If a handful of almonds contains 1600 kilojoules of energy, and a chipmunk eats them, how much energy will end up getting STORED in the chipmunk?
160 kilojoules
A large section of rainforest is cleared and burned to make space for farmland.
Question: How will this affect the amount of carbon stored in different parts of the carbon cycle?
The burning will release CO2 into the air from the trees AND the new lack of trees will cause not as much CO2 to be taken out of the atmosphere.
In a river ecosystem, scientists noticed that when algal blooms occurred, the number of fish dropped dramatically. The blooms were often caused by fertilizer runoff from nearby farms adding too many nutrients to the water.
Question: Is this a biotic or abiotic factor?
This is an ABIOTIC factor (fertilizer) which was caused by humans.
Zebra mussels, introduced through ship ballast water, have spread throughout the Great Lakes, disrupting food webs and damaging infrastructure.
Propose a method to manage or reduce the spread of zebra mussels without harming native species.
If it makes sense, give yourself points.
Examples: ship filtration system, encouraging fishermen to catch zebra mussels
What does this graph show?
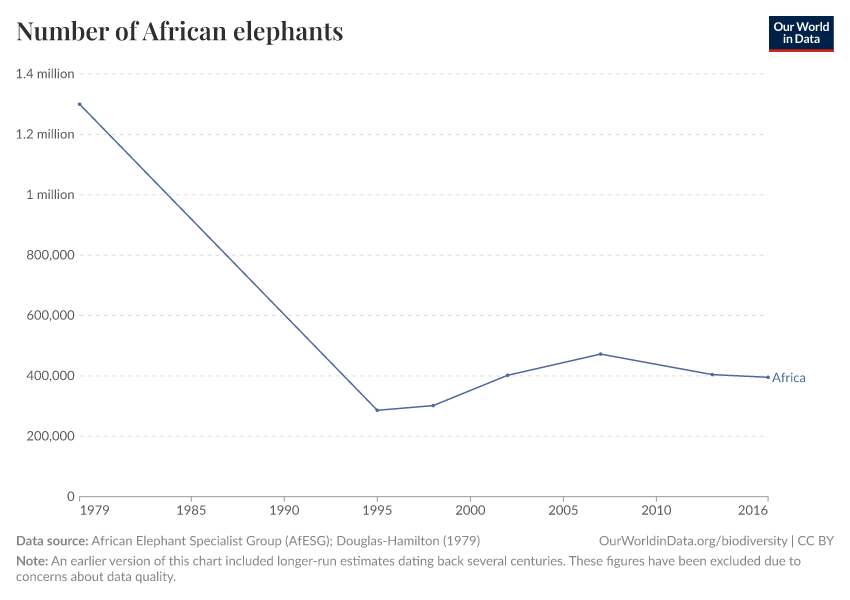
The number of African elephants has declined since 1979.
Label each species below with its role in the ecosystem.
Grass -> grasshopper -> frog -> snake -> bacteria (when the snake has died)
producer, primary consumer, secondary consumer, tertiary consumer, decomposer
A scientist studies a patch of ocean where microscopic algae are thriving. The algae absorb large amounts of carbon dioxide from the atmosphere during the day.
Question: What process are the algae performing, and how does this affect carbon levels in the atmosphere?
They are performing photosynthesis, and this will decrease the amount of CO2 in the atmosphere.
A student conducts a simulation where they model a fish tank with different numbers of fish but fixed amounts of oxygen and food. As more fish are added, survival rates drop.
Questions: What are the main limiting factors in this simulation? Why did survival rates drop?
- the available amount of oxygen and food
- survival rates dropped because once the population hit carrying capacity, there were not enough resources for all fish to survive
Permafrost in the Arctic is thawing, releasing methane—a potent greenhouse gas—into the atmosphere, accelerating climate change.
Develop a solution that could slow permafrost thaw or reduce methane emissions from thawing soils.
If it makes sense, give yourself points. It can be unrealistic as long as it's possible!
Examples: creating a membrane net that traps methane, stop burning fossil fuels that exacerbate global warming, etc.
What do you learn from this graph?

Fossil fuels, cement and flaring cause more CO2 emissions than forestry and other land use
Grass -> grasshopper -> frog -> snake
A grasshopper eats grass throughout its life, consuming a total of 400,000 kilojoules of energy from grass before being eaten by a frog. How much energy from this grass will end up being STORED in the snake from that grass?
400 kilojoules stored in the snake
During the winter, the rate of photosynthesis decreases in forests because trees lose their leaves.
Question: How does this seasonal change affect the amount of carbon in the atmosphere?
During the winter, there are increased levels of CO2 in the atmosphere compared to when all trees have their leaves.
After several years of abundant rainfall, a desert ecosystem in Arizona saw a surge in plant growth and a boom in the jackrabbit population. But when a drought hit, the jackrabbit numbers declined sharply.
Question: How did abiotic factors play a role in the population changes of the jackrabbits?
The absence of enough water (an abiotic factor) meant there were not enough plants growing to feed the jackrabbits. Food availability was a limiting factor that caused the carrying capacity to drop.
A growing city is expanding into nearby forests and wetlands, leading to habitat fragmentation and species displacement.
Design a plan to support human development while conserving natural ecosystems.
Give yourself points if it makes sense.
Examples: creating protected regions, legislation banning certain building types, building treehouses, building houses on stilts above the wetlands
What does this graph show? What does that mean for the carbon cycle or global warming?
Deforestation RATES are decreasing. (But deforestation is still continuing).
This still means means that less CO2 is being taken out of the atmosphere and into forests.
DESCRIBE the 10% rule for energy transfer in an ecosystem and EXPLAIN why it happens.
- only 10% of energy consumed will be stored in the body (or will become part of the body)
- this happens because organisms use around 90% of the energy they consume for cellular respiration, movement, etc. which is lost as heat to the environment
A company builds a factory that captures carbon dioxide emissions and stores them underground.
Question: How does this action alter the carbon cycle compared to traditional industrial processes?
There will be decreased amounts of CO2 entering the atmosphere.
(this is a real thing called CCS! Look it up!)
Deer are adapted to survive in the cold. They can develop fat reserves to help them store energy for this time, and they slow their metabolism to conserve energy. During a particularly harsh winter, a population of deer in a forest decreased dramatically. By spring, the population began to recover.
Question: How did seasonal abiotic changes affect the carrying capacity of the environment for these deer? (in other words, why did this happen?)
Acceptable answers:
- The cold winter eliminated (or covered with deep snow) a lot of the plants available for food
- Deer starved when their fat reserves ran out
- The cold made the deer more susceptible to predation
Fertilizers from farms are washing into rivers and ending up in the ocean, creating oxygen-depleted "dead zones" where few organisms can survive.
Design a solution to reduce or prevent nutrient pollution from agriculture.
Give yourself points if your solution makes sense.
Examples: runoff filtration systems, stopping fertilizer use

Which of the following statements is supported by the graph?
A) Wind energy alternatives are cheaper than solar
B) Wind energy alternatives have increased, but not solar
C) The US is increasing its use of wind energy alternatives at a faster rate than solar, but both are increasing
D) Solar and wind combined account for about 9% of energy generation in the US
C
Create a food web using the following information:
Grass is the main producer in this ecosystem.
Rabbits eat grass, and are eaten by hawks and foxes.
Mice eat grass, and are eaten by foxes, owls, and hawks.
Grasshoppers eat grass, and are eaten by frogs and birds.
Snakes eat frogs and birds, and are eaten by hawks.
Frogs are also eaten by owls.
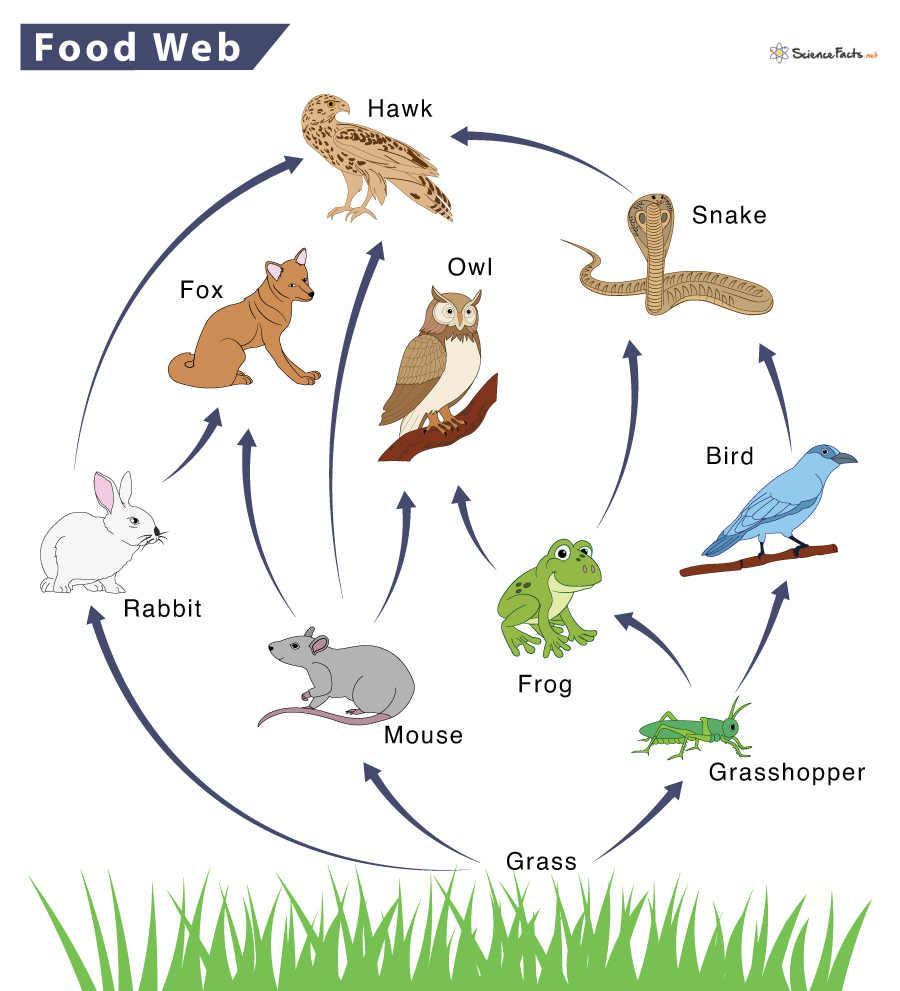
Diagram the carbon cycle.
(see class slides for this answer, your notes, or the study guide answer key)
You’re studying a population of frogs living in a small wetland. Over the past year, the frog population has declined. As part of your investigation, you gather a list of limiting factors that might be responsible.
Label each of these factors as abiotic (nonliving) or biotic (living or once-living):
🐍 Increased number of snakes that eat frogs
☀️ Unusually high temperatures during the summer
🌿 Reduction in aquatic plants frogs use for shelter
💧 Decreased rainfall leading to lower water levels
🦟 Fewer insects for frogs to eat
🦠 Spread of a fungal infection affecting frog skin
🧊 Water temperature too cold for breeding
👣 Habitat destruction due to human construction
🐍 Biotic
☀️ Abiotic
🌿 Biotic
💧 Abiotic
🦟 Biotic
🦠 Biotic
🧊 Abiotic
👣 Abiotic/Biotic (buildings aren't alive, but the humans that put them there are)
Large-scale deforestation for cattle ranching and farming is reducing biodiversity and contributing to increased atmospheric CO₂.
Design a sustainable strategy to reduce deforestation while supporting local communities’ needs.
If it makes sense, give yourself the points. This is a difficult one (500 points! be creative!)