Food Web
All the nonliving aspects of an ecosystem.
What are abiotic factors?
The energy used by organisms in the lowest trophic level originally comes from what?
What is the sun?
Other than fossil fuels, name two other human activities that increase the concentration of carbon in the atmosphere.
What is car driving and deforestation?
A type of growth in which growth rate slows or stops following a period of exponential growth.
What is logistic growth?
What is meant by the fact that water is a "polar" molecule?
A water molecule has one distinctly negatively charged end and one distinctly positively charged end.
A relationship between two species in which one organism benefits while the other is harmed.
What is parasitism?
Which of these organisms is a primary consumer in a terrestrial food web?
a. fungi
b. grasshopper
c. grass
d. hawk
b. grasshoppers are considered primary consumers in a terrestrial food web
This plant hosts nitrogen fixing bacteria in their roots, making them goof crops to plant to replenish the soil.
What are legumes?
When a population is reproducing at a constant rate with unlimited resources.
What is exponential growth?
In lakes in North Carolina that are exposed to acid rain, fish populations are declining. This is primarily due to changes in which lake condition?
a. Size
b. Temperature
c. pH
d. Location
What is pH?
All the organisms of the same species living in one area.
What is population?
Why does each trophic level have less energy than the trophic level below it?
What is the 10% rule?
- Some energy at each trophic level is lost as heat or through decomposers.
This biological process converts carbon from organic molecules to a gas and returns it to the atmosphere.
What is cellular respiration?
- Also acceptable: Cows digesting food and producing gas in the form of methane; decomposition of organic material by bacteria converts organic carbon into gases such as methane.
The largest number of individuals of a population that the environment can support.
What is carrying capacity?
Created an energy pyramid based on the food web below.
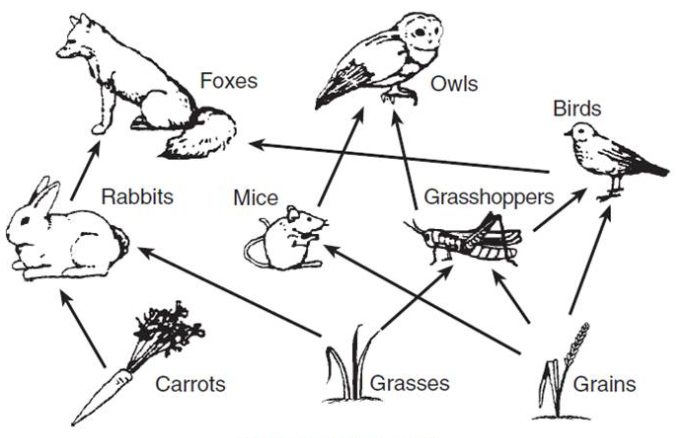
Producers - Grasses, grains, carrots
1st - Rabbits, mice, grasshoppers
2nd - Birds, owls
3rd - Foxes
A type of ecological succession that begins in a place without any soil.
What is primary succession?
If the trophic level of the quail in the food web above contains 70kCal of energy, how much energy is found at the opossum's highest trophic level?
What is 7.0 kCal?
This biological process removes carbon from the atmosphere and converts it into organic molecules.
What is photosynthesis?
The carrying capacity for herbivores in a habitat is most directly affected by the availability of:
a. carbon dioxide in the atmosphere
b. heat energy released by carnivores
c. decomposers in the soil
d. photosynthetic organisms
D. photosynthetic organisms
Bears can be a 1st or second level consumer, why?
They can eat berries or other animals, like fish
This type of ecological succession begins in a place that already has soil and was once the home of living organisms.
What is secondary succession?
A continuous decrease in the size of the rabbit population would most likely cause a decrease in which other population?
What is mountain lion?
Nitrogen is also a fundamental organic material that all living organisms need. What is the process by which living organisms incorporate nitrogen (and carbon) into their bodies? Why is it important?
What is assimilation?
What causes a shift from exponential to logistic growth?
What is (many answers are possible)?
- Decrease in birth rate
- Increase in death rate
- Increased competition
- Decrease in available shelter
Which trophic level will always have the highest number of individuals? Why?
Producers