Economics is
A study of how people make choices under conditions of scarcity, and of the results of those choices for society.
The terms of Trade
The agreed upon conditions that would benefit both countries
Solve elasticity of Demand coefficiant
% change in quantity divided by % change in price
Fours market structures
Perfect competition, oligopoly, monopolistic completion, monopoly
Label X, A, and points on the curve.
Point x is beyond the economy's ability to produce and point A is inefficient. All points on the curve are completely efficient.
The difference between Micro economics and Macro economics is
Microeconomics studies individuals and business decisions, while macroeconomics analyzes the decisions made by countries and governments.
Comparative and Absolute Advantage
The ability to produce a product with fewer opportunity cost and the ability to produce more product than another.
Equilibrium is from
Intersection of demand and supply curve
MR DARP
Marginal Revenue, Demand, Average Revenue, Price.
Supply curve (Draw)
/supply_curve_final-465c4c4a89504d0faeaa85485b237109.png)
Opportunity cost is
the loss of potential gain from other alternatives when one alternative is chosen.
Circular flow market
The individuals can sell their work to firms. Earning income to go back into households. While the firms produce product, making money by selling them within the market. Which is purchased by individuals. The governments role is to create policies (which can help) and collect taxes.
Shift in demand and shift in quantity
A change in the curves placement and a movement along the curve.
Profit Maximizing Rule
MC = MR
Demand Curve (Draw)
The 5 assumptions of economics are
1. Society's wants are unlimited, but ALL resources are limited (scarcity)
2. Due to scarcity, choices must be made. Every choice has a cost (a trade-off)
3. Everyone's goal is to make choices that maximize their satisfaction. Everyone acts in their own "self-interest" (utility)
4. Everyone acts rationally by comparing the marginal costs and marginal benefits of every choice
5. Real-life situations can be explained and analyzed through simplified models and graphs
What does it mean if a point exists in a ppc.
The economy is producing inefficiently.
Shifters of Demand
Preferences, Population, Income, price of related goods, future expectation
Allocative and Productive Efficiency
P = MC and P = any curve point.
The change in Quantity and Price
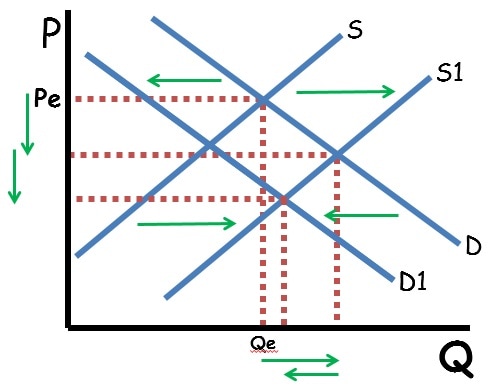
Price has decreased and quantity is indeterminant.
2 Principles of Economics are
1.People Face Tradeoffs
2.The Cost of Something is What You Give Up to Get It
3.Rational People Think at the Margin
4.People Respond to Incentives
5.Trade Can Make Everyone Better Off
6.Markets Are Usually a Good Way to Organize Economic Activity
7.Governments Can Sometimes Improve Economic Outcomes
8.The Standard of Living Depends on a Country's Production
9.Prices Rise When the Government Prints Too Much Money
10.Society Faces a Short-Run Tradeoff Between Inflation and Unemployment
Marginal Utlitity
Added satisfaction
Shifters of supply
Input price, price of related goods, technology, expectations, competitors, and government action.
Economic Profit
TR - (Explicit + Implicit Cost)
Pe = $5,
MRDARP=
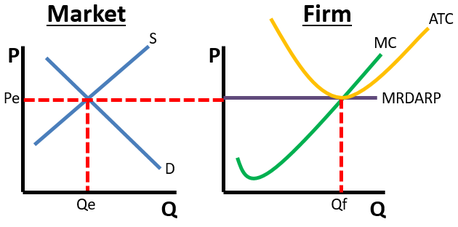
MRDARP = $5