The amount of energy available to primary consumers if the producers in an ecosystem make 23,000 J of energy.
What is 2,300 J?
The producer in the food web shown below.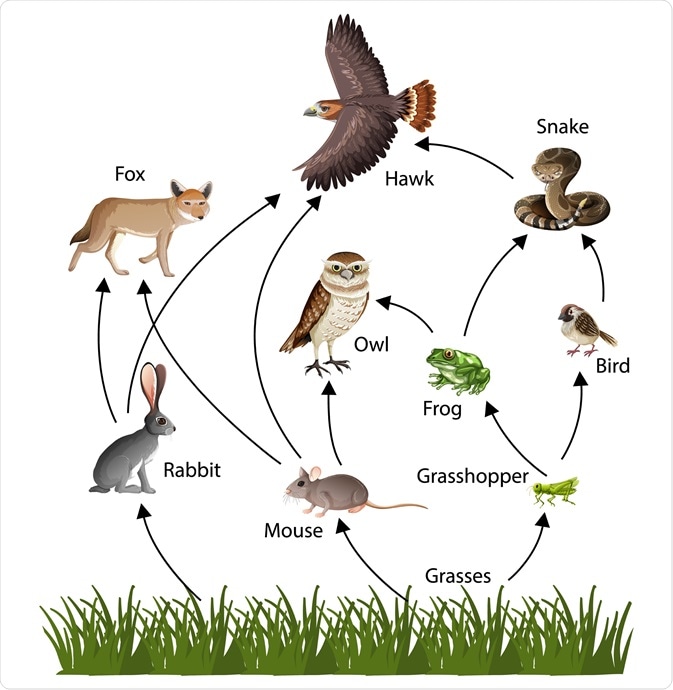
What is grass?
The trophic level that gets their energy from the sun and makes their own food.
What are producers? +100 for autotrophs
The smallest living thing. The building blocks of life.
What are cells?
The type of succession that starts from bare rock and takes much longer.
What is Primary Succession?
The part of the water cycle where liquid water turns into a vapor and rises into the air.
What is evaporation?
A relationship where one animal hunts and eats another.
Ex. A fox hunting a rabbit.
What is predation?
The amount of energy available to the tertiary consumers in an ecosystem if the primary consumers contain 460,000 kCal of energy.
What is 4,600 kCal?
The three primary consumers shown in the food web below. 
What are grasshoppers, mice, and rabbits?
An organism that eats a primary consumer.
Ex. A hawk eating a rabbit.
What is a secondary consumer?
A group of the same type of cells all working together.
What is a tissue?
They type of succession that starts with established soil and moves much quicker.
What is Secondary Succession?
The two main sources of carbon dioxide in the carbon cycle.
What are respiration and combustion?
A relationship where two or more organisms are both trying to use the same resource.
Ex. A tree and a bush competing for sunlight.
What is competition?
The amount of energy available to the tertiary consumers in an ecosystem if the producers make 8,200 J of energy.
What is 8.2 J?
The two sources of food for the herring.
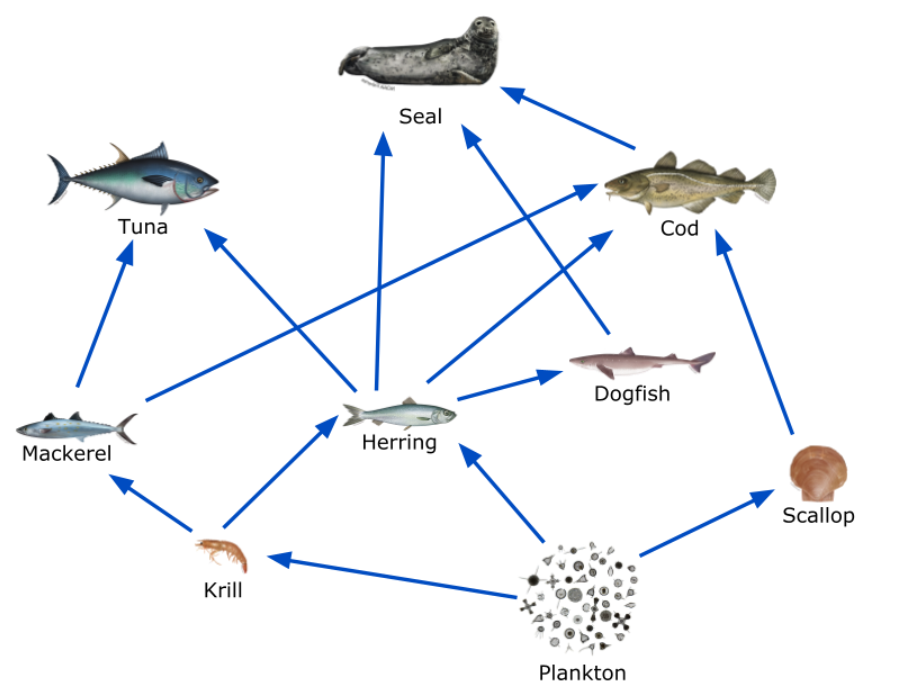
What are krill and plankton?
An organism that eats producers.
Ex. A deer eating acorns
What is a primary consumer?
A group of the same species of organism all living in the same area.
What is a population?
The first organisms to colonize a new area during primary succession.
What are lichens and mosses? +100 for pioneer species
The organisms in the soil that take nitrogen gas and convert it into a form that plants can use.
What are bacteria?
A relationship where one organism benefits, but harms the other.
Ex. A flea lives on a dog and drinks it's blood.
Daily Double!
How much energy must be present at the level of the producers if there are 48,900 kCal of energy available to the secondary consumers?
The 4 different predators of the herring.
What are tuna, dogfish, seals, and cod?
An organism that eats secondary consumers.
Ex. A dolphin eating a speckled trout
What is a tertiary consumer?
All of the living and non-living (Biotic and Abiotic) components of a given area
What is an ecosystem?
The reason why trees can't be the first type of plant to colonize a new area.
What is a lack of soil?
The process that plants use to take in Carbon dioxide and convert it into food for themselves.
What is photosynthesis?
A relationship where both organisms gain some kind of benefit.
Ex. An oxpecker bird eats bugs off of an elephants back.
How much energy must be available to the primary consumers if there is 54 J of energy available to the Quaternary consumers?
What is 54,000 J?
The two organisms in this food web that do not have any predators.
What are buzzards and foxes?
Any organism that has to eat other organisms to get energy and nutrients. Another term for consumers
What are heterotrophs?
The small pieces that make up a cell.
What are organelles?
One possible reason for secondary succession to occur.
What is a wildfire or other natural disaster?
The other way for nitrogen gas to be processed into nitrates, besides being fixed by bacteria.
What is lightning?
A relationship where one organism benefits and the other is not affected.
Ex. A bird builds its nest in a tree.
What is commensalism?