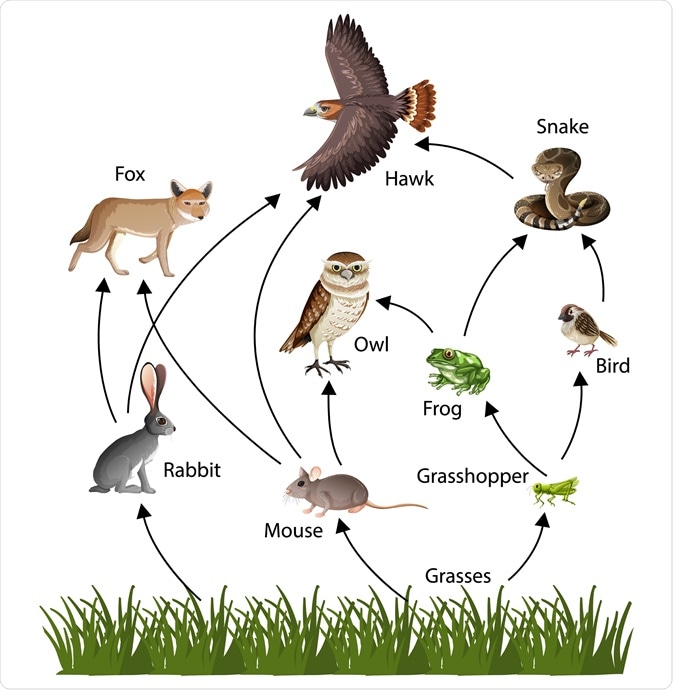
If a fungus that decomposes dead hawks was introduced into the food web, answer the following questions:
1. What type of organism is the fungus?
2. What are the trophic levels of the fungus?
3. If the grass in the Grass --> Grasshopper --> Bird --> Snake --> Hawk food chain contained 10,000 kcal of energy, how much energy would the fungus receive?
1. decomposer
2. 4 and 6
3. 0.1 kcal
SPEED ROUND
What cycle is ammonification a part of, and what does it yield?
Nitrogen cycle, ammonium (NH4+)
Answer the following questions:
- How do all populations begin growing?
- What is required to maintain this type of growth?
- Why could this not continue forever? What does the population reach?
- After the population reaches what is described in the previous question, what type of growth will it have?
- Exponentially
- Births > deaths, little predators, unlimited resources, good climate, etc.
- Environment cannot sustain population, reaches carrying capacity
- Logistic
What are the two freshwater ecosystems? Describe both of them.
Estuary: forms when a river flows into an ocean, has a mix of fresh and salt water
Wetlands: contains lots of nutrients as well as marshes, bogs, and swamps
Identify the following biomes based on their traits:
- Warm and forested, soil not very nutritious
- Trees lose leaves in the fall and grow leaves in the spring
- Permafrost blocks plant life
- Has animals such as caribous and lynxes
- Nights are cold and animals are nocturnal
- Flat and warm
- Tropical rainforest
- Deciduous forest
- Tundra
- Taiga
- Desert
- Grassland
SPEED ROUND
Explain the difference between a detritivore and a decomposer.
A detritivore consumes once living organism, while a decomposer breaks them down.
Label the following diagram:

- Evaporation
- Transpiration
- Condensation
- Precipitation
- Surface runoff
- Infiltration
8. Groundwater movement
The following questions regard symbiotic relationships.
- What are the three symbiotic relationships?
- In all three relationships, one organism benefits. In each of the three relationships, what happens to the other?
- A bird sits on a bull's head and feeds on the ticks on its fur. What symbiotic relationship is this an example of? Justify your answer.
- Mutualism, parasitism, commensalism
- Benefits/is harmed/is not affected
- Commensalism, the bull is not said to have been harmed from this action.
DOUBLE JEOPARDY
Answer the following questions:
- List the zones of the ocean from most pressure to least pressure.
- Which zone(s) is/are photic?
- Which zone of the ocean has animals with the greatest range of motion? Why?
- Abyssal, bathyal, neritic, intertidal
- Neritic zone
- Intertidal zone; it is the zone that includes the land as well as the continental shelf, meaning that for an animal to effectively live there, they would have to be mobile in land as well as water.
Fill in the blanks:
_____ resources can be replaced indefinitely. They do not contribute to the __________. Two examples of this are _____ and _____. On the other hand, _____ resources cannot be replaced in the span of our lifetimes. Two examples of this are _____ and _____. These resources can contribute to several types of _____, such as _____ erosion, _____ and _____ pollution, and __________.
- Renewable
- Greenhouse effect
- Possible answers: solar, hydropower, biomass, wind, geothermal
- Possible answers: solar, hydropower, biomass, wind, geothermal
- Nonrenewable
- Possible answers: oil, coal, natural gas, fossil fuels
- Possible answers: oil, coal, natural gas, fossil fuels
- Pollution
- Soil
- Water
- Air
- Habitat fragmentation