Any arrangement that brings buyers and sellers together to do business with each other is known as a
Market
to be in short supply of a good or service is known as
Scarcity
A stateless, classless society envisioned by Karl Marx is known as...
Communism
Fair and just distribution of an economy’s resources is known as
Economic Equity
True or False: Trade Makes People Better Off
True
The production, distribution, and consumption of goods and services is known as the
Economy
Is this PPF constant or increasing?
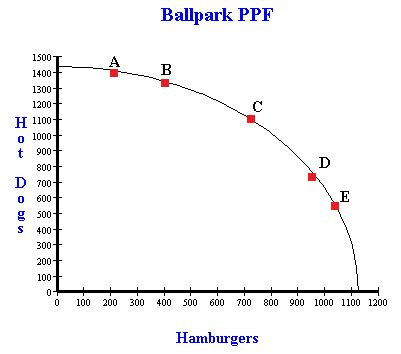
Increasing
a political and economic theory that calls for property to be owned by society as a whole, rather than individuals, for the benefit of all.
Socialism
The ability to make our own economic decisions without interference from the government is known as
Economic Freedom
the ability to perform a task at a lower opportunity cost than someone else.
Comparative Advantage
Who is often considered the "Father of Capitalism"?
Adam Smith
What are the Factors of Production (ie: This + This + This = Goods and Services)
Land + Labor + Capital = Goods and Services
Who is often considered the "Father of Communism"?
Karl Marx
What are the Three Basic Economic Questions?
What will be produced? How will it be produced? For whom it will be produced? (Shortened as: What, How, Who?)
the process of concentrating on and becoming expert in a particular subject or skill.
Specialization
Name three Principles of Economic Thinking
Viable Answers Include:
Scarcity Forces Tradeoffs
Costs vs Benefits
Thinking at the Margin
Incentives Matter
Trade Makes People Better Off
Markets Coordinate Trade
Future Consequences Count
Oil, Coal, and Natural Gas are all examples of what kind of resource?
Non-renewable
Name three characteristics of the US economic system
Viable Answers:
Economic Freedom
Competition
Equal Opportunity*
Binding Contracts
Property Rights
Profit Motive
Limited Government
Production and Distribution is based on tradition and culture. Ie: Women produce the clothes, men raise cattle or hunt. Chieftains get a larger portion than the rest of the tribe OR all tribe members get equal distribution of goods.
Traditional Economy
the dependence of two or more people or things on each other is known as
Interdependence
Name two tools of Economics
Viable Answers Include:
The Scientific Method
Graphing
- Economic Models
What is the opportunity cost of shifting production from A to C?
300 Hot Dogs
When you open up a bag of potato chips and enjoy the first potato chip, but as you continue eating, the satisfaction gradually diminishes. This is an example of what law of economics?
Diminishing Marginal Utility
Where economic decisions are made and influenced by individual producers and consumers, as well as the government.
Mixed Economy
Explain How Does Specialization Lead to Economic Interdependence?
Answers may vary, up to the discretion of Mr. Reynolds