Relationships
Relationships
When one organism benefits and the other is harmed, the relationship is called __________.
What is parasitism?
Choose the correct answer:
Energy flows through an ecosystem in one/two direction(s).
What is one?
Plants take in carbon dioxide during __________.
What is photosynthesis?
A diagram that shows one possible path of energy transfer is called a food ______.
What is food chain?
The variety of life in an ecosystem is called __________.
What is biodiversity?
A bird eats insects off the back of a cow. The cow gets rid of pests, and the bird gets food. What type of symbiotic relationship is this?
What is mutualism?
What percentage of energy typically passes from one trophic level to the next?
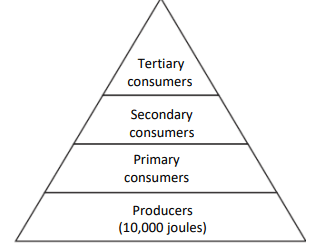
What is 10%?
Which organisms are responsible for nitrogen fixation in the soil?
What are bacteria?
A hawk eats a snake that ate a mouse. The hawk is what level of consumer?
What is a tertiary consumer?
Name one example of a human activity that reduces biodiversity.
What is deforestation, pollution, overfishing, habitat destruction, climate change, etc?
A remora attaches to a shark, eating scraps of food but not harming the shark. Identify the relationship.
What is commensalism?
Grass → Grasshopper → Frog → Snake → Hawk. Identify the producer.
What is grass?
A factory releases carbon dioxide into the air. Which process in the carbon cycle would help balance this increase?
What is photosynthesis by plants?
In a food web, the population of rabbits decreases. Predict how this affects foxes.
What is the fox population may decrease due to less food?
A keystone species such as sea otters is removed from an ecosystem. Predict what could happen to biodiversity.
What is biodiversity would decrease because the ecosystem balance collapses?
Identify this relationship.

What is competition?
Why are there usually fewer top predators than producers in an ecosystem?
What is energy is lost as heat at each level, so less energy supports fewer top predators?
Explain how animals get the nitrogen they need.
What is by eating plants or other animals that contain nitrogen-based compounds?
If all the producers are removed, what happens to the rest of the web?
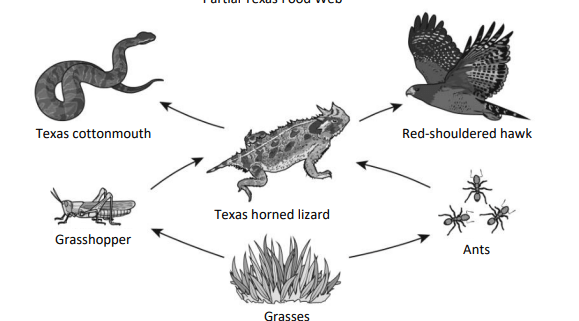
What is consumers eventually die out because energy flow stops?
Year vs. Species in Rainforest
2000 - 300
2020 - 180
Describe the trend and suggest one cause.
What is biodiversity is decreasing, possibly due to deforestation or climate change?
Predator–prey cycles often show peaks and valleys. Explain why the predator population usually lags behind the prey population.
What is predator population growth depends on prey availability; predators increase after prey increases, and decrease after prey declines?
Producers
10,000
Primary C.
1,000
Secondary C.
100
Tertiary C.
10
Based on the data, explain the 10% Rule.
What is only about 10% of energy/biomass transfers to the next trophic level?
Analyze the diagram. Identify the process where bacteria return nitrogen gas to the atmosphere.
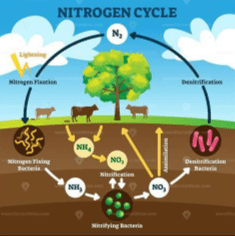
What is denitrification?
Why is a food web more realistic than a food chain for representing ecosystems?
What is food webs show multiple feeding relationships, not just one linear path?
Explain why biodiversity is important for ecosystem stability.
What is high biodiversity increases resilience, making ecosystems more stable and able to recover from disruptions?