A ____ is a law that keeps the price from rising above a certain level whereas a ____ is a law that keeps the price from falling below a certain level.
Price Ceiling
Price Floor
Indicate the relevant part of the demand curve given this price ceiling. (The part of the demand curve impacted)

The relevant part of demand curve is the portion directly over the price ceiling. It indicates the consumers that will participate in the market given the current price.
In a Negative Externality, the Social Optimum is ___ the Market Equilibrium
In a Positive Externality, the Social Optimum is ___ the Market Equilibrium
(<,>, or =)
SO < ME
SO > ME
In the following graph, identify the deadweight loss from a negative externality

Deadweight loss is the area within point e.This is because the DWL occurs where Marginal Social Cost is greater than the Marginal Private Cost
____ means it is nearly impossible to stop someone from using the good or service.
____ means when one person uses the good or service, another person can also use it
Non-Excludable
Non-Rivalrous
In a ____ QD>QS
In a ____ QS>QD
Shortage (Caused by price ceiling)
Excess (Caused by price floor)
Indicate the relevant part of the supply curve in a price ceiling.

The relevant part of the supply curve when there's a price ceiling is the portion directly below the line that indicates the ceiling. It indicates the suppliers that will participate in the market given the current price.
The ___ equilibrium is where the demand curve intersects the supply curve
The ___ equilibrium is where the demand curve intersects the social costs curve
Market
Efficiency
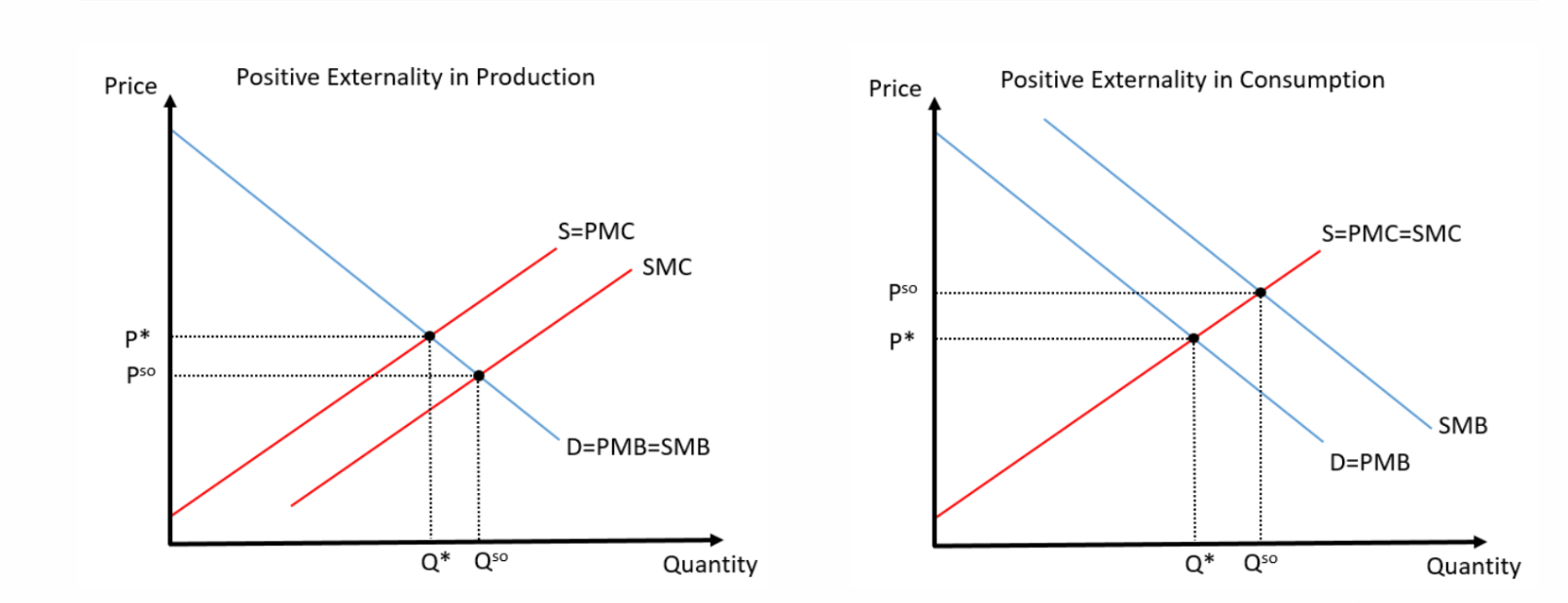
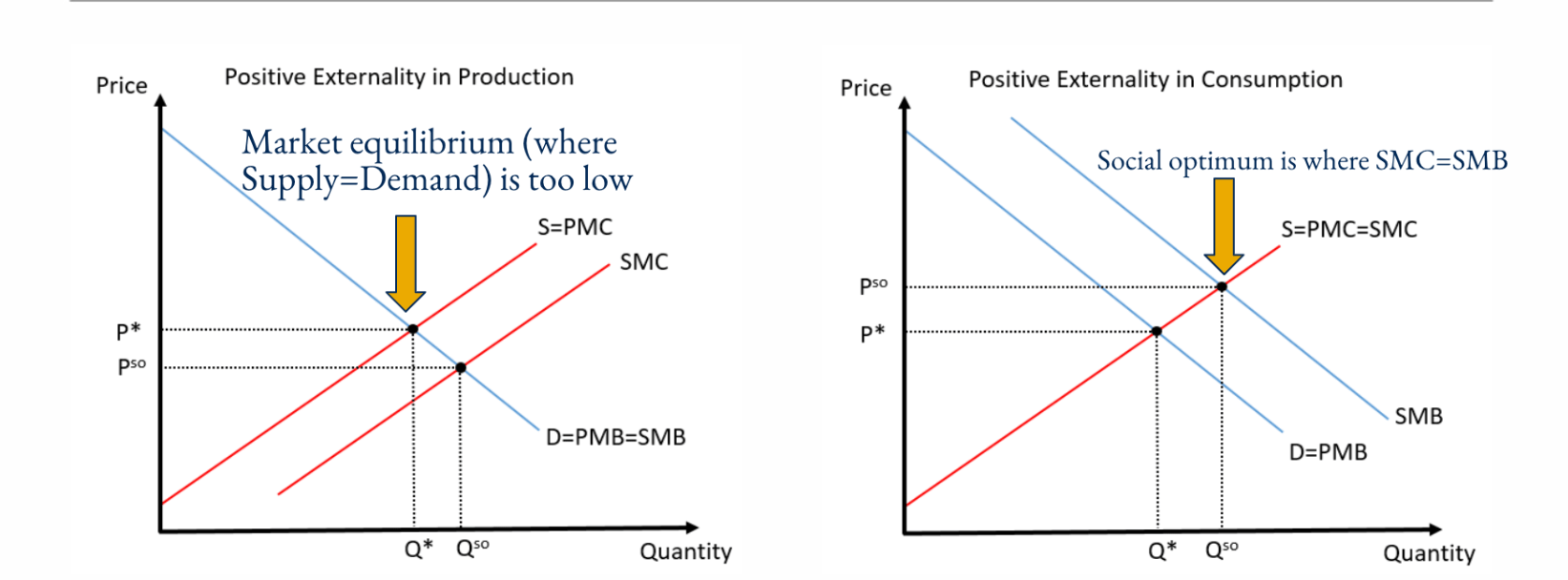
In these graphs of positive externalities, locate the Market Equilibrium and the Efficient Equilibrium (The social optimum). This is a positive externality because production is ____ (Higher or Lower) than the social optimum.
This is a positive externality because production is Lower than the social optimum. There is the opposite of a negative externality where production is higher than the social optimum.
If national defense is a non-excludable, non-rivalrous good, what type of good is it?
If cable TV is a an excludable, non-rivalrous good, what type of good is it?
Public Good
Club Good
The government enacts a national price ceiling on oil. This results in cold regions having barely enough oil to heat their homes while warm regions have enough oil to heat up their hot tubs. Of the 5 main negative consequences of price ceilings, which best describes this situation?
(1. Creates Shortages, 2. Reductions in Quality/ Service, 3. Wasteful Lines and Search Costs 4. A Loss in Gains from Trade (DWL), 5. Misallocation of Resources)
Misallocation of resources
(No incentive for entrepreneurs to buy low/sell high because of price ceiling. No flow from low value use to high value use)
If the government enacts a $20 price ceiling on Nacho Cheese Doritos, how many units of Doritos will be available to consumers?

2,000 Units
Suppliers are only willing to supply 2,000 units at that price.
This exists to offset 3rd party costs. It shifts the private cost supply curve to the social cost supply curve where Efficient Equilibrium = Market Equilibrium
Pigouvian tax (Opposite of Pigouvian Subsidy)
In the following graph of a negative externality, which point(s) represent the overuse?

Overuse is the difference between the Market Equilibrium and the Efficient Equilibrium. In this graph, the Market Equilibrium is Q1 and the Efficient Equilibrium is at Q2, so the overuse is the value between Q1 and Q2
This problem results when people benefit from public or common goods but either underpay for them or don't pay for them at all.
Free-Rider Problem
A price ___ is binding when it is above the equilibrium price.
A price ___ is binding when it is below the equilibrium price.
Price Floor
Price Ceiling
If the government enacts a price ceiling of $20 on Nacho Cheese Doritos, there would be a shortage of how many units of Doritos?

There would be a shortage of 2,000 units.
Consumers are willing to purchase 4,000 units at that price but suppliers are only willing to supply 2,000. (4,000 - 2,000 = 2,000)
# 1 In this type of regulation, firms must increase cost for anti-pollution equipment for example, attempt to get firms to account for social costs
#2 These, however, create incentives to allow firms some flexibility in reducing pollution. The three main categories of market-oriented approaches to pollution control are pollution charges, marketable permits, and better-defined property rights.
#1 Command and Control Regulations
#2 Market-Oriented Tools
The 1st graph is a ____ externality of _____ and the 2nd graph is a _____ externality of _____.
#1
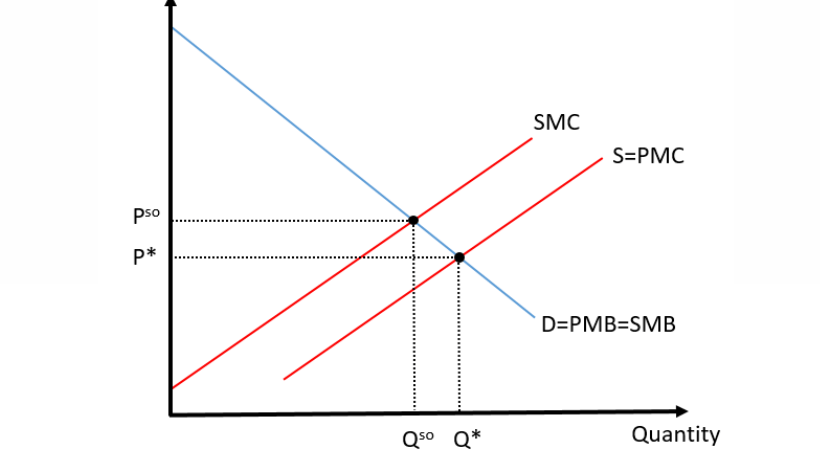
#2
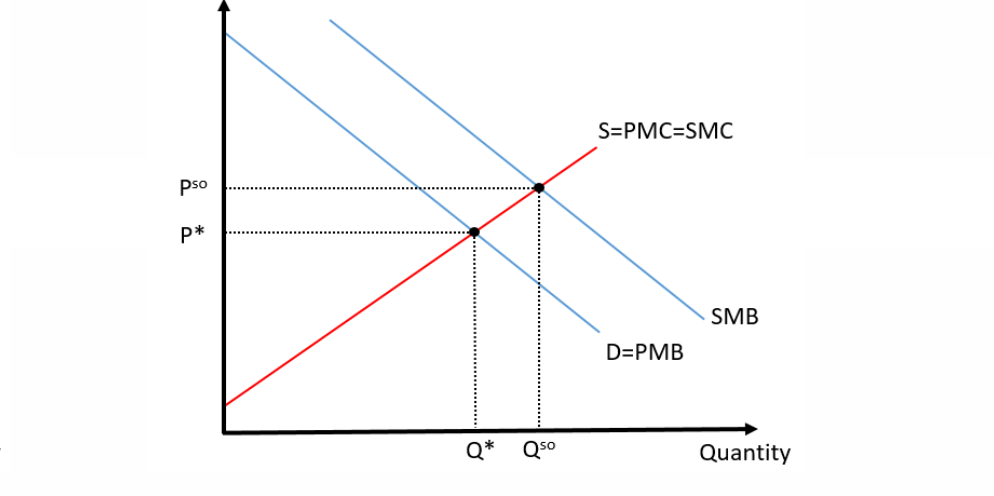
#1 Negative Externality of Production
#2 Positive Externality of Consumption
This results when 2 or more individuals compete for a single common pool of resources that don't have clear property rights
The tragedy of the commons
(Overfishing of the world's oceans, for example.)
In a price floor, the consumer surplus is _____ than at equilibrium
In a price floor, the producer surplus is _____ than at equilibrium
smaller (Fewer consumers will participate in the market given the artificially high price)
larger (More producers will participate in the market given the artificially high price)
If a price floor is set at point P2 and Quantity Demanded is at point Qd, where is the consumer and producer surplus located? Where is the deadweight loss?

Consumer surplus is the triangular area within G, P2, and B
Producer surplus is the rectangular area within P2, B, C, and P3.
Deadweight loss is the area at within B,C, and A
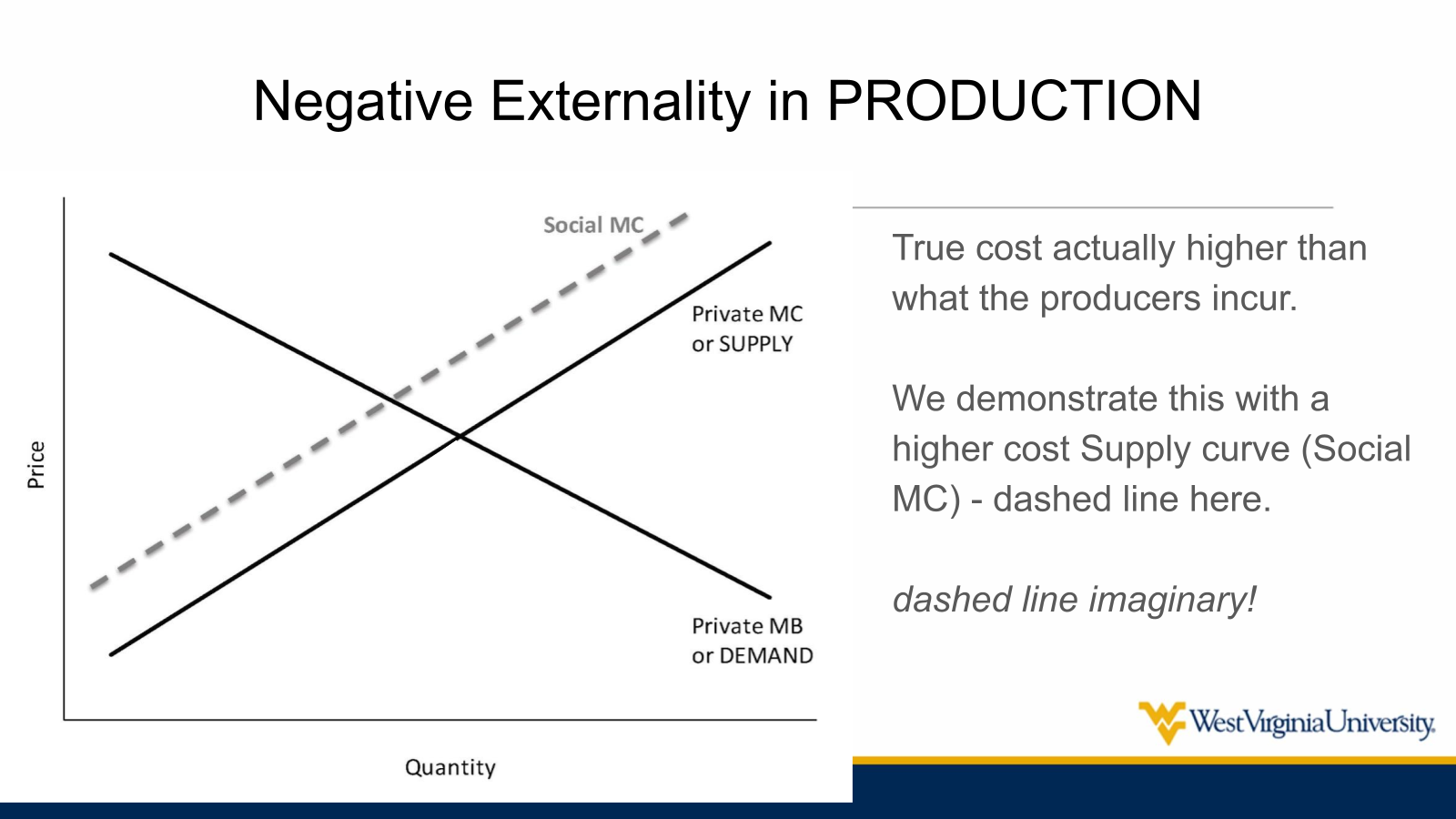
In a ____ externality of ____, it costs society more to produce than is represented by the demand curve
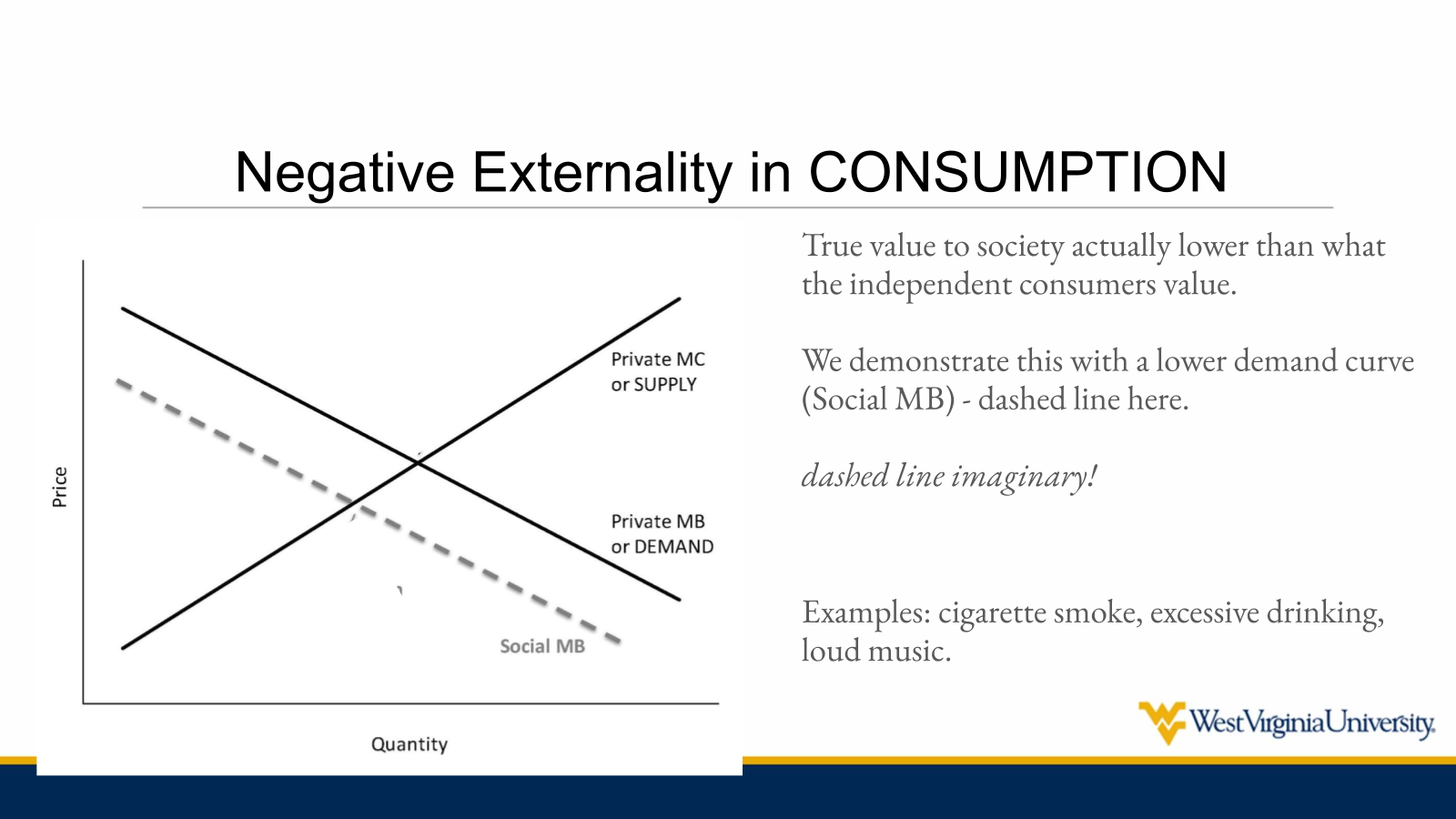
In a ____ externality of ____, the true value to society is actually lower than what the independent customers value
negative externality of production
negative externality of consumption
The 1st graph is a ____ externality of _____ and the 2nd graph is a _____ externality of _____.
#1
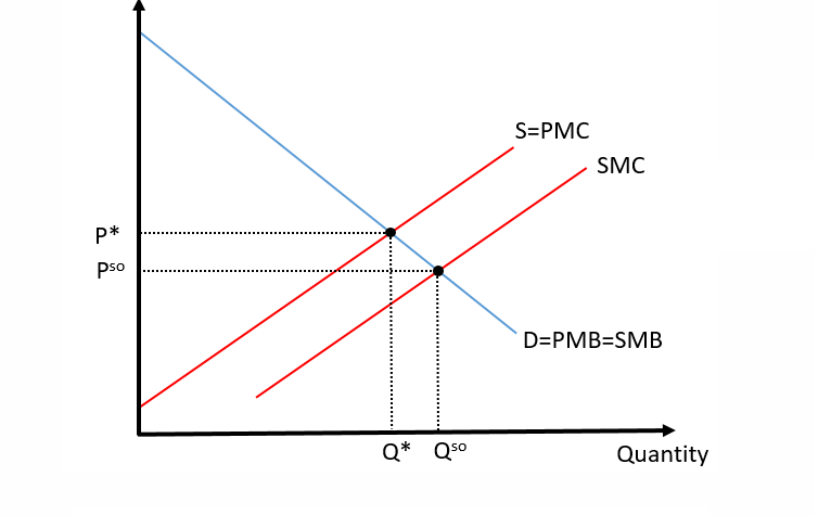
#2
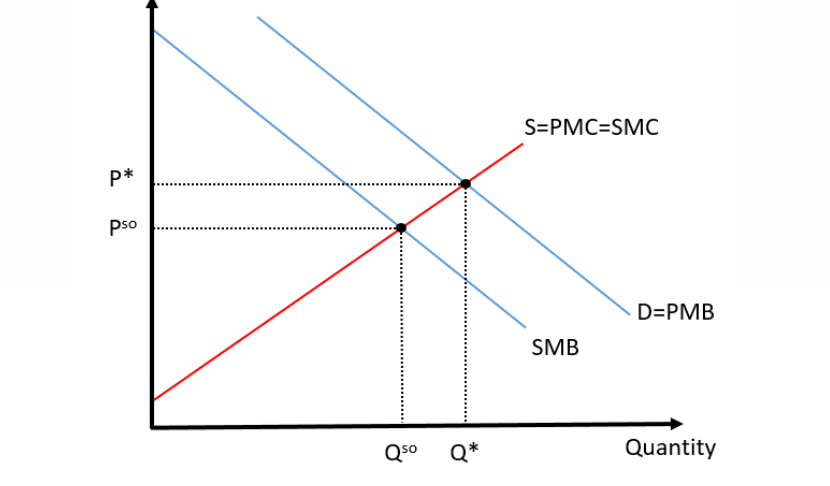
#1 Positive Externality of Production
#2 Negative Externality of Consumption
Fill in the following table by labeling each of the 4 sections as either public goods, common goods, private goods, or club goods.
Excludable Non-excludable
Rivalrous
Non-rivalrous